Electrolyte in the battery - volume, filling rules, density
The industry produces conventional and dry-charged car batteries; batteries of the second type are supplied from the factory empty, unfilled with sulfuric acid solution. But in any case, you need to pour electrolyte into the battery; without it, the battery will not work.
Since batteries come in different capacities, they require different amounts of sulfur solution. In this article we will look at how much electrolyte should be poured into batteries of large and small sizes, and how to properly use and dilute a sulfuric acid solution.
Electrolyte volume in batteries 55 and 60 A/h
The capacity of the battery varies; the energy storage device can be designed for either 35 or 230 Ampere-hours.
But low-capacity car batteries (from 35 to 45 A/h) are rarely used in practice; they do not provide the required starting current and drain faster from the load.
The most common standard for passenger cars is 55 and 60 Ampere-hours; batteries of these types are usually used on cars with engines up to 2 liters, with any type of transmission and a small amount of additional equipment.
To fully refill a “55” battery, approximately two and a half liters of electrolyte are required; depending on the type and manufacturer, the weight of the battery may vary slightly, but on average it is 15 kilograms. An empty 60 Ah battery should be filled with 2.7 to 3 liters of sulfur solution (H2SO4), the mass of a charged and ready-to-use energy storage device is approximately 17-18 kg.
How much electrolyte is poured into batteries 75, 90 and 190 A/h
“Seventy-fifths” and “nineties” batteries are considered powerful for passenger cars; they are more often used in SUVs and premium cars with a lot of additional equipment (climate control, full power accessories, cruise control, headlight washers, etc.). Batteries require a fairly large energy consumption, so they must provide power to all consumers with a reserve.
Such batteries already weigh more significantly; a charged “75th” battery weighs about 20, and a “90th” battery weighs about 25 kg. To fill an empty case with electrolyte from a battery with a capacity of 75 Amp-hours, you will need from 3.7 to 4 liters of solution; approximately 4.4-4.8 liters should be poured into the “90th” battery.
The 190 A/h battery is practically not used in passenger cars; it is intended for trucks, PAZ or KAvZ buses, and various special equipment. Such a battery without electrolyte can weigh 42 kg, and refilling requires up to 10 liters of sulfur solution.
There are also batteries with a capacity of 110, 132, 140, 215 Ah; there are other ratings, but they are not so widely popular and widespread.
Rules for filling electrolyte
A sulfuric acid solution is poured into the battery according to certain rules that must be followed if you want the battery to last a long time:
- the liquid should cover the plates and be approximately 10-15 mm above their level; the electrolyte cannot be poured “up to the very neck”, otherwise it will boil and spill out;
- the density of the composition must be certain, corresponding to the season (in winter the density is always higher);
- Only distilled water is allowed to be added to jars; the electrolyte itself cannot be used as an additive; it can damage the battery;
- if the density is too low, the voltage at the terminals is below normal, the battery must be charged.
When working with sulfuric acid, you must wear rubber gloves and avoid getting the solution in your eyes or on your skin. If electrolyte does get in, you should immediately wash the contact area with running water. In this case, it is advisable to use special work clothes - if drops of electrolyte get in, the fabric is corroded and things become unusable.
To pour the sulfur solution, you must use special containers that are resistant to acid.
When mixing water with acid in large quantities, heat is generated, so as not to accidentally suffer from splashes, a concentrated solution is always added to the water, and not vice versa.
An exception is adding water directly to the battery, but here the electrolyte is not so concentrated, and it is located quite deep inside the battery case itself.
Importance of Density Values
The main parameter that determines the properties of the electrolyte is density. The parts of water and sulfuric acid in the solution must be contained in a certain proportion: an electrolyte that is too dense contributes to the rapid failure of the plates, and the sulfation process is activated.
If the density is less than the established norm, the battery may freeze in the cold winter; the reduced concentration of the solution contributes to the rapid discharge of the battery. To increase the density, the battery is charged; in winter, the electrolyte concentration should always be higher, and lower in warm times, especially in the heat. The density in the battery is measured with a hydrometer, the values are within the range:
- for the summer season – 1.23-1.25 g/cm³;
- in winter – 1.26-1.29 g/cm³.
For machines operated in the Far North, the density can reach higher values, but all these indicators are relative, and they can only be taken as a general recommendation. If you have no idea what concentration the solution in the battery should be, it is better to consult a specialist; there is conflicting information on the Internet and other media.
Dry charged batteries
Dry-charged batteries are the same as conventional batteries with lead plates, but differ in the absence of electrolyte.
First, such batteries are charged at the factory, then the electrolyte is poured out of them.
This method allows you to store an energy storage device without loss of properties for several years, while the jars with the plates are reliably sealed - covered with a special packaging film.
Before use, electrolyte is poured into the battery, and the density must be checked. When the concentration of the solution is weak, charging is carried out, and only after that the battery is ready for use.
If the battery is recently manufactured (no more than one year has passed since production), it does not need to be charged; it is only important to fill it with electrolyte of the required density.
It is unacceptable to operate an empty battery, and even if you try, it will not work - a discharged and dry battery does not have any power, it will not be able to make the engine starter rotate.
If the density is below normal
When the density of the electrolyte in any of the cans is below normal, the battery will not work normally and will not be able to start the engine.
There is an opinion that you should pour the liquid out of the battery and fill in a new sulfur solution, but this is not recommended - when the battery is turned over, particles of lead sediment from the bottom can short-circuit the plates, and then the battery will fail. There are several proven ways to restore density:
- charging the battery using a charger with a small current;
- electrolyte replacement - using a bulb, pump out some of the old liquid from the jar (which is located on top of the plates), add a fresh solution, the concentration may be even higher than normal;
- adding pure sulfuric acid, but this method is not popular.
If the density is still lost and it is impossible to restore it, there is no point in “revitalizing” the battery; it must be replaced.
Source: https://avtobrands.ru/elektrolit-v-akkumulyatore-obem-pravila-zalivki-plotnost/
What kind of acid is in a car battery and what is its density
Car owners often wonder what kind of acid is in a car battery, which determines its service life. Manufacturers of these products mainly fill in sulfuric acid, which is an acid-water solution of a certain density and concentration.
It is called an electrolyte, and to control its quality you need to know certain handling, testing and technical specifications. Some batteries use an alkaline electrolyte consisting of the elements lithium, sodium, potassium and their combinations.
These are mainly dry-charged power sources that are used in harsh climatic conditions.
Electrolyte composition
Electrolyte, or sulfuric acid, is used by modern industry to produce current sources:
- in batteries;
- batteries;
- electrical capacitors.
Sulfuric acid is poured into the batteries in a diluted ratio with water - approximately 70% water, 30% H2SO4. If it is missing, the device is not suitable for operation. The density of the liquid also deserves special attention, which should be checked and increased if necessary.
Density control
The density in a lead-acid car battery is measured in g/cm³, and it must be proportional to the concentration of the solution with an inverse relationship to the temperature of the liquid. The normal value is 1.27-1.29 g/cm³.
This indicator allows you to determine the condition of the battery, and if it does not hold a charge, then you need to check the amount of substance. Over time, the electrolyte level of a car battery decreases, and accordingly, the density increases due to hydrolysis of water and heat.
To do this, you need to periodically add distilled water, reducing the concentration of sulfuric acid. The procedure can be performed independently if you know how much is required for a certain model of substance.
Electrolyte for batteries can be purchased in stores, or you can make it yourself and learn how to adjust the density, measure and care for the device in a timely manner to extend its service life.
For preparation you will need the following components:
- Sulfuric acid.
- Distilled water.
- Container made of glass, lead, ceramic, resistant to chemicals.
- Ebonite jar for stirring.
To prepare, distilled water is poured into the container, then sulfuric acid, and the resulting mixture is simultaneously stirred with a stick. The procedure is carried out sequentially, since the reverse option can cause burns.
If the climate where vehicles are used is moderate, then the following proportion of substances should be adhered to: per 1 liter of water - 0.36 liters of acid. For warm climates, 0.33 liters of acid should be added to 1 liter of water. The resulting substance is covered and left for a day until precipitation forms and cools.
When replacing the electrolyte in the battery, wear rubber gloves and goggles to protect your eyes.
Let us recall that when refilling, in particular with the first water, a reaction of hydration and heat formation in the acid is possible. It is likely that the water will boil and cause splashing.
The battery density must be checked every three months. To do this, use a hydrometer.
Component of the battery structure
Without the presence of electrolyte in the battery, its main function will not be performed, since the substance is an activator of charge and discharge. There should be a lot of liquid in the device’s capacity, and, accordingly, the weight of the battery is not small.
The approximate ratio of the design is up to 20% of the weight of the liquid, up to 25% of the plastic and the lead component reaches up to 80% of the weight. The positive plates are made of lead dioxide, the negative monolithic plates are pure lead.
The plates are used to assemble packages that promote charge accumulation.
It should be noted that the battery differs by model, and, in particular, the 55 A/h model is one of the lightest that can be found quite often in passenger cars. Its weight does not exceed 16 kg. There are more compact models with low weight, such as 40 A/h and other options.
Electrolyte neutralization
If the battery is completely damaged, it must be disposed of properly. But also in the event of an electrolyte leak from the battery, you need to find out how to neutralize it.
There are situations when, if the battery breaks down, a separate part at its location may be flooded. To do this, you need to remove the battery and clean it.
Neutralization of this substance from a battery is usually carried out using special equipment and technology. This is important from an economic and environmental point of view.
If neutralization is carried out in an unorganized manner, significant harm to the environment can be caused.
There are currently two industrially produced acid neutralizing options.
The first involves the elimination of acid discharge into wastewater by a filter method, passing through magnesite, limestone and other materials, and the second method is the regeneration of acid by special treatment with the subsequent production of a marketable product.
But in practice, many drivers recommend using an alkaline solution made from baking soda and water in case of a spill of a dangerous substance.
By regularly checking the battery, including monitoring the density and electrolyte level, you can avoid many problems and extend the life of the battery and prevent mechanical damage.
It is always necessary to pay close attention to devices during operation, especially in winter, when at low temperatures and reduced density of the electrolyte, it may freeze or destroy the plates.
Source: https://batteryk.com/kakaya-kislota-v-akkumulyatore-avtomobilya
Studying the electrolyte level and other parameters of a car battery
Home » Battery » Studying the electrolyte level and other parameters of a car battery
What are the technical requirements for batteries, what should be the current strength, resistance and density of the battery, how to find out and check these parameters?
Before introducing you to the main technical features, let’s look at the types of batteries:
- Dry-charged devices, their distinctive characteristic is the absence of working fluid, that is, an electrolyte solution in cans. The advantage of this type of battery is the ability to store it for a long time. In this case, long-term storage of the battery in a warehouse or garage after purchase will not affect its functionality. But before you start using the battery fully, you will need to fill it with electrolyte.
- Charged batteries that are initially supplied filled with electrolyte. This type of battery does not require preparation before use, since such devices are initially supplied in working condition. But before installing such a battery in your car, you need to make sure that it contains the required volume of liquid.
What do you need to know about battery characteristics?
Now let's move on to the issue of technical characteristics. Is it possible to prepare electrolyte for the battery of your car, how much should you fill it with, what are the consequences of fluid leaks and how many volts should the battery produce? Check out the main features.
Weight
The weight of the device, as well as its dimensions, is one of the product parameters. Please note that the weight of the device is an imprecise parameter and may vary depending on the model and manufacturer. As for the sizes, they may differ depending on the specific vehicle, but in general the products have similar dimensions.
The weight can also be different, in this case it all depends on the degree of destruction of the internal plates made of lead.
This usually occurs as a result of long-term use of products; as a result of destruction, lead will begin to interact with the working solution.
Therefore, in principle, a small discrepancy is typical for many batteries; in this case, a difference of about 0.5 kg is allowed compared to the norm.
Current strength
A parameter such as current strength is considered more important for the product, so this characteristic should be looked at first when purchasing a product.
The current parameter is measured at an ambient temperature of 18 degrees below zero and must correspond to the value indicated on the battery case or in the technical documentation. If the battery is fully charged, it should produce at least 125 amperes.
To make sure that the battery installed in your car meets the standardized parameters, you need to take a measurement.
For diagnostics you will need a voltmeter or ammeter; the verification procedure is performed as follows:
- First of all, you should turn off all voltage consumers in the car, in particular, the stove, optics, acoustics, recorder and GPS navigator, if any, as well as other equipment.
- Then the hood of the car is opened and the terminal from the battery is disconnected. Using a tester, you should measure the parameter of current flow through the electrical network; to do this, install the tester contacts between the probe and the terminal.
- The minimum current flow value should be about 15 mA, the maximum - 70 mA. If diagnostics show that the readings obtained do not differ much, for example, by 0.02-0.05 A, this is, in principle, not bad, such a leak is considered insignificant. But if the values you received are very different from the nominal values, then most likely there is a strong leak in the product. Accordingly, the car owner must check the battery for leaks.
- If a leak has been identified, then you will need to remove each relay and fuse from the mounting block in turn, while monitoring the values on the tester display. If, after removing the next safety element, you notice that the readings on the tester display have decreased to optimal levels, this indicates that you have discovered a leak. Now all you have to do is test the electrical circuit and determine the location of the break, and then replace the damaged wire.
Capacity
The capacity of the product is measured in ampere hours and is also considered one of the main parameters; this value indicates the duration of the battery or the amount of current that it can deliver.
It must be taken into account that the battery capacity is determined by many factors, namely, design characteristics, ambient temperature, charging current, and the level of the working fluid.
If the current value increases, this will contribute to a decrease in the level of the product’s capacitance, but with temperature the opposite is true - if it increases, then the capacitance drops.
If during diagnostics you have recorded a decrease in the volume of electrolyte solution in the battery banks, you must take into account that this can lead to a decrease in capacity and discharge of the device.
Therefore, in order to prevent rapid discharge of the battery and increase its power, it will be necessary to add an electrolytic solution to the jars of the design. But before that, it will need to be properly prepared. Many car owners do it simpler - they simply fill a jar with ordinary distilled water.
In principle, this is correct, but not entirely, since the electrolytic solution must also contain sulfuric acid.
To make your own liquid, follow these steps:
- First you need to prepare a container in which the solution will be made. Please note that the prepared tank must not only be clean, but also acid-resistant.
- Next, pour distilled water into the reservoir.
- Having done this, carefully add sulfuric acid to the distillate in a small stream, while simultaneously mixing it with water. Wear gloves to avoid getting the sulfuric acid on your skin, and use a glass rod to mix the solution. Sulfuric acid should be added to the distillate in minimal portions, and it should be mixed as evenly as possible.
- When adding sulfuric acid and mixing it with water, regularly check the density of the resulting solution; a hydrometer is used to measure the density. Remember that the density of the solution may vary; in this case, much depends on the conditions of use of the battery, as well as the ambient temperature. As a rule, the density value should be around 1.21-1.31 g/cm3.
Photo gallery “Preparing electrolyte”
1. Pour the distillate into the container.2. Add sulfuric acid.3. Check the density.4. Pour electrolyte into the battery.
Voltage
One of the most important battery parameters is the voltage of the device. Taking into account the voltage, the car owner can also determine possible malfunctions in the operation of the product.
Naturally, if the voltage and power levels are normal, this may indicate normal battery operation. If the product is fully operational, it will produce voltage up to 12.
6 volts, an acceptable option is a value around 12.2 volts.
Each individual can of the product should produce about 2-2.1 volts, this figure is considered standardized.
The voltage value determines the possibility of connecting various energy consumers to the on-board network, in particular, chargers for phones, video recorders, navigators, etc.
The longer the battery drains, the lower the voltage at its terminals will be (the author of the video about self-diagnosis of a car battery is the Advice for Car Enthusiasts channel).
How to change the electrolyte in a battery: is it possible?
We have already talked about how to make an electrolyte, and now let’s talk about how to replace the solution with your own hands. Let’s say right away that replacing the electrolyte is an extreme measure that should be taken in exceptional cases.
The replacement procedure is performed as follows:
- First you need to disconnect the product from the terminals, then dismantle it by removing the mount and place it on a flat surface.
- If there is a protective strip, then it needs to be removed; if not, then immediately unscrew the plugs.
- Next, you need to get rid of the old electrolyte; to do this, use a rubber bulb. Slowly suck out all the electrolyte. If the solution accidentally gets on your hands, wash with soap and water.
- When the liquid has been sucked out, the jars will need to be rinsed with distillate, this will remove the remnants of the old solution.
- Next, you need to dry the jars.
- After this, the product is refilled with a new electrolyte. During the addition process, it is necessary to control the density of the liquid, as mentioned above, this is done using a hydrometer. The solution is poured according to the level of the plastic chips in the jars.
- When these steps are completed, you need to charge the battery. To do this, it is best to use a starting-charger; the procedure for restoring density is carried out by repeating several charging and discharging cycles. Please note that in this case the current parameter should be about 0.1 ampere. The charging procedure can be considered complete when the voltage in each section is about 2.4 volts. Or the total battery voltage at the terminals will be approximately 14 volts.
Loading …
Video “How to correctly measure the electrolyte in battery banks?”
Visual instructions on the topic of measuring the electrolyte value in sections of a car battery with a description of the main nuances and features of this process are given in the video below (the author of the video is the KuzZzin Technology channel).
Do you have any questions? Specialists and readers of the AVTOKLEMA website will help you ask a question
Source: https://avtoklema.com/akkymylyator/uroven-jelektrolita-v-avtomobilnom-akkumuljatore-880/
Rechargeable battery - how to extend its service life?
Operating rechargeable batteries is, in principle, not particularly difficult. First of all, you should respect its service life. You can, of course, wait until it refuses, but this may not happen at the most opportune moment.
So, if the battery life is already impressive, then it is worth changing it. The operation of the battery depends on the nature of the operation of a particular vehicle. For example, the use of a car in a taxi service is characterized by frequent starts.
Accordingly, the battery will wear out much faster than when the car is used only for private purposes by one or even a group of people.
There are different ways to test the battery
The primary task of the battery is to start the engine.
If the car starts poorly or does not start at all, then experienced drivers recommend checking, first of all, the performance of the battery; most likely, this is its whims.
But don't rush to get rid of the battery; it may just need some simple maintenance. Of course, if the battery has already served for 3-5 years, problems with starting the car are explained by natural wear and tear of the battery.
Modern batteries are increasingly being manufactured as maintenance-free, that is, they no longer require any maintenance during operation. You just need to charge this battery periodically. However, if there is such a possibility, then the service life of the battery can be extended.
Serviced batteries are distinguished by the presence of plugs on each compartment (bank) on top.
Maintenance-free batteries, in turn, are equipped only with an indicator, which in the normal operating state of the battery lights up green, and when the charge level decreases or the battery fails, it becomes dim or white.
Battery check:
The caps that each battery jar is equipped with should not be unscrewed with a regular screwdriver - the cap may be damaged. A regular coin will do in this situation. Diagnosis of the battery condition consists of several points:
- Checking electrolyte density
- Checking the electrolyte level in the battery
- Measuring battery charge without load and with load
Usually the battery is provided with a minimum and maximum mark on the case. But if they are not there, then the measurement is made using a glass tube of the appropriate diameter.
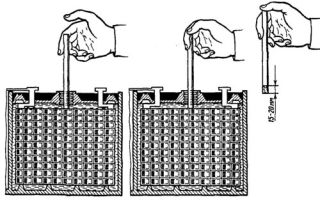
The order of measurements is as follows:
- Unscrew the battery plug
- Taking a glass tube, lower it into the battery
- Plug the tube tightly with your finger and pull it out
- Measure the length of the electrolyte column in the tube
The normal electrolyte level in the battery ranges between 12 and 15 mm. The battery plates must be covered with exactly this level of electrolyte. Operating a battery with an electrolyte level below 12 mm is not allowed. Low electrolyte levels lead to oxidation and destruction of battery plates. Also, exceeding the maximum level is not permissible.
Sometimes you should check the battery charge of your car
The electrolyte level decreases as the water boils. That is, to restore the previous value, you should add water, and distilled water. Water is added to the filler neck to the bottom end of its tube. After topping up, the battery must be charged.
In a charged battery, the density of the electrolyte is checked; normally it is 1.27-1.29 g/cm3. To check the density of the electrolyte, a device called a hydrometer is used. If you added liquid to the battery, you should not measure the density immediately; it will take 3-4 hours for the water to mix with the electrolyte.
And when taking any measurements, it is important to be careful, because sulfuric acid is used as an electrolyte in the battery.
Here the norm is given for the winter period, when battery performance is especially important. When the density is above the specified level, the electrolyte is diluted with water. If the density is low, electrolyte is added.
It is also possible to measure the battery charge. To do this, you need a device called a voltmeter. The battery must be disconnected from the on-board network.
And if the car has just been in operation, it is better to postpone the measurements for an hour. Measurements should be taken in a warm room.
The charge level should be approximately 12.5 volts for a fully charged battery. To check the charge with a load, a special load fork is used.
Measuring battery density:
Pay attention to the color of the electrolyte. Normally it should be transparent. A reddish or dark color indicates the destruction of the plates. Such a device should be disposed of as quickly as possible; it cannot be repaired or restored.
Now, having learned the answers to a number of important questions regarding the operation of the battery, namely, what the electrolyte level, charge level and battery electrolyte density should be, the driver can avoid a number of problems. Timely diagnostics, identification and elimination of battery faults will extend its service life and also avoid ending up in an unexpected unpleasant situation.
If, even after the operation of the battery has been diagnosed, faults have been identified and eliminated, the car experiences difficulty starting, the starter and the car's electrical wiring should be checked for faults.
Source: http://AvtoMotoSpec.ru/poleznoe/uroven-elektrolita-v-akkumulyatore-diagnostika-akb.html
Electrolyte for batteries: ways to solve possible problems
The electrolyte in a battery is the medium in which chemical reactions occur that allow electrical energy to be stored and released.
Naturally, the uninterrupted operation of the battery and its service life depend on the quality of the electrolyte. What you need to know about electrolyte?
…
So, what indicators are used to evaluate an electrolyte and how to solve problems associated with it? Let's look at it in order.
Characteristics of electrolyte for car batteries
The electrolyte in car batteries is nothing more than a solution of concentrated sulfuric acid H2SO4 in distilled water H2O.
The acid of maximum concentration has a density of 1.84 g/cm³, but an aqueous solution of 1.40 g/cm³ is most often used to prepare the electrolyte. Dilution of H2SO4 with water results in extremely large heat release.
To prepare electrolytes, only special sulfuric acid for batteries, which has a high degree of purification, should be used. Requirements for it are regulated by GOST 667-73.
Any impurities, even in small quantities, reduce service life.
The most important indicator is the density of the electrolyte in the battery. It should be in the range from 1.07 to 1.30 g/cm³, which corresponds to a mass fraction of sulfuric acid in water from 28 to 40%. Electrolyte density indicators in all reference books and instructions are always given at a temperature of 15°C. If the temperature is different, an amendment is made according to the table below.
Table 1. Density corrections depending on temperature
Checking the electrolyte in the battery
This operation must be carried out twice a year - before the summer and winter seasons.
To check you will need:
- A device for determining the density of an electrolyte is a hydrometer (densimeter). You can buy it very inexpensively at any auto store, and it will last for many years.
- A glass tube with a diameter of 5 mm, if it is not available, a sheet of clean paper.
To find out how to check the electrolyte in a battery, you need to decide by what indicators it is checked. The main ones are density and level. How to check them?
- To check the density of the electrolyte, you should carefully unscrew the battery plugs (if it is serviceable), lower the hydrometer spout into the electrolyte and, using a bulb, draw such a volume of electrolyte into the flask so that the hydrometer float floats freely in it without touching the walls of the flask.
- Measurements are made at an outside air temperature of about 20°C. The line of contact of the electrolyte with the rod having a measuring scale will indicate the density of the electrolyte, which is best recorded.
- Measurements should be made in all jars. The density in them should not differ from each other by more than + - 0.02-0.03 g/cm³. the measured density eloquently indicates the battery charge level, as can be seen from the table.
Table 2. Determination of battery charge level
The table shows the values at an ambient temperature of 20-25°C. If the density is insufficient, it is necessary to charge the battery, at which the density should increase.
The next important indicator that requires monitoring is the electrolyte level in the battery. It should be 10-15 mm above the plates.
To measure it, you need to lower the glass tube perpendicularly into the battery jar until the lower end of the tube rests on the plate. Then plug the top end with your finger and pull it out. The amount of water in the tube will show the level. If it is insufficient, then distilled water is added to the jar. It is this that boils away when the electrolyte boils.
There is no need to add electrolyte under any circumstances! Such an incorrect action can ruin the battery. If there is no tube, you can put a folded piece of clean paper into the jar. The level of electrolyte can be judged by the level of its wetting.
Requirements for electrolyte density in various climatic zones
It is known that it is better to have a higher density of electrolyte in a battery in winter, since a denser electrolyte freezes at a lower temperature. In summer, it is better to have lower densities, since lower densities contribute to a long battery life.
Experienced battery technicians can increase the density of the battery electrolyte by adding a correction solution of 1.4 g/cm³ or lower it by adding distilled water.
However, car enthusiasts are not recommended to do this, since the wrong action will quickly damage the expensive battery. Therefore, for different climatic zones, average density indicators have been adopted, with which the battery can be operated all year round. These indicators are summarized in a table.
Table 3. Battery electrolyte density standards
When abnormal frosts occur in the central and southern climatic regions, it is better to remove the battery and bring it into a warm room, where you can check the charge and recharge if necessary. A completely discharged battery with an electrolyte density of 1.10 g/cm³ can freeze already at -5°C. You need to know about this and take timely measures.
Electrolyte preparation
In most cases, batteries are sold already filled with electrolyte and completely ready for use. But sometimes so-called dry-charged batteries are sold, which require filling with electrolyte. It is best for car enthusiasts to buy ready-made electrolyte of the required density for their climatic region, but it happens that the electrolyte has to be prepared by itself.
What will it take?
- Sulfuric acid with a density of 1.84 g/cm³ or 1.40 g/cm³ (whichever is preferable) in the required quantity.
- Distilled water.
- Measuring chemical containers in which the volume of liquid can be accurately measured.
- Clean glass, ebonite or polyethylene containers where the electrolyte will be prepared.
- Glass or ebonite stirring stick.
- Protective equipment: glasses, gloves.
When preparing electrolyte, observe the following rules.
- It is prohibited to pour water into sulfuric acid! This can lead to boiling, water and acid splashes and, as a result, severe chemical burns. You can only pour sulfuric acid into water in a very thin stream.
- The acid should be poured in small portions, and then stir the solution with a stick.
When finished, be sure to check the density with a hydrometer.
When preparing electrolyte, you should know how much electrolyte is in the battery.
For different batteries, the most common capacity in passenger cars is 55-60 Ah, it can vary from 2.6 to 3.7 liters. Therefore, to fill one battery, it is better to prepare 4 liters of electrolyte.
The amounts of water and acid to prepare the required electrolyte are summarized in the following table.
Table 4. The amount of distilled water, sulfuric acid or its solution of 1.40 g/cm³ required to prepare 1 liter of electrolyte of the required density
Filling electrolyte into the battery. Preparation for use
The electrolyte is poured using a glass or polyethylene funnel and a glass mug to a level of 10-15 mm above the plates. After this, the battery is left to soak for 2 hours. The density may drop.
Next, the battery is charged with a current 10 times less than its capacity (for example, for a 60 A*h battery, the charge current is 6 A) for 4 hours. After checking the density and electrolyte level, the battery is ready for use.
Solving possible problems
During the operation of the battery, problems may arise that require prompt solutions. The most typical are:
- During winter frosts, the electrolyte in the battery froze. In this case, it is necessary to remove the battery from the car, bring it into a warm room and leave it to thaw naturally for 24 hours. If the battery case is swollen and burst, then you can safely take the battery to a metal collection point. It is unfit for further use. If the case is intact and the electrolyte is in place, then it should be charged with a low current of 1 A for a period of 2 days, periodically checking the density. If the density increases, then the battery “takes” a charge and there is hope that it will last for some time.
- It happens that when completely discharged, the battery refuses to “take” a charge. This is expressed in a long-term absence of changes in density. The last hope to revive such a battery is to replace the electrolyte in the battery. To do this, the old electrolyte is drained, the battery is washed with distilled water, and after the water is completely drained, a new electrolyte is poured in. After 2 hours allotted for impregnation of the plates, you can try to charge the battery with a small current of 0.5-1 A for a long time - up to two days. If the density of the electrolyte increases, then there is hope that it will last for some time. It should be charged until the charge density and voltage remain constant for 2 hours.
- The quality of the electrolyte largely determines the reliable and long operation of the battery.
- The density and level of electrolyte must be monitored at least twice a year, before the change of seasons.
- If the electrolyte level in the battery banks drops, only distilled water should be added.
- To fill dry-charged batteries, it is better to use ready-made electrolyte of the required density from well-known manufacturers.
- Self-preparation of electrolyte should be done only in extreme cases, observing all safety rules and using protective equipment.
The video describes in detail how to check the density of the electrolyte in the battery.
Source: http://mylandrover.ru/rashodniki/elektrolit-dlya-akkumulyatorov.html
Methods for checking the electrolyte level in different types of batteries
It is believed that modern batteries do not require special monitoring and fully perform their functions without any maintenance. This is partly true - if operation occurs under normal conditions, nothing needs to be done.
However, with extreme driving and frequent charging/discharging cycles, the amount of liquid in the compartments gradually decreases, which leads to a decrease in battery capacity.
In this article we will tell you how to check the electrolyte level in a battery without the help of a mechanic.
Methods for determining the level in a maintenance-free power supply
Conventionally, batteries can be divided into two types: serviced and maintenance-free. In the latter case, the design does not provide access to the compartments and manufacturers do not recommend opening the case yourself.
Otherwise, you will break the seal, and you will hardly be able to seal the plastic case properly. Such manipulation will lead to the fact that the battery will have to be thrown away.
In a maintenance-free battery, the amount of electrolytic mixture can be determined in two ways.
On the body of such batteries there are “min” and “max” marks placed on an oval eye made of transparent material. The electrolyte level should be between these marks. If it is lower, it means that some of the distilled water has evaporated or flowed out through the safety valves. This usually happens due to improper charging or after the service life has expired.
If there is no peephole, carefully inspect the surface of the case. It is usually made of transparent plastic, and has a scale on one side. The marks will be the same as on the transparent eye.
By indicators
Modern models of imported and domestic batteries can be equipped with indicators. People call them “magic eyes”. The indicator changes color depending on the amount of charge and the density of the electrolytic mixture. To check the solution level in your car battery, follow these steps:
- using a clean rag, thoroughly wipe away the dirt and dust near the indicator;
- lightly tap the indicator with your finger - this will remove oxygen bubbles and you will be able to see it better;
- look at the color that appears on the indicator.
Green indicates that the level is normal, the charge is maximum. White – you need to connect the charger. Red – increased acidity of the solution, that is, the amount of water has decreased.
This control method is the most inaccurate; it can only be used if the battery is maintenance-free and other diagnostic methods are not available.
Inspect the battery housing.
Methods for checking the level in a serviced power source
The serviced battery is designed so that the owner can perform all the work independently. You can determine the fluid level in battery cans of this type with greater accuracy and, if necessary, add distilled water. There are two methods that allow you to control the amount of electrolytic mixture in the compartments. Let's look at each of them.
Using a measuring tube
You can check how much electrolyte is left in the battery using a simple device, which is a transparent tube whose diameter is smaller than the diameter of the plug. In exceptional cases, you can use part of a transparent ballpoint pen by first unscrewing the caps from it. The measurement is performed in the following sequence:
- remove dirt and dust from around the plugs;
- place the battery on a flat surface;
- carefully lower the tube into the compartment without tilting it;
- pinch the top hole with your finger;
- remove the tube without removing your finger, measure the amount of liquid in it.
Normally, the solution should cover the electrodes by 1 - 1.5 cm. If you have that much liquid in the tube, there is nothing to worry about. If it’s more, it means that last time you filled in more than you needed, pump out the excess.
You can clearly see how much electrolyte is in the jars.
Visual definition
This method can be used if the housing design provides special recesses at the bottom of the neck. The upper layer of liquid, touching the recesses, bends, forming the so-called “meniscus” or “eye”. By its location you can understand what the electrolyte level is at the moment. The “eye” is clearly visible - the level is normal; if it is not visible, the amount of solution has decreased.
We recommend using a portable flashlight to clearly see the meniscus. Some manufacturers make a high neck, so without an additional light source you will not see anything.
Car enthusiasts often ask what the acid level in the battery should be. The wording of this question is incorrect. An electrolyte consisting of distilled water and acid is poured into the jars. Therefore, the methods described above make it possible to determine how much of the electrolytic mixture remains, and not its components.
The amount of electrolyte in batteries of different capacities
In some cases, it is necessary to completely replace the solution. Trying to find out how much liquid is required based on the level in the jars will not give any result. Unfortunately, manufacturers do not indicate the volume of the compartments, so you have to calculate it based on the battery capacity.
For these cases, we have prepared a table of correspondence between the amount of solution and the parameters declared by the manufacturer; you just need to find these values on the stickers or in the instructions.
|
Battery type |
Nominal capacity (Ah) |
Electrolyte quantity (liters) |
|
6ST-45 |
45 |
3,0 |
|
6TST-50 |
50 |
3,5 |
|
6ST-55 |
55 |
3,7 |
|
6ST-60 |
60 |
3,8 |
|
6ST-75 |
75 |
5,0 |
|
6TST-82 |
82 |
5,4 |
|
6ST-90 |
90 |
6,0 |
|
6STM-128 |
128 |
8,0 |
|
6ST-132 |
132 |
8,0 |
|
6TST-182 |
182 |
11,5 |
|
6ST-190 |
190 |
12,0 |
The indicators given in the table are relevant for domestic batteries. The maximum permissible error in the electrolyte volume should not exceed +/- 100 g. If you have an imported power source, then rely on its capacity indicated on the case or in the manufacturer’s instructions. In difficult cases, it is better to get additional advice from the seller or an auto electrician.
Now you know how to check the electrolyte level in the battery. We recommend performing this procedure at least once a month in order to notice the problem in time and take measures to eliminate it.
Source: http://pro-tachku.ru/pro-avtoservis/kak-proverit-uroven-elektrolita-v-akkumulyatore.html