Car starter: device and principle of operation
As the name suggests, a car starter is used to start an internal combustion engine. To do this, it ensures the primary rotation of the crankshaft at the required frequency. The starter is an integral part of the electrical equipment of any modern car.
Structurally, it is a four-pole DC electric motor, powered by a battery.
Its power varies depending on the specific modification of the car, but a 3 kW starter is sufficient to start most gasoline engines.
This article will discuss in detail the design and operating principle of a “classic” starter.
Car starter: device and main functions.
As you know, the internal combustion engine generates the energy necessary to move the car due to crankshaft revolutions.
All electrical equipment of the car operates from the same energy. When stationary, the motor is unable to produce either torque or electrical energy.
In this regard, you have to “spin it up” using a special electric motor (starter) and an external power source (battery).
The starter device includes the following main components:
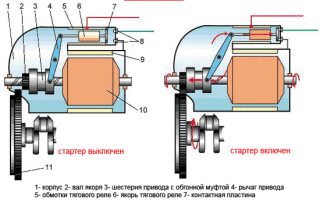
- Housing (electric motor). Cylindrical steel part. It houses the field windings and cores.
- Anchor. Made in the form of an axis made of alloy steel. The core and collector plates are pressed onto the armature.
- Solenoid relay. Designed to supply power to the starter motor from the ignition switch. At the same time, it performs another important function - it pushes out the overrunning clutch. The relay has power contracts and a movable jumper in its design.
- Overrunning clutch (Bendix) and drive gear. A roller mechanism that transmits torque to the flywheel crown through a special engagement gear. After starting the engine, it disconnects the drive gear and the flywheel crown, thereby ensuring the safety of the starter.
- Brush holders and brushes. Designed to supply operating voltage to the armature commutator plates. They increase the power of the electric motor during the main operating cycle of the starter.
The design of most starters is similar to each other and certainly includes the “classic” components listed above. The differences may be only minor. Most often they affect the automatic gear disengagement mechanism.
In addition, on cars with automatic transmissions, the starter is equipped with additional retaining windings.
They are designed to prevent the engine from starting if the “automatic” selector is set to any driving position (L, 1, 2, 3, D, R).
The working principle of a car starter. The working process of an electric starter can be divided into three stages: connecting the drive gear to the flywheel ring, starting the starter, disconnecting the flywheel and the drive gear. The starter's operating cycle is short-term, because it does not participate in the subsequent movement of the car - its main task is to start the engine.
If we look in more detail, the principle of operation of the starter is as follows: 1) Turn the key in the ignition switch to the “start” position.
The current is transmitted through the circuit from the battery to the ignition switch and then to the traction relay; 2) The overrunning clutch (Bendix) drive gear engages with the flywheel; 3) Simultaneously with the movement and engagement of the gear, the circuit is closed and voltage is supplied to the electric motor;
4) The engine is started and after its speed exceeds the starter speed, the overrunning clutch disconnects the drive gear and the electric motor shaft.
What else do you need to know about the starter?
In addition to those listed, there are two more classifiers of car starters. According to the type of its design, it can be:
- with gearbox
- without gearbox.
On engines with a diesel power system, as well as on high-power engines, a starter with a gearbox is installed. A planetary gearbox, consisting of several gears, is mounted in the starter housing. It increases the passing voltage several times, thereby increasing the torque. A starter with a gearbox has the following advantages:
- it is more efficient, has high efficiency;
- consumes much less current during cold engine starts;
- the gear starter has more compact overall dimensions;
- maintains high efficiency and excellent performance even when the battery's starting current drops.
The principle of operation of gearless starters is direct contact with a rotating gear. Among the advantages of such a device are:
- simplicity of the device and higher maintainability;
- faster engine start due to instant connection with the flywheel crown after current is applied;
- resistance to high loads.
Source: http://yamotorist.ru/index.php/kontent/starter-ustrojstvo-i-printsip-raboty
Operating principle and design of the starter
The starter's operation precedes the movement of any vehicle. Knowledge of the structure and operating principle of this unit helps to start the engine correctly and quickly find the causes of poor starting.
Car starter device
Currently, starters for all cars have minimal design features and differ slightly from each other. Thus, knowing the design of the starter of one car, you can easily understand the design features of this unit from another car.
A typical starter consists of the following main parts:
- DC motor;
- solenoid (traction) relay;
- bendix.
The main unit is the electric motor, which, after turning on the ignition, begins to rotate the engine crankshaft with the gears of its shaft.
The retractor relay moves the bendix with the working gear along the electric motor shaft, closes the contacts of the electric motor after the flywheel ring and gear are engaged.
Bendix provides a temporary connection between the flywheel ring and the starter shaft to rotate the crankshaft.
The starter circuit diagram is shown in the following figure:
The principle of operation of a car starter
A car starter is an electromechanical device. Its main task is to convert battery electricity into mechanical rotating force. Before the engine starts, the following processes occur:
- After the ignition is turned on, electric current flows through the starter relay to the solenoid relay.
- The retractor armature moves inside the starter housing and extends the bendix to engage its gear with the flywheel ring.
- After the armature of the solenoid relay reaches the end point, the contacts close, then the current flows to the starter motor winding and the holding winding of the relay.
- The rotating starter shaft starts the car engine. After the rotation speed of the starter shaft becomes lower than the rotation speed of the flywheel, the bendix disengages from the ring and returns to its original position using a return spring.
- After starting the engine, the supply of electric current to the starter is stopped.
As you can see, the design of a car starter is not particularly difficult. To carry out independent repairs, it is enough to master the principle of operation, study the technical characteristics of a specific model (torque, shaft speed, current consumption, power and rated voltage).
all-drive.net
Engine starting system. Starter
The engine starting system is designed to create primary torque of the engine crankshaft at the speed necessary to form the required compression ratio to ignite the combustible mixture. The launch system can be controlled manually, automatically or remotely.
The engine starting system consists of the main functional devices:
- Accumulator battery
- Starter
- Start control mechanisms (ignition switch, automatic start control unit, remote control system)
- Large cross-section connecting wires (stranded copper).
Requirements for the launch system:
- reliability of the starter (no breakdowns after 45-50 thousand kilometers)
- Possibility of reliable starting in low temperature conditions
- the ability of the system to perform repeated starts within a short time.
Car starter device
The main component of the engine starting system is the starter. It is a DC electric motor with a voltage of 12 volts and develops approximately 5000 rpm at idle.
The starter consists of five main elements:
- The starter housing is made of steel and has the shape of a cylinder. The field windings (usually four) together with the cores (poles) are attached to the inner wall of the housing. Fastening occurs with a screw connection. The screw is screwed into the core, which presses the winding against the wall. The housing has threaded technological holes for fastening the front part, in which the overrunning clutch moves.
- The starter armature is an alloy steel axis onto which the armature core and commutator plates are pressed. The core has grooves for laying armature windings. The ends of the windings are securely attached to the collector plates. The collector plates are arranged in a circle and are rigidly mounted on a dielectric base. The diameter of the core is directly related to the internal diameter of the housing (together with the windings). The armature is mounted in the front cover of the starter and in the rear cover using bushings made of brass, less often copper. Bushings are also bearings.
- The solenoid relay or traction relay is installed on the starter housing. In the housing of the traction relay, in the rear part there are power contacts - “nickels”, and a movable jumper contact, made of soft metals. “Pyataki” are ordinary bolts pressed into the ebonite cover of the traction relay. Using nuts, power wires from the battery and from the positive starter brushes are attached to them. The core of the traction relay is connected through a movable “rocker arm” to an overrunning clutch, popularly called a bendix.
- The overrunning clutch (Bendix) is movably mounted on the armature shaft and is a roller mechanism that is connected to the engagement gear with the flywheel ring. The design is assembled in such a way that when torque is applied to the bendix in one direction, the rollers located in the cage come out of the grooves of the cage and rigidly fix the gear to the outer race. When rotating in the opposite direction, the rollers fall into the cage, and the gear rotates independently of the outer race.
- The brush holder is a starter element through which operating voltage is supplied to the copper-graphite brushes and then transmitted to the armature commutator plates. The brush holder is made in the form of a dielectric cage with metal inserts, inside of which there are brushes. The brush contacts (soft stranded wire) are spot welded to the pole plates. The pole plates are usually the “tails” of the field windings.
Operating principle of the starting system and starter
The stages of operation of the starter are as follows: docking with the flywheel ring gear, starting the starter, uncoupling the starter.
In fact, it looks like this: when you turn on the ignition switch and turn the key to the “start” position, along the “+” circuit, battery – ignition switch – traction relay winding – “+” starter output – positive brush – armature winding – negative brush, it is triggered traction relay. Under the action of the relay core, the moving contact closes the power contacts, through which current is supplied from the battery to the positive wire of the starter. The starter positive is connected to the positive pole plate and positive brushes. The minus is permanently connected by default.
After current is supplied, magnetic fluxes arise around the armature windings and field windings, which are directed in one direction and, as is known, identical poles of a magnet repel each other, so a circular movement of the armature occurs.
At the moment the retractor relay is activated, the “rocker arm” begins to move together with the relay core and pushes the bendix on the armature splines towards the flywheel crown.
At this moment the anchor begins to rotate and drives the flywheel.
If the car engine has started and the ignition key has not yet been released, a moment comes when the engine speed exceeds the starter speed, in which case the Bendix overrunning mechanism is activated.
For diesel engines or high-power engines, a different mechanism for feeding rotation to the bendix is used. A gearbox built into the starter housing is used.
The gearbox is a transmission drive mechanism, i.e. Three satellites rotate along the inner gear ring, which drive the shaft on which the bendix is movable.
The advantage of such starters is their small size and high power.
| WE RECOMMEND ALSO READ: _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ |
autoustroistvo.ru
Which starter is better - geared or conventional? Differences, principle of operation and device
Technical progress does not stand still and is constantly evolving. Every year new technologies emerge, allowing engineers to improve or create completely new parts. This also applies to mechanical engineering.
Hundreds of thousands of modern cars are sold in Russia every year. Each of them contains the latest technologies.
We will talk about such a small unit as a starter, and we will figure out which starter is better: a gearbox or a regular one.
General information
The first starter used on a car had a number of significant shortcomings. Over time, the design was gradually improved and significantly transformed.
The starter is a 4-band electric motor, which is necessary to rotate the crankshaft when starting the engine. It takes energy from the battery and increases the starting current several times.
Due to this, any internal combustion engine starts. The principle of operation of the starter has not changed over the years.
Nevertheless, its design has been constantly improved. The weight of the part was reduced, the service life was increased due to the use of higher quality and new materials, etc. All this led to the fact that the starter was transformed quite significantly and even a new type appeared - gearbox. This is exactly what we will talk about now.
Classic starter: operating principle and design
The key feature of such a device is that there is no such intermediate unit as a gearbox. This allows rotation to be transmitted directly from the starter to the crankshaft.
Consequently, the device is simpler to manufacture and much easier to repair. Another feature of such a starter is that the electric current supplied to the switch allows you to instantly engage the gear and flywheel.
This helps the car to start, as drivers say, in a snap.
Currently, they are trying to replace such starters with reduction ones. However, most cars used to have a classic starter. The operating principle and design made this unit extremely durable. Such units almost never fail due to electrical influence, but much more often they need to be repaired due to low temperatures.
Construction and something else
During operation, the internal combustion engine produces a fairly large amount of energy. It is enough for lighting devices, music, wipers, etc. In general, while driving, the main load goes to the generator. In a static position, the motor does not produce anything, so it needs to be started somehow.
For this purpose, various types of starters are used along with the battery. The electric motor itself, that is, the housing, is made in a cylindrical shape. It houses the cores and exciting windings. It is clear that there is an anchor - one of the most important and expensive parts.
The collector springs and cores are pressed onto it. It has an axial shape. There is also a starter solenoid relay. The price of this spare part is relatively small, although the part performs extremely important functions. First, it supplies energy from the ignition switch to the electric motor.
Secondly, it pushes out the overrunning clutch.
Most often, it is the starter solenoid relay that fails. Its price is fortunately affordable and starts from 500 rubles and ends in several thousand. In addition, the design includes a bendix with a drive gear and brushes.
Starter operation stages
This node works as follows:
- connection of the gear to the flywheel;
- starting the starter;
- disconnecting the gear and flywheel.
Naturally, the starter only works when the engine starts, and then turns off. If this does not happen, then one of the mechanisms is faulty.
After the driver inserts the key into the ignition and turns it to the operating position, current is supplied from the battery to the traction relay.
Thanks to this, the bendix of the gear starter engages the gears, at the same time, due to the supply of voltage to the electric motor, the circuit is closed and the car starts. Once the engine speed exceeds the speed of our starter, it turns off.
It turns on only the next time the engine is started. Well, now let's look at how a gear starter differs from a regular starter. There are some interesting details here.
Gear starter
The general principle of operation is no different. Electrical energy is also converted into mechanical energy. The only difference is the presence of a gearbox. In addition, this starter also has permanent magnets in the winding, which makes it possible to slightly increase the reliability of the electric motor as a whole.
Of course, there are some peculiarities here. In particular, many are interested in how much a starter of this type costs. In most cases, a little more expensive than classic ones, but not much. On average by 10-15%. But its service life is an order of magnitude longer, and this is definitely worth taking into account.
The service life of such a starter directly depends on the quality of the gearbox. The better the steel used when casting the gears, the less chance that the teeth will stick together after the hundredth start.
In general, the design is popular today, and more and more gear starters are appearing.
Advantages and disadvantages of the classic version
So we are actually gradually approaching the answer to the question of which starter is better: gear or conventional. To do this, let's look at the strengths of the classic version. They are as follows:
- low cost;
- high maintainability;
- You can find spare parts almost everywhere.
But there are also some disadvantages, which are expressed in the following:
- high base current required;
- rapid wear of parts;
- does not work well at low temperatures;
- large weight and size.
In general, this is a fairly reliable design with proper maintenance. But development does not stand still, and this has led to more advanced gear starters. Let's look at their strengths and weaknesses.
A starter with a gearbox: what is good and what are its disadvantages
We have already figured out how this device works and what its fundamental differences are. It is no longer difficult to guess which starter is better, gearbox or conventional. The fact is that the first option has the following strengths:
- small size and weight;
- long service life regardless of ambient temperature;
- low energy consumption (40% less than the classic version).
As for the disadvantages, they are there too and are as follows:
- complexity of repair work;
- lack of spare parts in stores;
- high cost of the product;
- low quality gearbox.
Often the main reason for the breakdown of a starter with a gearbox is that low-quality components are installed. This leads to breakdowns and various types of malfunctions. In general, such a unit has more prospects in the future than a conventional starter. And this is not due to the fact that one is good and the other is bad, but due to scientific and technological progress.
Let's sum it up
If you decide to replace this unit, then you first need to decide where the starter is located. This is usually the driver's side under or to the side of the engine. To remove it, you need to make room.
Depending on the location, it may be necessary to remove the engine protection or the air filter with the box. Next, disconnect the wires and unscrew the bolts. Determining where the starter is located is not difficult.
It has a cylindrical shape, and several wires come from it, secured with a nut. Everything is done quite simply and quickly.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AU0Yy14tBdU
So we answered the question about which starter is better: gear or conventional. Classic starters are good in their own way, but are gradually being phased out. But they also have their strengths, just as gearboxes have their weaknesses.
For example, in the outback it will be difficult to find spare parts for a starter with a gearbox, but for a regular one – no problem. The same can be said about repairs - not everyone has encountered gearboxes on the starter and not everyone will undertake it.
How much does a starter with gearbox cost? It all depends on the brand of the car; a normal one will cost 5-7 thousand rubles.
fb.ru
Source: http://autoprivat.ru/remont_avto/princip_raboty_i_ustrojstvo_startera.html
Starter operating principle
The time required for a novice car enthusiast to go from ordinary driving to independently performing repair and restoration work on his car is usually small.
And it’s better to prepare for this moment in advance. However, the question immediately arises: “Where to start?” Experienced car owners are mostly unanimous in their answer to this question. From studying the starter device.
Why? Everything is very simple.
A car starter is a unit on the reliable functioning of which the stable start of the power unit depends, without which the movement of the car is in principle impossible.
In addition, knowledge of the design features of such an important unit, which is the vehicle starter, will allow you not only to perform the starting procedure technically competently, but also to easily identify the sources of problems that arise, and, therefore, eliminate them in a timely manner.
Car starter device
Figure 1, at the beginning of the article, shows the main elements of the starter.
Any automobile starter, which is essentially an electric motor, consists of a fairly large number of structural elements (from four to six dozen) included in its main components:
- The actual electric motor.
- Overrunning clutch, or bendix (the latter name, which is the name of the inventor, is most common among car enthusiasts).
- Solenoid or traction relay (hereinafter referred to as VR).
Understanding the design of a starter as a unit lies in the plane of knowledge of the functional purpose of each of the components, its degree of priority, operational capabilities, etc.
The electric motor, which is the main unit, is functionally designed to transmit torque from its shaft to the crankshaft of the power plant.
The other two nodes are auxiliary, and their functional purpose is:
– longitudinal movement of the overrunning clutch, which in turn ensures the movement of its working gear, caused by the movement of the relay armature;
– closing of the contacts of the electric motor at the moment of engagement of the teeth of the flywheel rim with the teeth of the working gear;
- Bendix. Ensuring a reliable connection between the electric motor shaft and the flywheel crown.
Starter circuit
The schematic diagram for ensuring the start of the power unit, in which the starter (item 3) is involved, looks as shown in Fig. 2, and its main elements are: battery (item 1), generator (item 2) and switch (lock ) ignition (item 4).
Fig.2
In addition, in this section of the article, we considered it appropriate to place another diagram that allows for a fairly effective test of the starter’s performance.
Connection diagram for testing the starter on a stand
To check (on a bench) the mechanical and electrical parameters of the starter, assemble a simple circuit shown in Figure 3. Its elements are:
- the starter itself (item 1);
- digital or pointer voltmeter, the scale limit of which is at least 15 Volts (item 2);
- slider rheostat, approximately 800 Amperes (item 3);
- digital or pointer ammeter, the shunt value of which is 1000 Amperes (item 4);
- switch (pos. 5);
- car battery with a capacity of 55 A/h (item 6).
- connecting wires with a cross-section of 16.0 square millimeters or more.
As mentioned above, the starter, which is an electromechanical device, has an operating principle based on the use of electrical energy received from the car’s battery and converting it into mechanical energy, that is, the energy of the car’s engine.
In this case, the following happens inside the starter and other circuit elements (see Fig. 2):
- Through the closed contacts of the ignition switch (pos. 4), the current flows to the contacts of the starter relay (pos. 3), and then to the terminals of the VR retractor winding.
- The armature BP, performing a translational movement inside its (BP) body, moves the overrunning clutch until the teeth of its working gear engage with the teeth of the flywheel ring.
- Reaching the final position by the VR armature causes the contacts to close, which, in turn, causes current to flow to the electric motor winding and the (holding) relay winding.
- The starter shaft, transmitting torque to the engine crankshaft (via the flywheel), ensures the start of the power plant.
- When the flywheel reaches a rotation speed exceeding the rotation speed of the starter motor shaft, the teeth of the Bendix working gear disengage with the ring teeth, and the return spring will ensure that the overrunning clutch returns to its original (before starting) position.
- Returning the key to the ignition switch stops the supply of current to the starter contacts from the battery, and further operation of the power plant occurs without its (starter) participation.
Summarizing the above, we note that along with knowledge of the design and principle of operation of the starter, a novice car enthusiast absolutely needs to know such characteristics of the starter as: rated power, rated supply voltage, amount of current consumed, shaft speed, torque value, etc.
Video - Design and operation of the starter
Source: http://VipWash.ru/starter/princip-raboty-startera
How a car starter works: principle of operation and malfunctions
Content
A starter is an attachment to a vehicle that is required to rotate the engine crankshaft to start it. To start a working engine, it is enough to rotate the crankshaft for 3–5 seconds. Features of starters For starting the engine of passenger cars, special DC electric motors have been developed, powered by the battery.
The short-term operating mode of the starting device allowed the designers to calculate a highly optimized design with virtually no reserves of characteristics necessary for long-term operation of the product. This made it possible to reduce the dimensions and simplify the motor, reducing the cost of the product.
On a new car, this decision justifies itself. During operation, the car engine loses its original characteristics. Additional loads arise on the starter.
For long-term uninterrupted operation of the electric motor, it is important to consider many vehicle operating parameters and the materials that were used by the starter manufacturer.
At the same time, during the operation of the vehicle, quite often problems with starting the power plant arise precisely because of the failure of the vehicle starter. In this article we will look at the main faults of the starter, as well as why the starter does not turn off after starting the engine.
The design of a car engine starter and its operating principle
The main components of the starter:
⇒ electric motor;
⇒ solenoid relay;
⇒ gear with bendix;
In a nutshell, a flywheel with a ring gear is installed on the engine crankshaft. When the starter is turned on, the starter gear meshes with the flywheel crown and the electric motor turns the crankshaft. After the engine starts, the starter overrunning clutch disengages the gear from the shaft when the engine speed exceeds the starter speed.
⇒ If we take a closer look at the starter, its electric motor consists of a housing, inside of which there is a stator and a rotor rotating in two bushings.
⇒ The brush assembly consists of three or four brushes, which are supplied with voltage from the battery. The brushes, in turn, connect to part of the rotor and supply voltage to it, causing the starter motor to rotate.
⇒ The gear and bendix, located on the rotor shaft, moving forward and backward along it, engage with the flywheel. The solenoid relay turns the electric starter into operation.
The principle of operation of the starter is as follows. The vehicle interior has an ignition switch that has several positions, including the “On” position and the “Start” position. When the key is turned in the ignition switch in the “Start” position, the current transmitted through the circuit from the battery is supplied to the starter solenoid relay.
The solenoid relay is an electromagnet with a coil and a core. The core, under the influence of the electromagnetic field, begins to move to the side, while the fork connecting the core and the bendix pushes the bendix and gear along the shaft forward to engage it with the flywheel.
The relay has two contacts, one of which is supplied with voltage from the battery, and the other is connected to the brushes of the electric motor. When the core reaches the end of the relay, with the gears already engaged with the flywheel, the copper plate located at the end of the core closes these two contacts and voltage flows to the electric motor.
The electric motor begins to rotate, and accordingly, the engine crankshaft also rotates, after which the vehicle’s internal combustion engine starts.
After starting, the core will return to its original position, the bendix will disengage with the flywheel and the starter will be disconnected from the engine.
Then the internal combustion engine begins to work in autonomous mode and does not require the connection of third-party power sources, and the car’s generator charges the battery.
As for the types of starters, there are:
⇒ A starter with a gearbox, which consists of several gears and is mounted directly to its housing. The electric motor of such starters is highly efficient and consumes much less current when starting the engine. It is installed on cars with diesel engines and on gasoline cars with more powerful engines.
⇒ A starter without a gearbox, having high resistance to loads, ensures quick starting of the motor due to instant connection with the flywheel crown after current is applied.
In this case, starters may differ from each other, but not significantly. In most cases, their difference lies in the mechanics of automatic gear disengagement.
It usually takes a few seconds for the engine to start. But in practice, malfunctions may occur when, after the first turn of the key, the engine does not start, after starting the engine, the starter spins along with the engine, etc.
Basic starter malfunctions
First of all, it is important to remember that with numerous attempts and a long time to start the engine, the starter itself and the battery suffer. Moreover, prolonged rotation of the starter can damage the device.
The average starter service life is 120,000 km of vehicle mileage in mixed operating mode. It is assumed that the engine starts in 4 - 7 seconds the first time.
Bad gasoline and engine wear increase the frequency of use of the starter and the duration of engine starting. In winter, engine oil is more viscous.
There may be condensation on the spark plugs, making it difficult to start the engine.
So, if the engine does not start, first of all you need to check the battery charge, since after repeatedly running the starter, the battery may simply discharge. In this case, the battery will need to be charged.
Also, failure of the starter itself should not be ruled out. The starter can overheat when cranked for quite a long time, resulting in damage to the armature or rotor. With repeated attempts to start the car engine, there is a risk of damage to the splines on the coupling, which protects the starter from impacts from the teeth of a spinning flywheel.
One way or another, failure of the starter will require its repair or replacement. Among the main malfunctions of the electric starter, the following should be highlighted:
⇒ Under the influence of high currents, the copper contacts burn, and the starter begins to turn weakly. The problem is solved by cleaning the contacts or replacing them with new ones.
⇒ The most common malfunction is wear of the bushings (the starter “shoes”). As we know, the rotor shaft is located in two bushings. If these bushings wear out, the shaft, warping, begins to cling to the stator with its rotor. In this case, not only mechanical friction occurs, but also a short circuit.
⇒ In this case, the starter turns very slowly, this can be determined by ear. When working this way, it is unable to quickly spin up the engine, and there is also a heavy load on the battery. The starter must be removed to replace faulty bushings.
⇒ Less wear on brushes. If this happens, they are changed. Also, if the starter turns, but the engine does not, most likely the problem is in the bendix. In simple words, rotation is not transmitted from the rotor shaft to the flywheel. In this case, the overrunning clutch, i.e. the Bendix, is replaced.
⇒ A situation also arises when the starter rotates with the engine. This means that the starter does not disengage; voltage remains on its power contacts or on the contacts of the pre-start relay. The problem is often that the starter armature is clogged; in this case, the bendix may become jammed and it will not disengage.
In the latter case, it is necessary to check the contacts on the solenoid relay circuit, the contact group of the ignition switch and check the starter bendix. If problems are identified, they must be corrected.
You can also check an additional relay (installed separately), which serves to protect the starter from accidental combustion of contacts in the ignition switch, which occurs during wear or prolonged starting.
How to check the starter
First of all, without having certain skills and abilities, it is better to contact a service station, where experienced specialists will determine exactly what caused the starter to fail.
The initial check of the starter is carried out by measuring the voltage in the wire going to the control contact of the solenoid relay when turning the car's ignition key.
In operating condition, the voltage should be 12 - 24 Volts (depending on the type of vehicle when testing the starter of a car or truck).
The neutral position of the ignition key in the lock means that the voltage on the solenoid relay control wire should disappear.
In a similar way, performance is determined using a test lamp. When you turn the ignition key, the lamp should light up; accordingly, when you turn the key to its original position, the lamp goes out.
If the contacts on the solenoid relay circuit are in order, then the problem should be looked for in the overrunning clutch bendix, which was mentioned earlier.
If the overrunning clutch continues to spin after starting the engine, it is jammed on the starter shaft.
This happens when the Bendix gears wear out or the flywheel teeth wear out. This problem can only be solved by replacing the bendix or flywheel assembly. If the solenoid relay, gear and overrunning clutch (Bendix), as well as the flywheel and combustion lock are all fine, but the problem remains, then the starter must be removed for repair or replacement.
Eventually
As you can see, any problems with starting the engine are a reason for diagnostics. Moreover, if the culprit is the starter, then the problem often tends to progress.
In practice, problems are indicated by the fact that the starter turns hard or clicks, but does not turn the engine, knocks are heard, a grinding noise appears when trying to start the engine, the starter does not turn off after starting the engine, etc.
Such symptoms indicate that in the future there is a high probability of needing to repair/replace not only the starter itself, but also the flywheel (and the flywheel itself is an expensive part). For this reason, it is optimal to perform starter diagnostics immediately after the first signs of malfunction appear.
For successful long-term operation of the starter, many factors must be taken into account. Timely seasonal oil changes, monitoring the condition of the engine, and preventive maintenance of electrical equipment will keep the starter in working condition throughout the entire life of your car.
Source: http://avtoviraj.ru/kak-rabotaet-starter-avtomobilya-princip-raboty-i-neispravnosti/
How does a starter work: device and principle of operation? – Automotoguru
The car starter starts the engine. Let's consider the features of its design and the conditions under which the service life of the motor will be long and uninterrupted.
Design features of starters To start the engine of passenger cars, special DC electric motors have been developed.
To start a working engine, it is enough to rotate the crankshaft for 3–5 seconds. The short-term operating mode of the starting device allowed the designers to calculate a highly optimized design with virtually no reserves of characteristics necessary for long-term operation of the product.
This made it possible to reduce the dimensions and simplify the motor, reducing the cost of the product. On a new car, this decision justifies itself. During operation, the car engine loses its original characteristics. Additional loads arise on the starter.
For long-term uninterrupted operation of the electric motor, it is important to consider many vehicle operating parameters and the materials that were used by the starter manufacturer.
Starters from different manufacturers are structurally similar; the general structure is shown in Fig. 1.
In general, the design includes:
• The motor housing is made of steel. Structurally, it not only performs load-bearing functions, but also serves to remove heat and cool the armature and stator windings due to the inertial thermal properties of the metal. Modern housings are made with good water-repellent properties, allowing you to wash the engine if necessary without the fear of moisture getting into the current-carrying elements.
• A solenoid relay is located on the housing. Through a lever, the relay connects the starter gear to the flywheel of the car engine, providing the ability to transmit torque when starting. The retracted relay core connects the copper contacts, providing power to the stator and armature of the motor.
• The armature contains the winding, movable gear and commutator plates.
• Bendix (overrunning clutch) is used to connect the starter to the flywheel during starting. As soon as the car starts, the spring returns the gear to its original position and the relay core, opening the contacts.
• Brush holders provide fastening of the electric motor brushes and the ability to easily replace them when servicing the unit.
Starter operating principle
A typical electrical circuit diagram for connecting a starter is shown in Figure 2. When the owner turns the ignition key, it closes an electrical circuit, applying voltage to the solenoid relay.
The core retracts, connecting the gears and completing the current-carrying cable from the battery to the starter windings. The electric motor rotates and spins the engine flywheel.
Once the engine speed exceeds the starter speed, Bendix will disengage the starter gears. At this point, the operation of the electric motor ends until the next start.
Typically, electric motors with a power of 2 to 3 kW are used in a passenger car. In this case, the starting current can exceed 300 A. This current heats the motor windings and can cause sparks when the contacts are connected.
Pro Tip: When starting the engine, do not operate the starter for more than 15 seconds. Before restarting the engine, pause for at least 1 - 3 minutes in the cool season. In summer, the pause should be increased to 5 minutes.
Overheating of the housing leads to winding failure. Manufacturers of electric motors for starting an engine are trying to reduce the current consumption of the device and increase torque. This is possible when using a gearbox, see Fig. 3.
A starter with a gearbox spins the engine flywheel faster and has lower starting currents. Repair and maintenance of such starters is difficult. In addition, some manufacturers use plastic in the manufacture of gears, see Fig. 4.
Overheating of the housing of such a starter leads to gearbox failure.
Professional advice: choose starters without the use of plastic if the car is operated at air temperatures below minus 15 degrees C.
Basic starter malfunctions The average starter service life is 120,000 km of vehicle mileage in mixed operating mode. It is assumed that the engine starts in 4 - 7 seconds the first time.
Bad gasoline and engine wear increase the frequency of use of the starter and the duration of engine starting. In winter, engine oil is more viscous.
There may be condensation on the spark plugs, making it difficult to start the engine.
Pro tip: in winter, start a cold engine with the clutch pedal depressed. Before starting, purge the engine combustion chambers by pressing the gas pedal all the way and turning on the starter for 3 seconds. This will disperse the oil and provide good conditions for starting the engine.
The cold season, a dead battery and engine wear lead to the need to rotate the crankshaft for longer than the 5–7 seconds for which the starter is designed. This significantly reduces the service life of the electric motor. It is recommended to carry out preventive maintenance and replace wear parts of the starter after every 60,000 km, if the car has traveled more than 100,000 km.
During operation, the sliding bearings (bushings) of the motor wear out first. This increases the misalignment of the armature, which can lead to poor gear engagement and licking of the teeth. Friction forces increase when the starter operates. Due to the friction of parts inside the electric motor, the torque decreases and the speed of the piston in the combustion chamber decreases.
Premature heating of the body occurs.
Pro tip: a decrease in crankshaft rotation speed when starting a warm engine indicates wear on the starter. Urgently replace the bushings, gears and brushes of the electric motor.
Wires in cars often oxidize. This increases the resistance of current-carrying cables at the connection points. If the starter does not turn, you need to check the cable contacts on the battery. Parking a car for a long time in winter leads to a complete discharge of the battery. These faults must be corrected for the starter to operate.
Usually, during the next maintenance of the car, the owner talks about the first signs of starter wear and the necessary prevention. The electrician checks the capacity of the battery and the motor power circuit. The starter is removed and disassembled if its design allows changing wear parts. Or they change the mechanism completely to a new one.
Pro Tip: Be sure to clean and grind the starter armature commutator plates. Often this is not done when changing brushes. Lack of grinding will lead to accelerated wear of the brushes and possible breakage of the armature contact groups.
Severe wear on the starter bushings leads to armature misalignment and gear wear. When starting, an unpleasant wheezing sound is heard, the engine flywheel does not spin. The second or third attempt to start may be successful.
Operating the starter with a licked gear can lead to failure of the engine flywheel crown. Wear of the bushings also leads to breakdown of the starter gearbox, if it is structurally provided for, see fig. 5.
Frequent starting attempts lead to premature burnout of the solenoid relay contact. Connecting the battery to the electric motor is impossible.
In case of such a breakdown, you must contact a workshop to replace the contact group and carry out servicing of the starter. As a temporary output in some relays, you can rotate the contacts 180 degrees, extending the life of the current-carrying plates.
This can be done in the field, if such a repair option is structurally possible.
Pro Tip: If the starter relay contacts burn out, the car can be started.
To do this, you need to put the gear shift lever in the neutral position, put the car on the handbrake, turn on the ignition and, getting out of the car, connect the contacts of the starter solenoid relay with a powerful jumper (pliers). After starting the engine, the jumper must be removed immediately. Use this method only as a last resort.
For successful long-term operation of the starter, many factors must be taken into account. Timely seasonal oil changes, monitoring the condition of the engine, and preventive maintenance of electrical equipment will keep the starter in working condition throughout the entire life of your car.
Source: https://avtomotoguru.ru/kak-rabotaet-starter-ustroystvo-i-princip-raboty/