Vehicle stability control system. What it is?
Rating: 4 / 5
In this article we will talk about the car's exchange rate stability system . You will find out what it is and why this system is needed at all.
If you look at the cars produced 15 years ago and those coming off the assembly line today, you can identify a lot of differences.
It has already become common to see a car with a rain and light sensor, a Stop-Start system, an ascent and descent assist system, a lane change assistance system, etc. and so on. All this, of course, is created not so much for the sake of comfort and prestige, but to ensure greater safety when driving.
And our today's hero is direct proof of this statement. What's special about it?
Why do you need a vehicle stability control system?
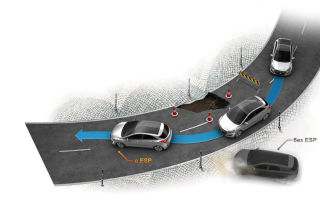
The vehicle's exchange rate stability system serves to prevent skidding in the event of a critical situation on the road in the form of loss of stability and controllability (for example, when accelerating on wet asphalt or a sharp turn), to ensure movement exactly along the trajectory that the driver has set...otherwise in other words, to help the car maintain stability.
Even though there is a category of people who are skeptical about such a development, mistakenly believing that they want to steal more money from them, the vehicle's stability control system is actually a very effective means of road assistance.
Depending on the situation, the system can change the engine torque, the angle of rotation of the front wheels (or slow them down), and, if the car has an adaptive suspension, affect the degree of damping of the shock absorbers. It is triggered precisely at the moment when the vehicle’s stability has occurred or may occur.
This system is mainly installed on premium cars. Unfortunately, it is not available on cheaper cars (the exception is the Ford Focus II). The system comes either as a standard option or as an additional option.
{typography pre_red}INTERESTING VIDEO{/typography} The approximate cost of installation is 10,000 rubles (it all depends on the specific brand of car). But at the same time, the car must still have an ABS anti-lock braking system, since most of the components of these two systems are combined together.
Each manufacturing company calls the vehicle's stability control system differently.
So, for example, on Kia and Hyundai models it is called ESC or Electronic Stability Control (electronic stabilization system), BMW, Jaguar calls it DSC or Dynamic Stability Control (dynamic stabilization system), Infiniti, Nissan and Subaru - VDS or Vehicle Dynamic Control (dynamic control mechanism), ESP or Electronic Stability Program (electronic stabilization program) is perhaps the most popular and is installed on most American and European cars.
The vehicle's directional stability system consists of special sensors (steering angle, wheel angular speed, vehicle turning speed, pressure in the brake system, etc.
), from which the control unit receives signals.
In turn, the control unit gives commands to the corresponding actuators: high-pressure switching valves of the traction control system, valves of the ABS system, etc.
Although vehicle stability control is a very effective means of active safety, it cannot be completely relied upon because there are situations when the electronics are unable to do anything due to the existing laws of physics (for example, when the driver enters very suddenly and at high speed). into a sharp turn). This should always be kept in mind.
It is worth noting that in some countries (Australia, Israel, America) this system is already legally required equipment for cars.
Vehicle stability control system
Source: http://auto-observer.ru/sistemi-auto/80-sistema-kursovoy-ustoychivosti-avtomobilya-chto-eto-takoe.html
Vehicle stability control system
More recently, for ordinary motorists, the presence of electronic systems supported by automation in a car was a wonder. Today, many similar assistants are used, some of which take an active part in direct driving control.
One of the most significant is the directional stability system, which is responsible for correcting wheel torque. This technology is labeled as ESC (Electronic Stability Control) and is most often available as an option for models not lower than the middle class.
However, some automakers are beginning to offer similar devices for budget vehicles.
Technical implementation of the system
The mechanism for ensuring directional or dynamic stability is a set of functional components, including a control unit, sensors and hydraulic actuators.
During operation, sensitive elements (sensors) record vehicle movement parameters and evaluate the driver’s actions, sending the corresponding data to the control unit.
For example, the angle of rotation of the steering wheel, the state of the brake light, the speed of rotation of the wheels and the level of pressure in the brakes are taken into account. Next, the control unit of the directional stability stabilization system, based on the received signals, sends commands to the executive equipment.
This step involves valves, brake pressure switches, optical elements, etc.
Hydraulic devices, depending on the settings, can control the behavior of the car on the road, influencing, among other things, the gearbox.
Operating principle
The moment the system enters the control process can be considered a potentially dangerous or emergency situation, the risk of which the stabilizer determines by comparing the machine’s movement parameters and the owner’s actions.
So, if the exchange rate stability system detects a difference between the actual indicators of the vehicle’s condition and those previously established, then the situation will be recognized as uncontrollable and control will partly pass to the ESC modules.
Here it is important to note the significance of the parameters that are considered critical. The user himself configures them in advance, and if during driving for one reason or another they are violated, the system comes into operation automatically.
Now another question - how is direct control achieved? Much depends on the specific version, but standard ESC stability control systems implement control through the following actions:
- Changing the torque of the power unit.
- Braking the wheels (all or some individually).
- Correction of the degree of shock absorption damping (if the car is equipped with adaptive suspension).
- Changing the angle of rotation of the wheels (if active steering is provided).
Additional functionality
ESC modules can have different configurations - from basic to advanced with a specific set of subsystems.
In particular, brake boosters, moisture removal devices, temperature correctors, units that prevent the machine from tipping over, etc. can be optionally added.
It is also possible to expand functions at the software level. This refers to electronically changing torque settings or activating sound and light signals.
In vehicles equipped with a coupling device, the directional stability system can be supplemented with stabilization of the road train. This mechanism is designed to prevent vibrations when driving with a trailer.
Active means of improving brake reliability usually focus on regulating their power function, but ESC also allows you to correct insufficient adhesion between brake discs and pads.
Differences from ESP technology
Fundamentally, these systems differ little, and the key tasks are completely the same. This is to prevent skidding, maintain trajectory and generally eliminate any risk of collision.
The only difference is in the ways to achieve these goals.
Thus, the ESP exchange rate stability system is more focused on software regulation of driving parameters and a connection with an anti-slip protective module.
In terms of technical design, the technologies are also largely the same. The ESP kit contains the same electronic control unit and sensors, which are called G-sensors.
That is, the emphasis is on the quality of recording operating parameters, and not on the means of practically changing them.
The ESP exchange rate stability system intervenes in the control process not through its own infrastructure, but by changing the current functional parameters of the engine, braking system and devices responsible for active safety - the same traction control module.
What is needed to install the ESC complex?
It is precisely because of the interaction of stabilizers with related safety systems that such equipment will require an appropriate kit. Depending on the type of ESC and the assigned functional tasks, the preliminary installation of an anti-lock braking system and engine control unit may be required.
There are also nuances to using an electronic stability control system on cars with manual transmissions. In this case, full control control through regulation of the transmission unit will not be provided. The possibility of connecting electrical devices, including sensors, to the on-board network is also calculated in advance.
Disadvantages of the stability control system
ESC modules have many benefits related to driver safety. In addition, this assistant is also an ergonomic addition, in some cases simplifying driving.
But there are situations in which this same module will appear from negative sides. For example, if an experienced driver, using a proven scheme, wants to get out of a skid by increasing the gas.
In this case, the car's exchange rate stability system will not allow this, limiting the fuel supply and cutting torque.
The way out will be the stabilizer shutdown button, which is worth remembering in such conflicting situations.
Finally
Electronic driver assistance systems show an example of effective interaction between a car's software and mechanics. Moreover, every year leading auto giants offer new and more advanced modifications of such assistants.
For example, in the latest versions of the ESC stability control system, a response is provided in just 20 ms. And this is regardless of the current speed and driving mode. But, as already noted, this technology is not available to all car enthusiasts.
For owners of inexpensive domestic models, for example, it can only be purchased as an option and for a lot of money compared to other additional equipment.
Source
Source: https://drive.temaretik.com/1348723368322664867/sistema-kursovoj-ustojchivosti-avtomobilya/
What is ESP and how does it work
ESP is an abbreviation for "Electronic Stability Program" or "Electronic Stability Program". As for how ESP works, it increases the chances of surviving a dangerous situation on the road.
This is especially useful on slippery surfaces or when making sudden maneuvers on the road, such as when negotiating obstacles or turning at extreme angles.
In such situations, this device recognizes the threat in the early stages and helps the driver keep the car in the correct position.
A big step forward in driving safety was made in the mid-1990s when the first electronic stability control was introduced. The first device was developed by German supplier Bosch, and the first series of Mercedes-Benz S-Class and BMW 7 Series featured new regulatory safety designs for the first time.
This was about 25 years ago. And although the term ESP entered everyday language, the right to use this name remained with Bosch, since it was they who patented it.
Therefore, in many other brands this system is designated differently, for example, DSC (BMW), VSA (Honda), ESC (Kia), VDC (Nissan), VSC (Toyota), DSTC (Volvo). The names are different, but the principle of operation is the same.
In addition to ESP, the most commonly mentioned are ESC (Electronic Stability Control - Electronic Stability Control) and DSC (Dynamic Stability Control).
All of these devices, regardless of their name, use high-tech sensors, the vehicle's central computer, and mechanical measures to assist in driving safety.
We often read about high-performance cars having a tendency to understeer or oversteer, but the truth is that any vehicle can veer off course, especially if poor road conditions contribute to it.
Video about the ESP system:
Understeer occurs when the front wheels lack traction and the car continues to move forward instead of turning. Oversteer is just the opposite: the car turns much more than the driver wants. Electronic stability control can help correct both of these situations.
Understanding how the exchange rate stabilization program works is quite difficult, because such a device does not work completely alone. It uses the vehicle's other regulatory safety devices, such as anti-lock braking and traction control, to correct problems before an accident occurs.
The ESP center is also the center of the car. This sensor is almost always located as close as possible to the very center of the vehicle. If you are sitting in the driver's seat, the sensor will be under your right elbow, somewhere between you and the passenger seat.
If stability control detects that the vehicle is swaying too much, it will intervene to help.
Using all modern electronic devices, ESP can activate one or more individual brakes, depending on the increase in driving safety, and control the throttle to reduce speed if necessary. The sensor looks for differences between the steering of the left wheel and the direction of the car and makes the necessary adjustments to the car's computer to adjust the direction to what the driver wants.
Video: ESP testing:
Electronic components of the device
Electronic stability control uses ABS and traction control, as well as several dedicated sensors, to do its job.
ABS system
Before the 1990s, the driver had to press the brake pedal very hard to maintain brake lock and cause deceleration. With the invention of anti-lock brakes, driving safely has become much easier.
ABS with an electronic pump brakes faster than the driver himself, thereby causing understeer or oversteer.
ESP uses a device to correct the problem by activating ABS, as needed, for an individual wheel.
Traction control system
ESP also uses traction control for driving safety. While it is responsible for monitoring side-to-side movement around a vertical axis, traction control is responsible for forward-backward movement. When the traction control detects wheel slip, the electronic stability control sensor acts on one side.
In the video - what is ESP of a car:
The device works quite dynamically - information is supplied to the car’s central computer using three types of sensors:
- Wheel speed sensor. Such sensors are located on each wheel and measure the speed in motion, the computer compares it with the speed of the engine.
- Steering angle sensors. These sensors are located in the steering column and measure the direction the driver takes while driving.
- Angular velocity sensor . Located in the middle of the car and measures the movement from side to side of the car.
Additional features
Since its launch, ESP has been constantly updated. On the one hand, the weight of the entire device is reduced (the Bosch model weighs less than 2 kg), and on the other hand, the number of functions that it can perform increases.
Stability control helps prevent the vehicle from rolling when traveling uphill. The brakes automatically maintain pressure until the driver presses the gas pedal again.
The video shows how the system works:
Benefits of Electronic Stability Control
ESP plays the most important role in driving safety, thereby reducing the number and severity of accidents.
Almost every driver has encountered unpleasant, difficult road conditions at some point, be it a rainstorm, a sudden hailstorm or an icy road.
Electronic stability control, along with other safety and regulatory devices on board modern vehicles, can help the driver maintain control on the road.
Source: http://365cars.ru/soveti/sistema-kursovoj-stabilizacii-esp.html
ESP Stability Control Overview
The main purpose of exchange rate stability systems (dynamic stabilization systems) is to maintain the stability and controllability of a vehicle by timely identifying and eliminating critical situations on the road. Since 2011, all new passenger cars in the United States, Canada and the European Union must include stability control.
The result of the system is that the car maintains the trajectory specified by the driver in all driving modes, be it acceleration, braking, straight movement, turning or free rolling.
Stability control systems from different manufacturers have different names:
- ESP (Electronic Stability Program) - installed on the vast majority of cars in Europe and America;
- ESC (Electronic Stability Control) – installed on Honda, Kia, Hyundai cars;
- DSC (Dynamic Stability Control) - on BMW, Jaguar, Rover;
- DTSC (Dynamic Stability Traction Control) - on Volvo;
- VSA (Vehicle Stability Assist) - on Honda, Acura;
- VSC (Vehicle Stability Control) - on Toyota;
- VDC (Vehicle Dynamic Control) - on Infiniti, Nissan, Subaru.
The most common exchange rate stability system is the EPS system, the design and principle of operation of which we will consider further.
Stability control system
Stability control is a high-level active safety system and includes:
- anti-lock braking system (ABS)
- brake force distribution (EBD) system
- electronic differential lock (EDS)
- anti-traction system (ASR)
The system also includes sensors, a control unit and a hydraulic unit (which is an actuator).
Diagram of the ESP stability control system
The vehicle parameters are received by the system sensors and transformed by them into electrical signals. Further, based on the information recorded by the sensors, the dynamic stabilization system evaluates the driver’s actions and vehicle movement parameters.
To assess the current situation on the road, the system uses information from the following sensors:
- steering angle
- brake system pressure
- wheel speed
- longitudinal and transverse acceleration
- car angular velocity
- and etc.
The received information is analyzed by the ESP system control unit, which subsequently sends commands to the actuators controlled by the active safety system:
- intake and exhaust valves of the ABS system;
- switching and high pressure valves of the ASR system;
- warning lamps for ESP and ABS systems, brake systems.
Also, the ESP control unit interacts with the engine management system and automatic transmission and, if necessary, adjusts their operation.
How the stability control system works
As a result of comparing the driver’s actions and vehicle movement parameters, the system determines the occurrence of an emergency situation. If the actual driving parameters differ from the standard ones, the ESP system considers the situation to be out of control and makes adjustments to the operation of the vehicle.
The stability control system can stabilize the vehicle's movement in the following ways:
- braking of one or more wheels;
- changing engine torque;
- changing the angle of rotation of the front wheels (if the car has an active steering system
- management);
- changing the degree of damping of the shock absorbers (if adaptive suspension is installed)
In the event of understeer, ESP prevents the vehicle from drifting out of the corner by applying brakes to the inside rear wheel and altering engine torque.
In the event of oversteer, the system prevents the vehicle from skidding in a corner by braking the front outer wheel and changing engine torque.
To brake the wheels, the appropriate active safety systems are activated.
The ESP system changes engine torque in one of the following ways:
- by changing the throttle position;
- missed fuel injection;
- skipping ignition pulses;
- changing the ignition timing;
- canceling the gear shift in the automatic transmission;
- redistribution of torque between axles (if all-wheel drive is used).
Such a system, which combines stability control, steering and suspension, is called an integrated vehicle dynamics control system.
Additional Stability Control Features
With the help of the exchange rate stability system, additional functions can be implemented such as:
- hydraulic brake booster
- rollover prevention
- collision avoidance
- road train stabilization
- Increased brake efficiency when warmed up
- removing moisture from brake discs
- and etc.
As a rule, these systems do not have their own structural elements and are included in the ESP programmatically.
ROP (Roll Over Prevention) - rollover prevention system , which performs its function by braking the front wheels and reducing engine torque. Additional pressure in the brake system is created by the active brake booster.
Collision avoidance system (Braking Guard) . For it to work, the car must have adaptive cruise control. Collision prevention is achieved by visual and audible signals, and in critical situations by increasing the pressure in the brake system by automatically turning on the return pump.
The road train stabilization system can be implemented in a vehicle equipped with a towbar. Trailer yaw is stopped by braking the wheels or reducing torque.
FBS (Fading Brake Support or Over Boost) . The task of the system for increasing the efficiency of brakes during heating is to counteract the insufficient adhesion of the brake pads to the heated brake discs, which is achieved by additionally increasing the pressure in the brake drive.
The system for removing moisture from the brake discs is activated at 50 km/h or more and the windshield wipers are on. Evaporation of moisture is achieved by a short-term increase in pressure in the front wheel circuit, causing the brake pads to come into contact with the discs.
Video: How ESP Bosch works
Source: http://ustroistvo-avtomobilya.ru/tormoznaya-sistema/obzor-sistemy-kursovoj-ustojchivosti-esp/
What does stability control system mean?
Modern cars are equipped with a large number of electronic equipment. They look more and more like robots. It is impossible to stop this development process. The machines are equipped with a large number of different systems. One such system is ESC.
What does Electronic Stability Program (ESP) mean?
Every motorist knows what ESP is. It is often also called “anti-skid” and “anti-skid”.
ESC is a dynamic stabilization system that ensures machine stability. It significantly improves driving safety. Therefore, ESP is one of the most popular security systems.
It can identify and eliminate critical situations in advance. For example, to maintain the controllability of the car.
It includes other machine systems:
Let's look at the main advantages:
- increased grip;
- maximum stability;
- easier control on various surfaces;
- increased safety.
What elements does ESP consist of?
Cars are stuffed with a large number of security systems that take care of the safety of the motorist. They combine their work with ESP. First of all, information from various sensors is used.
Now let's look at the main components of ESP:
- Special input sensors. They convert a physical quantity into a signal. This signal is then transmitted to the so-called control unit for further use.
- Special hydraulic block.
- Main control unit.
Each component deserves separate consideration.
So let's start in order:
1) Input sensors are important safety components. They are used to transmit Important information.
List of input sensors:
- vehicle turning speed;
- acceleration;
- angle of rotation;
- wheel speed angle;
- lateral acceleration;
- brake pressure.
The information obtained is used to evaluate the driver’s actions, as well as to diagnose driving parameters.
2) Special hydraulic unit of the vehicle. It is located between the wheel and brake cylinders. The block is used to control the brakes. And also other machine safety elements interact with the hydraulic unit:
3) The control unit is an important element of vehicle safety. It is to the control unit that all signals are transmitted. It is equipped with a special diagnostic system.
When a dangerous situation occurs, signals are transmitted to so-called execution devices. These devices are controlled by the control unit.
How the system works
Now let's take a closer look at the system that helps the motorist cope with the car in various conditions.
Why is this system installed in a car?
- helps maintain directional stability on poor surfaces;
- stabilizes the position of the machine;
- Helps maintain stability at high speed.
These are the main tasks of ESP, which it copes with effectively.
But ESP cannot work without other vehicle safety systems:
- a special powertrain control unit that controls various electrical subsystems in the car;
- ASR (Secondary Active Safety Element);
- ABS (anti-lock braking).
All these components are necessary for ESP to work. All these security elements are closely interconnected.
All modern cars are equipped with a large number of sensors. From these sensors signals are sent to the so-called controller unit.
It processes the received information:
- brake pressure;
- speed;
- steering wheel position;
- power unit speed;
- wheel rotation speed, etc.
But the main information is transmitted by two sensors that are installed in the lower part of the body. The first sensor transmits information about lateral acceleration, and the second about angular velocity. Motorists often call these sensors G-sensor.
The received information is processed by the electronic controller unit, as a result of which the ESP can maintain directional stability.
The block controller is a kind of mini-computer. Installed programs analyze the behavior of the machine. And if a dangerous situation occurs, the controller unit alerts the ESP and other safety components.
The coordinated work of all safety elements helps eliminate a dangerous situation. For example, getting a car out of a skid.
How can she correct a dangerous situation? It takes full control of the power unit and braking system. If it is necessary to return the car to the desired course, braking of several wheels can be used.
In this case, a special mini-computer processes the received information in order to properly slow down each wheel. And also, if necessary, the mini-computer issues a command to reduce the torque. This reduces the supply of gasoline.
Today, modern cars are equipped with an automatic transmission. The automatic transmission can receive commands.
Additional Stability Control Features
ESP has various functions, the presence of which, perhaps, even informed motorists are not aware of. They are also called software extensions.
List of additional features:
- Removing moisture from disks . This function removes moisture at speeds above 50 km per hour. At the same time, the windshield wipers operate. How does this feature work? The control unit slightly increases the pressure in the circuit. The pads are pressed against the steel disc. The moisture evaporates effectively in a few minutes.
- FadingBrakeSupport . This technology significantly increases the efficiency of the braking system when heated. FadingBrakeSuppor technology increases the pressure in the so-called brake actuator. This helps prevent insufficient adhesion between the brake discs and pads.
- Stabilization of the “road train” . The stabilization function is intended for vehicles that are equipped with some kind of trailer (TSU). This optional feature can reduce torque and control the vehicle's braking system. This prevents trailer yaw.
- BrakingGuard. This is a collision avoidance function. The additional BrakingGuard function is implemented in cars that have cruise control.
- RollOverPrevention . This feature helps prevent tip-over. RollOverPrevention stabilizes the movement of the machine when there is a threat of rollover.
Is the system effective or does it interfere with drivers?
According to the results of studies, the exchange rate stability system prevents up to 80% of cases of car skidding. Today, every second car is equipped with such a safety element. This development significantly reduces the number of accidents and deaths.
The exchange rate stability system helps keep the car within a given trajectory. And it also helps control the behavior of the car.
Source: https://autopravilo.ru/sovety/sistema-kursovoj-ustojchivosti-osnovnye-elementy-i-princip-raboty.html
Stability control
Nowadays, cars are equipped with a whole set of security systems that fall into the active category.
Their task is to increase the efficiency of some operating systems of the car, as well as adjust the behavior of the car under different driving conditions and eliminate driver errors.
Some of these systems are currently available only for premium and mid-segment models, but there are also some that have already become available on budget versions. These include the dynamic (course control) stabilization system (the most common abbreviation is ESP).
The ESP system appeared on cars not so long ago, but has become very widespread, since it is still considered one of the most effective means of increasing safety.
Purpose
The exchange rate stabilization system, like many others, is based on ABS. But at the same time it belongs to active systems of a higher level. If you look at her work as a whole, then ESP can most likely be called a complex, since she uses many others to do her job.
ESP system design
The task of the exchange rate stabilization system is to control the lateral dynamics of the vehicle and eliminate the likelihood of loss of stability and controllability by making certain corrections.
If we take a simple look at its functioning, the ESP system prevents the wheels from skidding when cornering at high speeds, ensuring the car moves along the trajectory set by the driver.
Design
Since the dynamic stabilization system is built on the basis of ABS, for its operation it uses its components - the control unit, wheel sensors and a hydraulic module.
But in addition to this, ESP also uses other sensors to obtain the necessary information:
- steering wheel position (rotation angle);
- pressure in brake lines;
- turning on the brake light;
- transverse and longitudinal accelerations (accelerometer, G-sensor).
ESP system diagram
All the information received gives the system an idea of the behavior of the car and the actions of the driver. If the trajectory set by the driver does not correspond to the actual movement, the dynamic stabilization system is activated and makes adjustments. As a result, the car returns to the specified trajectory.
To achieve its goal, ESP uses the following systems:
- Anti-lock braking system (ABS);
- Effort Distribution (EBD);
- Electric differential lock (EDS);
- Anti-slip (ASR).
In addition, ESP makes adjustments to the operation of certain powertrain systems to influence torque. In some models equipped with an automatic transmission, it may also affect its operation.
To obtain the required result, ESP can independently:
- Change the throttle valve position;
- Make the fuel supply or sparks miss on the spark plugs;
- Change the ignition timing;
- Cancel the upshift in the automatic transmission.
On premium cars, ESP can also adjust the steering (change the angle of rotation of the wheels without driver intervention) and the active suspension (change the stiffness of the shock absorbers). But this is a more advanced safety feature called an integrated dynamics control system.
Principle of operation
All this is aimed at preventing the car from changing its trajectory under the influence of external forces. It is noteworthy that the dynamic stabilization system acts proactively, that is, even at the initial stage of the car leaving the trajectory, ESP turns on and eliminates the situation that has arisen.
ESP is activated in two cases - understeer and oversteer. To put it simply, it turns on when, due to the action of external forces, the front wheels lose traction with the road (the car does not fit into the turn) or the rear wheels (skidding due to a sharp turning angle).
When the front end begins to drift, the control unit, based on signals received from the rotation speed, steering angle and accelerometer sensors, detects this and activates the brake mechanism of the rear wheel running along the inner radius. By braking, a force is created that returns the front axle wheels to the desired trajectory. At the same time, ESP reduces engine torque to restore traction to the wheels.
If the wheels of the rear axle begin to drift, ESP applies the brake to the front wheel moving on the outer side. As a result of this action, the rear of the car is leveled.
There is another situation in which ESP is activated - slipping of all four wheels when hitting a slippery section of the road. In this case, it alternately uses the required braking mechanisms to maintain the trajectory of movement.
Maneuvering a car at speed
Since the system carries out its main action using brake mechanisms, it is clear that this is all done by the ABS hydraulic module.
Advantages and disadvantages
ESP is a high-speed response system. From the moment it is determined that the car’s movement has ceased to correspond to the specified one and until the required brake mechanism is activated, only 20 milliseconds pass.
At the same time, the dynamic stabilization system operates completely independently and quite smoothly, so the driver learns about its operation only by the indicator light. The rest of the time, while the car maintains its trajectory, the system is in standby mode.
Many cars provide forcible deactivation of this system using a key on the dashboard. But not all cars have this function. On some, the shutdown function is not provided at all, while on others, ESP is disabled temporarily, that is, it is activated again after a certain period of time.
At the same time, you should understand that it is auxiliary, and in certain situations it will not help. When trying to enter a sharp turn at high speed, ESP cannot cope and the car will simply be thrown off the road. Therefore, first of all, the driver himself needs to evaluate the behavior of the car, and the system will correct the movement and eliminate minor mistakes and shortcomings.
The main disadvantage of this system is the incorrect assessment of the driver's actions in certain situations. So, in some extreme cases, in order to “stretch” the car, you need to add speed. ESP will not allow you to do this.
It can also prevent you from pushing the car out of the mud or snowdrift by rocking. The problem will not arise if there is a function to disable ESP, which can be activated at any time.
Additional functions
More modern ESP systems have increased functionality, which increases its capabilities. And this is done through the interaction of ESP with other car systems. Additional ESP functions are also called systems, although, in general, they are not such, since they fully use the capabilities and components of ESP.
Thus, the functionality of the dynamic stability system may additionally include the following systems:
- ROP (Roll Over Prevention). In general, the operating principle of this function is not much different from the main one. When determining the probability of a rollover, which is characterized by high lateral acceleration, the front end of the car is braked with a simultaneous reduction in the torque of the power plant.
- BG (collision avoidance). Here ESP works in tandem with cruise control (adaptive). In the event of a likelihood of a collision, the car's light and sound signals are automatically turned on; if the situation worsens, braking occurs, ensuring increased pressure in the brake system due to the activation of the pump (emergency braking);
- Road train stabilization. Valid when towing a trailer. Its task is to eliminate the “swimming” of the trailer on the road by slowing down the car and reducing the traction force of the engine;
- FBS (increasing the efficiency of the brake system when the pads heat up). When the brakes get too hot, the friction force between the pads and the disc decreases, resulting in reduced braking efficiency. This can be eliminated by increasing the pressing force of the pads by increasing the pressure in the lines;
- Removing moisture from brake mechanisms. Here ESP works in tandem with windshield wipers. During rain, when the windshield wipers are turned on, ESP briefly presses the pads against the discs. As a result of friction and heating, water droplets on the disks simply evaporate. It turns on only at speeds above 50 km/h.
Since ESP is built on the basis of ABS and uses its components, their failures are identical. The most common problem they have is malfunction and damage to the wheel speed sensors. Otherwise it is quite reliable.
Source: http://autoleek.ru/sistemy-bezopasnosti/aktivnaya/sistema-kursovoj-ustojchivosti.html