Initialization of the Toyota Corolla robot - DRIVE2
Greetings! We repaired a robot on a 2008 Corolla and encountered a problem with initializing all three parameters, namely initializing the gearbox ECU, initializing the clutch, and initializing the transmission.
There is a lot of information and videos about setting up, but only one or two parameters are described.
Through trial and error, the correct algorithm for adjusting three parameters in turn was identified.
The first step is to adjust the clutch, since it has changed!
We save everything, register it and roll it out.
The second is the transmission! Save again and roll.
And finally, thirdly, we set up the controls!
These are my personal observations and have been tested on, so far, one machine.
And here, in fact, is the article from the corollafan forum. I took the most important things:
What is robot box initialization, and in what cases should it be performed?
Initialization is a reset and zeroing of the previous settings of the electronic transmission control unit. This procedure is carried out every time there is a malfunction of the gearbox and after performing the following repair work in the transmission system:
Replacement of the entire gearbox or its parts, which involved partial or complete disassembly of the gearbox; Replacement of the computer, electric drive for gear selection and shifting, sensors for shifting and gear selection mechanisms;
In these cases, the ECU or transmission is initialized, the control system is configured, and calibrated.
Replacement of the electric drive for engaging and disengaging the clutch, clutch travel sensor, clutch disc and its housing, release bearing, flywheel and crankshaft. In this case, after initialization and configuration, no additional calibration is required.
Important! Initialization must be carried out only for those nodes and elements of the robot box that have been replaced.
In what cases should initialization not be performed?
The ECU should not be initialized without a good reason. Frequent initialization is harmful to the clutch and leads to accelerated wear of its parts (especially the clutch disc). In addition, all the positive effects from it are short-lived. The most common misconceptions regarding the frequency of initialization:
There is a misconception that the position of the clutch feed mechanism rack may indicate the need for this procedure. It also cannot be carried out in order to eliminate jerks and shocks at low speeds. The opinion that after initialization the car starts easier is also incorrect.
How to initialize?
It is better to entrust the initialization, configuration and calibration of the robot box to specialists. If you do not have this opportunity, follow the steps of the following instructions as accurately and carefully as possible.
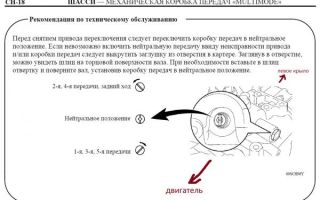
Put the car on the parking brake. Jumper pins 4 and 13 in the diagnostic connector, then wait 15 seconds. Turning on the ignition, quickly press the brake pedal 7 times (after which 2 beeps should sound).
While pressing and holding the brake pedal, move the gear selector to the following positions depending on the initialization destination. For ECU initialization: NE-M---M---M-M-EN. For clutch initialization: NE- M- +- M -—- M- +- M- — -EN.For transmission: NE- M- — -M- — -M- +- M- +- E- N.
Release and then press the brake pedal again (3 series of 2 beeps should sound). Within 2 seconds, press the brake pedal 3 times. If the procedure is completed successfully, sound signals should sound: 2 - when initializing the control unit, 3 - clutch, 4 - transmission.
Turn off the ignition and disconnect the inserted jumper from the diagnostic connector.
If the buzzer does not emit sound signals or the interval between them is more than 0.5 seconds, you should turn off the ignition, wait at least 15 seconds and start all over again (from step 1).
Setting up the transmission system
After initialization, you should configure the robot control system. To do this, follow these steps:
stop the car; move the gear shift knob to position N; the gear lever in the Toyota Corolla is in position N; turn off the ignition, then turn it on for 40 seconds; turn off the ignition again for 15 seconds; turn on the ignition, start the engine and depress the brake pedal.
If everything is successful, the N lever position indicator will start flashing. After 10 seconds it should light up steadily, indicating that the setup is complete.
And to the heap - a very detailed video, with a good explanation found there
Source: https://www.drive2.ru/b/2615974/
Initialization of the Toyota Corolla robot
Nowadays, the most expensive and frequent work in a Toyota service center includes such a process as initializing a robotic gearbox or, as it is also called, a “robotic” gearbox.
Robotic gearboxes are standard manual gearboxes that automate the clutch and gear shift functions, thereby making driving easier. Shifting the clutch and the gears themselves occurs fully automatically.
When the driver changes gear, the box reads the transmitted information, necessarily evaluates the conditions during which the vehicle is moving, and only after all this does the electronic control unit of the vehicle begin to process the information transmitted to it, after which it controls the operation of the robotic box with a given algorithm.
Advantages and disadvantages of robotic gearboxes
The main advantages of these boxes include:
- Minimum fuel consumption, which is achieved with proper use.
- Ease of control (especially noticeable in traffic jams).
- Smooth acceleration.
- Inexpensive selling price.
The main disadvantages of the robot are:
- Long transmission response time.
- The clutch disc is often subject to a lot of heat.
- A large number of robot failures (every 6–8 thousand kilometers).
- Minimum clutch disc strength.
- Short service life of the control unit.
- High costs associated with frequent robot repairs.
Thanks to the warranty on the Corolla, modern drivers can replace the gearbox control unit or the entire clutch package absolutely free. This can be done at any warranty service stations for Toyota vehicles.
How to initialize a robotic gearbox
Often such a process is required when any malfunctions in the gearbox appear. For example, the car moves jerkily. First, a team of specialists performs a complete reset of the unit’s previous settings, thanks to which the robot itself is controlled. After this, work related to the repair of the vehicle transmission system is carried out:
- Complete disassembly of the gearbox.
- Replacement of shift sensors and gear selection sensors.
- Installing a new electric clutch, clutch housing and disc, flywheel, release bearing, crankshaft and clutch travel sensor. After all the described steps have been completed, no further calibration is required.
When is initialization not recommended?
It is not recommended to do initialization without a reason, because if done frequently, it can damage the clutch and lead to rapid wear of the entire set of parts.
Although some owners believe that this, on the contrary, increases the service life of the clutch and this should be done after every 10 thousand mileage.
It is important to know that the position of the clutch feed rack or the elimination of shocks at low speeds does not indicate the need to initialize the ECU.
The most common misconceptions are about the number of times the initialization procedure should be carried out:
- the position of the clutch feed mechanism rack can indicate to the car owner whether initialization is necessary or not;
- to completely eliminate shocks that often bother the driver who moves at low speeds, initialization should never be carried out;
- After correct and high-quality initialization, the vehicle easily moves away.
What needs to be done to improve the quality of initialization work
First of all, it is better to entrust initialization only to the most trusted specialists, as this provides a guarantee for the correct and long-term operation of the car. But at the same time, we cannot hide the fact that today such pleasure is not available to every car enthusiast.
To do this yourself, you need to correctly and clearly follow the steps below:
- The first thing to do is put the car on the parking brake.
- Jumper the connectors of two contacts (fourth and thirteenth) in the diagnostic connector (located to the left of the steering wheel), wait 10-15 seconds.
- Turn on the ignition and press the brake exactly 7 times, as a result of which two beeps should be heard.
- Press and hold the brake pedal and move the gear selector.
- Press the brake three times. When you have done everything correctly, sound signals should sound: 2 beeps - initialization of the control unit, 3 beeps - clutch, 4 beeps - transmission.
- Disconnect the inserted jumper from the diagnostic connector.
- When the buzzer does not emit any sound signals or the interval between them is more than 0.5 seconds, you need to turn off the ignition, pause for 15 to 20 seconds and try again to do the above steps.
You can also watch a video about the initialization process:
This is how the robotic gearbox on a Toyota Corolla is initialized. If all of the above work did not help you, then it would be right to seek help from the service center specialists, where they will be able to accurately understand your problem.
Initialization of the robot box of a Toyota Corolla car Link to the main publication
Source: http://CorollaCar.ru/remont/transmissiya/inicializaciya-robota-tojota-korolla.html
Repair and service of passenger cars
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
Design and maintenance of the Toyota Corolla robotic gearbox
The robotic gearbox (robot gearbox) of Toyota Corolla and Toyota Auris cars is developed on the basis of a five-speed manual gearbox. For control, electric drives for clutch release, gear selection and shifting are installed on the gearbox housing. The electric drives are controlled by the robot box control unit based on sensor signals.
The basis for the gearbox of the robot Toyota Corolla, Toyota Auris was taken from a traditional “mechanics” equipped with electric drives.
Another known name for this Freetronic gearbox is MMT (Multimode). The robotic transmission can operate both automatically and manually.
Gear shifting in a robotic gearbox occurs using three electric motors. One of them is responsible for disengaging (squeezing) the clutch, and the other two are responsible for changing gears.
The operation of the drives is controlled by an electronic control unit (TCM) by processing signals from contactless sensors.
Fig.8. General structure of the robot box Toyota Corolla, Toyota Auris
1 – indicator in the car, 2 – gearshift lever limit switch, 3 – drive, 4 – sensor 1-2, 5 – reverse sensor, 6 – neutral sensor, 7 – speed sensor (gearbox), 8 – clutch position sensor, 9 – electronic control unit MMT – Fritronic. The TFT clutch in the Freetronic transmission is disengaged and engaged by controlling the amount of fluid pressure that is supplied to the clutch master cylinder. The Toyota Corolla robot box is equipped with sensors, some of which monitor the actual position of the gear selector, and others measure the speed of rotation of the gearbox input shaft. The shift lever is equipped with limit switches that alert the control unit to the driver's intentions to operate the gear shift lever. If there is a malfunction, the indicator on the instrument panel starts flashing. The indicator also alerts the driver if he attempts an incorrect shift.
The principle of operation of the Toyota Corolla robotic box
The clutch is always engaged until the engine starts.
Start
– After turning the key to the ignition position (gearbox position – neutral), the MMT unit “squeezes” the clutch and you can start the engine.
Start of movement
– When you engage first gear or reverse gear and press the gas pedal, the MMT gearbox unit of the robot Toyota Corolla, Toyota Auris instantly receives information about this through a signal from the sensors and issues a command to the spool valve to reduce the pressure, which leads to the engagement of the clutch and the car starts moving. – For smooth engagement of the clutch, the spool valve opens gradually, and its full engagement occurs after the speed of rotation of the crankshaft and the input shaft of the robot box is equalized. – The block at this moment gives the command to fully open the channel of the clutch master cylinder to drain.
Changing gears
– When you release the gas pedal and change the position of the Toyota Corolla gearbox lever, the corresponding sensors report this to the MMT unit. – The block gives the command to “squeeze” the clutch. Further engagement of the clutch occurs after receiving signals from the neutral sensors and the “limit switches” of the lever.
Stop
– When the vehicle is braking, the gearbox input shaft of the robot begins to rotate at a lower number of revolutions (below the specified norm) and the TFT control unit “squeezes” the clutch.
Buzzer
– Turns on when emergency situations occur: an error when shifting down, an attempt to start moving from a gear higher than 3rd, excessive load on the clutch, an attempt to start while the gear is engaged, the driver’s door is open with the engine running and the selector lever position corresponding to moving forward or backward (not neutral). The robotic manual transmission of Toyota Corolla, Toyota Auris has five forward gears and one reverse gear. The selected gear is shown in the left information display. The gearbox is equipped with a gear lock system to prevent incorrect operation of the gearbox, i.e. The lever can only be moved from the “N” position by pressing the brake pedal (the ignition key must be in the “ON” position).
There is a control mode scale on the floor tunnel cover. The selected control mode is shown in the left information display.
The following symbols are marked on the scale: M – movement in manual mode.
In this mode, the movement of the Toyota Corolla is controlled either using the gear shift lever (position “+” - upshift, position “-” - downshift), or using the steering column switches: R - reverse.
Move the lever to this position only after the vehicle has come to a complete stop.
To move the selector lever from the “M” or “E” position to the “R” position, you must press the brake pedal; E – movement in Easy mode.
The optimal gear is selected automatically depending on the position of the accelerator pedal and vehicle speed.
In addition to Easy mode, you can turn on Es mode, which provides faster vehicle acceleration than in Easy mode.
To enable Es mode, press the “M-MT Es” key; To turn off the mode, press the key again.
Replacing the clutch for a Toyota Corolla with a robot gearbox
Mechanical failure is damage to clutch components. As a rule, this is wear and overheating of the clutch, during which it loses its working functions.
The main sign of clutch wear is slippage, which leads to loss of torque at high speeds or during sudden starts. In the event of mechanical breakdowns, the system enters emergency mode, shifts the gear to neutral, at which point the error code lights up. To eliminate the problem, it is recommended to replace the clutch assembly.
Malfunctions of the electrical system of the Toyota Corolla, Toyota Auris robot box can be of several types:
– malfunctions in setting or initializing the clutch. A typical indicator is that the car jerks when starting off.
– reset to neutral when the clutch overheats. A red icon in the form of a gear lights up on the display, indicating a fault in the transmission.
– After some waiting time, the system starts working again. When performing diagnostics, you can find out the nature of the malfunction by the error code.
Work on replacing the clutch for a Toyota Corolla robot box:
– Remove the upper part of the air filter. – Unscrew the lower part of the air filter housing. – Disconnect the mass air flow sensor connector, air duct clamps and air filter housing cover latches. – Unscrew the lower part of the air filter housing. – We take out the bolt securing the cushion of the robot box of the robot box of Toyota Corolla, Toyota Auris. – Unscrew the upper gearbox mounting bolts. – Unscrew the bolt securing the box cushion, but do not remove it. – Disconnect all connectors from the Toyota Corolla robot gearbox. Then unscrew the top mounting bolts. – Remove the hub nuts to remove the drives. Unscrew the bolt and two nuts securing the ball joint. – Unscrew the hub nuts and the fastenings of the ball joint to the lever to remove the drive shafts. First drain the oil from the gearbox. – Disconnect the front mounting pad. We remove the drive shafts from the box. – We install thrust stands on the box and the engine so that it does not sag and slightly raise the box to dismantle the upper box mounting bolt, which has already been unscrewed from above. – Unscrew the mounting bolts in a circle and move the box away from the engine. – We remove the faulty clutch from the Toyota Corolla robot box. – Check the flywheel for wear. Wear should not exceed 0.3-0.5 mm. And its surface should be even and smooth. – We are replacing the clutch release bearings. – Install the new clutch on the flywheel and center the clutch disc. – We mount the box in the reverse order.
Removing and installing the control selector for the robotic transmission of Toyota Corolla, Toyota Auris
– Remove the floor tunnel lining. – Remove the four bolts securing the robotic gearbox control selector. – Squeeze the clamp and disconnect the wiring harness connector from the robotic transmission selector lever position sensor. – Squeeze the clamp and disconnect the wiring harness block from the robotic transmission selector illumination lamp. – Remove the robotic transmission control selector.
– Install all removed parts in the reverse order of removal.
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________
Source: http://autozapchastiremont.ru/toyota_corolla_kpp_robot.html
Toyota robotic box: how the box works
The Freetronic transmission was based on a traditional “mechanics” equipped with electric drives. Another well-known name for the Freetronic “robot” is MMT (Multimode). The robotic transmission can operate in either automatic or manual mode.
Gear shifting in the transmission occurs using three electric motors. One of them is responsible for disengaging (squeezing) the clutch, and the other two are responsible for changing gears. The operation of the drives is controlled by an electronic control unit (TCM) by processing signals from contactless sensors.
The Freetronic transmission was equipped with Toyota cars from 2005 to 2009. These are models such as: Corolla, Auris, Yaris, Aygo, Echo, Prius and others. Toyota is the first to install a TFT automatic clutch on the Yaris and Echo models.
General device
1 – indicator in the car, 2 – gearshift lever limit switch, 3 – drive, 4 – sensor 1-2, 5 – reverse sensor, 6 – neutral sensor, 7 – speed sensor (gearbox), 8 – clutch position sensor, 9 – electronic control unit MMT – Fritronic.
The TFT clutch in the Freetronic transmission is disengaged and engaged by controlling the amount of fluid pressure that is supplied to the clutch master cylinder.
The gearbox is equipped with sensors, some of which monitor the actual position of the gear selector, while others measure the speed of rotation of the gearbox input shaft. The shift lever is equipped with limit switches that alert the control unit to the driver's intentions to operate the gear shift lever.
If there is a malfunction, the indicator on the instrument panel starts flashing. The indicator also alerts the driver if he attempts an incorrect shift.
Operating principle of the Toyota robotic box
- The clutch is always engaged until the engine starts
- Start . After turning the key to the ignition position (gearbox position - neutral), the MMT unit “squeezes” the clutch and you can start the engine
- Start of movement . When you engage first gear or reverse gear and press the gas pedal, the MMT unit instantly receives information about this through a signal from the sensors and issues a command to the spool valve to reduce pressure, which leads to the clutch being engaged and the car moving off. To smoothly engage the clutch, the spool valve opens gradually, and its full engagement occurs after the rotation speed of the crankshaft and the gearbox input shaft are equalized. At this moment, the block gives the command to fully open the channel of the clutch master cylinder to drain.
- Changing gears . When you release the gas pedal and change the position of the gearshift lever, the corresponding sensors report this to the MMT unit. The block gives the command to “squeeze” the clutch. Further engagement of the clutch occurs after receiving signals from the neutral sensors and the “limit switches” of the lever.
- Stop . When the vehicle is braking, the gearbox input shaft begins to rotate at a lower number of revolutions (below the specified norm) and the TFT control unit “squeezes” the clutch.
- Buzzer. It turns on when emergency situations occur: an error when shifting down, an attempt to start moving from a gear higher than 3rd, excessive load on the clutch, an attempt to start while the gear is engaged, the driver's door is open with the engine running and the selector lever position corresponding to forward or backward movement (not neutral ).
Source: https://www.rekpp.ru/toyota/robot.html
Operating principle of the MMT Toyota robot box – Engine and transmission
Sent 07 December 2016 – 13:53
Operating principle of the robot box for corolla 150 MMT
1. Should I put it in neutral in traffic jams? No, because when stopping, with the brake pedal pressed, the clutch is completely open. Recommendations in the “manual” for moving the gear selector to “N” during long stops are related to traffic safety, for example, a tired leg, dulled vigilance, your leg slipped and you crashed into an obstacle.
2. Is it possible to apply the parking brake without moving the selector to N?
“When the parking brake switch is set to ON, the power take-off assist system is disabled.” That is, when the car is stopped, if the accelerator pedal is not pressed, when the parking brake is applied, the clutch is completely released. This does not cause clutch wear. Attention: When you press the accelerator pedal in this situation. The clutch is engaged and the car begins to move. An audible signal sounds and a warning appears on the display about the parking brake not being released.
3. Does MMT have a kick-down function?
“When the accelerator pedal is fully depressed until it clicks, the ECM on left-hand drive models interprets this as a downshift command. The forced downshift command influences the gear shift." In addition, "delta control" of the accelerator is implemented: "TCM interprets a sudden change in the state of the accelerator pedal as a driver command to accelerate or decelerate, and performs a downshift or locks the gear . [Accelerator pedal sharp control] When the accelerator pedal is pressed sharply, the system interprets this as an acceleration command and shortens the downshift time. [Accelerator pedal sudden release control] If the accelerator pedal is suddenly released, the system interprets this as a deceleration command and provides effective braking power to the engine without changing gear. This also ensures that sufficient traction is maintained for the subsequent acceleration cycle.”
4. When stopping in traffic jams, the car vibrates slightly for a few seconds, is this normal?
”Stop Control (Brake Control): When the drive shaft speed measured by the transmission speed sensor falls below a set value, the TCM automatically disengages the clutch. This allows the car to stop without turning off the engine.“ If you braked hard enough, at the moment of stopping, the complete disengagement of the clutch has not yet been completed, and in order to prevent the car from stalling, the ECU gives a command to increase the speed to 2200 - 2000. At this time moment vibration is felt - this is a normal situation. With sufficiently smooth braking, the clutch has time to completely disengage before coming to a complete stop. No such vibration is observed.
5 Is it possible to turn off a car with MMT without moving the selector to neutral?
“The multimode manual transmission does not have a parking position. Parking the car is possible in any position of the gear lever (N, E, M or R). If the lever is not in the N position when parking the vehicle, the vehicle is parked with the clutch engaged.“ Warning: “If the ignition switch is turned to the off position before the gear shift is complete, the gear may not shift. If a gear shift does not occur when the ignition is turned off, the buzzer will sound and the gear position indicator will flash, warning the driver.“
6 Is it possible to start a car with MMT “from a pusher”?
anyone:
Toyota does not have a documented ability to start the engine of a car with MMT in this way. Theoretically, based on the logic of the MMT ECU, this may not work.
Namely: when starting the internal combustion engine, as soon as power is supplied to the MMT ECU, it activates the clutch actuator, disengaging the clutch to avoid stopping the internal combustion engine when the gear is engaged. This may happen before the engine starts. It will not be possible to switch to neutral with a discharged battery.
There is no mechanical connection between the shift lever and the MMT. Even if the lever is in neutral, the shift will occur only after sufficient power has been supplied to operate the selection actuator and engage the gears.
source
Attached files
- actuator.jpg 75.1K 0 Number of downloads:
Source: http://taclub.ru/index.php?showtopic=4683
Toyota Corola 2006 MMT does not undergo robot adaptation – Toyota, Lexus
Posted 07 December 2014 – 18:44
Hello everyone. Toyota King 2006 multimod box.
I'll start from the very beginning.
The car arrived with the problem of error p0810, respectively, when the error appeared, the neutral icon blinks and the car does not drive. It’s worth waiting a little and then getting on the road again.
During the initial inspection, it was revealed that the clutch actuator bushings were worn out, after which new ones were machined. The actuator was assembled and installed on the car. The computer is adapting, the clutch is adapting, but there is no gearbox.
When selecting box adaptation, the process continues but the box does not click. We rolled the car out into the parking lot. After 5 days I decided to continue to get involved with it. I started it up, warmed it up without any manipulation, and lo and behold, the gearbox began to switch and accordingly the car drove off.
I decided to try to adapt and the adaptations went without any problems.
I let the car go for a ride. After 2 days, the client called and said that everything was the same and then the decision was made to change the clutch. The basket, disc and releaser were changed. The kit was purchased according to the appropriate TSB recommended by the factory.
Before replacing, I removed the clutch from the clamping mode as expected. The disc was placed on the required side. I checked this moment.
After the replacement, I began to train the box accordingly, and here again they do not undergo adaptation. The symptoms are the same: neutral blinks and does not respond to the gas pedal.
Then, on the advice of my colleague Sergei from the city of Grodno, I once again paid attention to the electric motor of the clutch actuator. As a result, it was revealed that it was faulty, after which the electric motor was replaced with a new one, modified again according to TSB Toyota.
After the replacement the situation did not change.
Then, out of despair, I started checking everything else:
1. All position sensors were checked with an oscilloscope. There were no deviations.
2. The gear shifting motors were checked. As a result of the check, it was revealed that one electric motor had a high induction current and was running out of brushes, and it was replaced with a new one. After the replacement, the adaptation also did not take place.
3, The timing marks of the gear shift mechanism were checked. Everything is normal and assembled according to the Toyota manual. There is no result. The adaptation also does not work.
I forgot to write. There are no errors in the MMT block or the others. All adaptation procedures were carried out on a fully warmed-up car.
The throttle assembly is clean. At the time of training, I installed an additional charger.
All procedures were carried out not with a break, but with the Techsrteam Licensed Program 9.20.021
Here are screenshots of the parameters with the car running.
Attached files
- 1.jpg 153.22K 43 Number of downloads:
- 2.jpg 141.11K 34 Number of downloads:
Post edited by vitaha76: 07 December 2014 – 20:55
Best regards, Vitaly. tel:89108103898 MTS
Sent 07 December 2014 – 18:51
They do not undergo adaptation, i.e. During the procedure, the gearbox does not click into gear only when selecting the following items:
-Shift and select actuator
-Shift stroke sensor
-select stroke sensor
When you select the others, everything clicks.
By adapting the same box to other cars, selecting all the points in order, i.e. adaptations pass with clicks of gears.
Post edited by vitaha76: 07 December 2014 – 18:53
Best regards, Vitaly. tel:89108103898 MTS
Posted 07 December 2014 – 18:53
Change or repair the MMT ECU
Software development, ECU repair, Chiptuning.
Posted 07 December 2014 – 19:03
Thank you Stanislav. I have the same impression. When opening the MMT block and examining the insides, no burnt transients, tracks or microcircuits were found.
There is also a photo with the parameters of a working melt with the same box that came for adaptation. I’ll post it a little later. I have questions about the parameters
And one more question. Does anyone know if MMT blocks with the same boxes are the same? Is it possible to take it from another similar car or a Toyota with the same box, throw in a block and try to carry out the adaptation?
Post edited by vitaha76: 07 December 2014 – 19:11
Best regards, Vitaly. tel:89108103898 MTS
Posted 07 December 2014 – 20:35
Identical blocks can be thrown from another machine.
I think you can throw a block onto a working machine from a non-working machine, where it will work.
It’s not clear what’s happening to the module. But this happens purely at the time of adaptation.
Post edited by alex888el: 07 December 2014 – 20:39
Posted 07 December 2014 – 21:01
At work there are newsletters for work. I can take a look tomorrow.
Posted 07 December 2014 – 21:12
I apologize for the quality, but this photo of the parameters is absolutely normal for a working Toyota Auris with MMT
I saw the bulletins. Due to error p0810, it is necessary to change the entire clutch, the MMT control unit and the clutch actuator.
Attached files
- 3.jpg 113.18K 43 Number of downloads:
- 4.jpg 91.56K 28 Number of downloads:
- 5.jpg 80.
18K 23 Number of downloads:
- 7.jpg 84.88K 21 Number of downloads:
- 9.jpg 69.17K 21 Number of downloads:
Best regards, Vitaly.
tel:89108103898 MTS
Posted 07 December 2014 – 21:14
And they have some kind of special lubricant...
Posted 07 December 2014 – 21:33
I'm interested in the Base clutch load and Current clutch load parameters
I have these parameters -172.58 and -175.55, and for a working car -79.15 and 2.65
What are these parameters and why is there such a difference?
Or are these parameters what the non-adapted box should have?
What kind of lubricant are you talking about? The one inside the clutch activator? For example, I filled it with a blue high-temperature mobile phone
Post edited by vitaha76: 07 December 2014 – 21:31
Best regards, Vitaly. tel:89108103898 MTS
Posted 07 December 2014 – 22:02
Posted 08 December 2014 – 03:12
There is no need to get into a fever and go into the wilds. The first and important condition is normal voltage on the actuators - that is, a normal battery and fastening of ground and plus to the internal combustion engine. When adapting, the clutch actuator adapts first and then the shifter. I don’t know how it is on techstream, but generally there are three stages. the first is the clutch, the second is the activator, the third is ESC reset and adaptation. Calmly, without hysteria.
Post edited by bachmann: 08 December 2014 – 03:13
Eduard 8-905-982-95 two five
Posted 08 December 2014 – 03:15
So that you don’t have to suffer with the camera, read http://mmcflash.ru/f...p?showtopic=577
Pay attention to the current consumption of the clutch actuator during adaptation or through activation. If memory serves, then more than 20A, if it exceeds, adaptation does not take place. See two parameters, calculated and actual.
The block can be transferred from the same car with the same engine, having previously considered the eeprom as an external programmer, so as not to carry out adaptation on a very used clutch, there may be problems. This topic has been discussed a thousand times on the forum.
Here you can repair the unit http://car-work.ru/
Post edited by Bruce Willis: 08 December 2014 – 03:18
- vitaha76 and Michael28 like this
Software development, ECU repair, Chiptuning.
Posted 08 December 2014 – 05:57
Your clutch is malfunctioning. Did you turn the clutch actuator with a screwdriver? I had a case where the end stops of the sleeve were made larger than the original, they clamped the shaft, hence the currents, 21A is a critical value. Also pay attention to the sleeve on which the release valve runs.
I have a hard time believing the problem with the ECU, even in difficult cases I had exotic malfunctions, but the ECU had nothing to do with it. I think that the ambush is in the bushings. By 200 thousand km there is huge wear, but nevertheless the cars drive as practice has shown.
It was in vain that we started repairing 0810 with the actuator.
Posted 08 December 2014 – 06:26
Learn Clutch Standby Point – Fail
Reinstall the clutch assembly and its actuator. The jamb is here.
I put it on the actuator itself.
Hands in oil, neck in sweat - we work in Toyota.
Posted 08 December 2014 – 06:37
In general, it is not clear from the first message how the clutch adaptation takes place separately from the shifter. If correct, then the actuator is unlikely.
Eduard 8-905-982-95 two five
Posted 08 December 2014 – 09:33
I tried to do as you write in scandoc. The result is the same.
The current consumption during activation was observed. It does not exceed 20A.
Release guide, normal mileage of the car is 98 thousand, original 100 percent.
The bushings are made with small tolerances so that there is no wedging or play.
I started with repairing the actuator because the bushings were worn down to the copper base and there was a lot of play.
Best regards, Vitaly. tel:89108103898 MTS
Posted 08 December 2014 – 10:02
I did it with scandoc like this.
1, removed the actuator from the clamp before replacing the clutch.
2, clutch initialization. box clicks
3 initialization of the box. The box does not click and all learning parameters are erased. After which the neutral does not light up.
4, initialization of the computer. The box clicks and remembers the learning parameters. But the learn-clutch standby poin-fail parameter
Best regards, Vitaly. tel:89108103898 MTS
Posted 08 December 2014 – 10:07
Initializing the box should only be done if the box is repaired, this is for the future. Do ECU Initialization, then clutch initialization. Then let the car think for a couple of minutes, then start it and try it.
Hands in oil, neck in sweat - we work in Toyota.
Posted 08 December 2014 – 11:30
The release guide bushing is an integral part of the gearbox housing.
Posted 08 December 2014 – 11:36
AND?
I didn't see anything unusual when examining the guide.
I tried this too, with no result.
I carry out all the procedures on other cars and they always go smoothly, changing gears.
Best regards, Vitaly. tel:89108103898 MTS
Posted 08 December 2014 – 12:06
When initializing the clutch, the box should not click. Clutch foot back and forth and that's it
Eduard 8-905-982-95 two five
Posted 08 December 2014 – 14:23
this happens if you first initialize the computer
Best regards, Vitaly. tel:89108103898 MTS
Posted 08 December 2014 – 16:29
Mode Changes - you have 18. If the initialization mode should be 14, if the control mode at start-up is 17, if the control mode is when the car is stationary then 26 - which is exactly what you have in the photo on a working car. And here 18 is some kind of intermediate value. What about the famous 12th tooth?
Sent 08 December 2014 – 17:25
and what is the famous 12th tooth?
please tell me what mode change means, how do I understand the change mode?
Post edited by vitaha76: 08 December 2014 – 17:27
Best regards, Vitaly. tel:89108103898 MTS
Posted 08 December 2014 – 19:24
broken in general view.jpg 27.13K 94 Number of downloads: Photo of 12 teeth. Honestly, the photo is not mine, taken from some forum.
Posted 08 December 2014 – 19:52
We recently did a replacement on a 2007 car. Adaptation did not take place until the starting charger was connected.
autoparts(GAV)front.ru
Posted 08 December 2014 – 21:11
I removed the switching mechanism and checked that the marks matched and the integrity of the gears and sectors. Everything was fine.
However, it does not work with additional power on board.
Victor46, please explain the purpose of the Mode Changes parameter
Best regards, Vitaly. tel:89108103898 MTS
Posted 08 December 2014 – 21:49
Posted 08 December 2014 – 23:48
The manuals are not clear. Here is a normal one about assembling the mechanical switch.
Attached files
- ACTUATOR ASSEMBLY TOYOTA.pdf 1.26MB 408 Number of downloads:
Best regards, Vitaly. tel:89108103898 MTS
Posted 09 December 2014 – 11:37
What does the shift mechanism have to do with it? You have a failure when initializing the clutch - Learn Clutch Standby Point - Fail. Swap the sensors from the clutch actuator and gear shift, do the initialization, post the date here. We'll see.
Post edited by kolyan750: 09 December 2014 – 11:41
Source: http://forum.adact.ru/index.php?showtopic=36993