Operating principle of alternating and direct current generator
As you know, when current passes through a conductor (coil), a magnetic field is formed. Conversely, when a conductor moves up and down through magnetic field lines, an electromotive force is generated.
If the movement of the conductor is slow, then the resulting electric current will be weak.
The current value is directly proportional to the magnetic field strength, the number of conductors, and, accordingly, the speed of their movement.
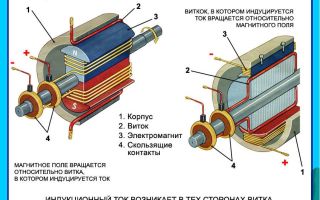
The simplest current generator consists of a coil made in the form of a drum on which wire is wound. The coil is attached to the shaft. A wire-wound drum is also called an armature.
current generator
To remove current from the coil, the end of each wire is soldered to current-collecting brushes. These brushes must be completely isolated from each other.
Electric motor
Alternator
alternator
When the armature rotates around its axis, the electromotive force changes. When the coil turns ninety degrees, the current is maximum. At the next turn it drops to zero.
alternator
A complete revolution of a turn in a current generator creates a period of current or, in other words, alternating current.
DC generator
DC generator
A switch is used to produce constant current. It consists of a ring cut into two parts, each of which is attached to different turns of the armature. With the correct installation of the ring halves and current-collecting brushes, for each period of change in the current strength in the device, direct current will flow into the external environment.
DC generator
A large industrial current generator has a stationary armature called a stator. A rotor rotates inside the stator, creating a magnetic field.
Be sure to read articles about car generators:
Any car has a current generator that operates while the car is moving to supply electrical energy to the battery, ignition systems, headlights, radio, etc. The rotor field winding is a source of magnetic field. In order for the magnetic flux of the field winding to be supplied to the stator winding without loss, the coils are placed in special grooves in the steel structure.
car current generator
Thus, the current generator is a modern device capable of converting the energy of mechanical movement into electrical energy.
Rate the quality of the article. Your opinion is important to us:
Source: http://electric-tolk.ru/princip-raboty-generatora-peremennogo-i-postoyannogo-toka/
Generator operating principle
The main purpose of the generator is to convert the carrier energy into electricity. The operating principle of an electric generator is almost the same as that of your fuel-powered car. The process seems extremely simple until you start delving into the details.
A generator, like a car, has an engine that runs on one of the fossil fuels: gasoline, diesel fuel or gas.
After fuel is injected into the cylinder, it begins to burn and turns into a rapidly expanding gaseous mixture, which pushes the piston upward.
When the piston moves, the crankshaft attached to it begins to move. The latter, in turn, rotates the drive shaft.
To rotate the crankshaft at higher speeds, multiple pistons can be used. Accordingly, greater output power will be obtained. This parameter is usually noted in the engine specifications as the number of cylinders.
As the crankshaft rotates, it is time to look at the process of converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. It is based on a physical law formulated by Michael Faraday and Joseph Henry. The law reveals the essence of the question of how an electric generator works.
This law states: if a conducting circuit rotates in a constant magnetic field, then a potential difference (electromotive force or voltage) appears in the circuit. And when voltage occurs in the circuit, electric current begins to flow through it.
Main Generator Components
It consists of two fundamental elements: the stator and the rotor.
The stator is the stationary part of the device. It consists of three copper windings, each of which is laid around a core made in the form of a set of plates made of mild electrical steel. Mild steel is necessary to strengthen and concentrate the magnetic field in the stator windings.
The second part, rotating thanks to the crankshaft, is called the rotor or armature. It contains a mechanism to create a magnetic field when rotated. For small generators, this mechanism consists of permanent magnets, and for large ones, it is a design based on the principle of electromagnetic induction (such devices are also called brushless).
Voltage adjustment
Another important element is the voltage regulator. It allows you to regulate the voltage and stabilize it when the rotation speed and load changes by controlling the excitation current.
This process occurs as follows: part of the generator output voltage is supplied to the excitation winding through rectifiers that convert alternating current into direct current. This direct current then strengthens or weakens the overall magnetic field created by the rotor. Such adjustment allows you to increase productivity and obtain the required output voltage level.
However, the process takes some time, during which the generator output voltage reaches the required value. With a sharp increase in loads, voltage regulators will help avoid voltage dips and ensure stable operation of the generator.
Generator cooling systems
There are two types of cooling systems: air and liquid.
The air cooling system is an installation of a fan and a radiator that dissipates heat. The main element of liquid cooling is the refrigerant, which circulates through the pipes, absorbing heat.
Correct and uninterrupted operation of this system will help you avoid overheating of the electric generator and its subsequent failure. Therefore, it is necessary to regularly check the operation of the cooling system.
All of the above elements are basic for any electric generator. Often they come with the following equally important components: batteries for the starter and a control panel for ease of operation.
Source: http://genport.ru/article/princip-raboty-generatora
Alternating current generator device
In order to ensure the most comfortable existence, man has developed and invented a huge variety of different technological devices and complex systems. But one of the most effective and efficient devices that allows the use of electricity has become an alternating current generator. You can get acquainted with the types and types of RCD here.
The photo shows alternators
What does it consist of?
Today there are two main types of construction:
- Devices with a stationary part - a stator and a rotating element - a magnetic pole. Elements of this type are widely used among the population, because the presence of a fixed winding eliminated the need for the user to remove excess electrical load.
- An electrical device with a rotating armature and a fixed magnetic pole.
It turns out that the design of the generator comes down to the presence of two main parts: moving and fixed, as well as elements that serve as a connecting link between them (brushes and wires).
Operating principle of a car alternator:
- the rotating part of the rotor or drive of the mechanism is nominally taken to be an electric magnet. It is he who will transmit the created magnetic field to the “body” of the stator. This is an external element of the device, which consists of coils with wires connected to them.
- voltage is transmitted through rings and commutator panels. The rings are made of copper and rotate simultaneously with the rotor and crankshaft. During movement, brushes are pressed against the surface of the rings. Consequently, current will be transferred from the stationary part to the moving part of the system.
Read about three-phase asynchronous motor, connection diagrams and operating principle on this page.
When purchasing an alternator, you need to focus on the following technical characteristics:
- Electric power;
- Operating voltage;
- Number of revolutions of the rotating part of the generator;
- Net power factor;
- Current strength.
These values are the main technical characteristics of alternating current.
Today, on the territory of the Russian Federation, various types of certified and unlicensed alternating current generators are sold. Review of household halogen lamps and how to choose here: http://howelektrik.ru/osveshhenie/lampy/galogenovye/bytovye-galogenovye-lampyobzor-i-kak-vybrat.html. The most popular of these devices are the following:
- Stirling engine with a linear alternating current generator - this option is suitable for those cases when a person needs a compact thermal energy converter;
- single-phase alternating current generator - the device is used for single-phase electrical systems;
- two-phase alternating current generator - the use of this device is determined by the characteristics of the system, i.e. at the moment it can only be used in two-phase systems;
- three-phase alternating current generator - experts say that equipment of this type has high technical characteristics and is distinguished by the fact that it can only be used for three-phase systems;
- 380V alternating current generator without engine - this type of generator is designed to operate in a system with a voltage of 380 V;
- alternating current generators 220 volts - a standard version of generators based on alternating current operation;
- alternating current generator on a thyristor - in this case, the constant component of the system is a thyristor. It is used in two possible enabled states of the system;
- synchronous alternating current generator - unlike an asynchronous generator, all processes occurring in the system coincide according to certain technical characteristics;
- ship alternating current generators - such elements are used on ships. They have a high level of protection from moisture and dust;
- induction alternating current generator – based on the operation of induction currents;
- portable alternating current generators – easy to operate and transport;
- welding alternating current generator from an asynchronous electric motor - the device has a complex design and is distinguished by high technical characteristics.
The photo shows a Stirling engine with a linear alternator
Homemade alternator in the photo
Portable alternating current generator in the photo
Device
To use an alternator correctly, you need to become familiar with its circuit diagram.
The figure shows a circuit diagram of an alternating current generator
It is also worth noting that household alternating current generators are also used in vehicles. But in this case, it is necessary to remember that the element that accumulates energy should not be completely discharged, because in the future this may have a negative impact on its technical capabilities. Read an overview of types and manufacturers of dimmers.
To excite an alternating electric current generator, it is necessary to apply an appropriate voltage to it, which will lead to the appearance of a magnetic field. It should be remembered that devices of this type often fail. Before starting, it is necessary to check the integrity of the field winding.
Alternator repair
To repair a generator, you need to know its structure and operating principle.
According to experts and service centers, you should not try to repair alternating current generators yourself. Any, even the most insignificant mistake can lead to serious problems and have a direct impact on human health.
Cost of household alternators
You can buy the necessary household equipment of this type only at specialized retail outlets. The cost of an alternating current generator intended for domestic use varies from 35,000 rubles to 70,000 rubles. The price of the device depends on the technical characteristics and the manufacturer.
Read the guide on how to make a generator from an asynchronous motor.
Where to buy an alternator?
Where to buy in Moscow:
- Aralex LLC, Moscow, Yaroslavskoe highway, building 2 Contact phone: +7 (903) 678-56-50;
- Expert Moscow LLC, Moscow, Ostapovsky proezd. 3, building 8 Contact phone: +7 (929) 573-03-64, +7 (903) 180-39-20;
- TSK Promgroup, Moscow, Vereyskaya St., 17. Business center Vereyskaya Plaza 2, Contact phone: +7 (495) 580-69-38 ext. 100, +7 (926) 363-62-49.
Where to buy in St. Petersburg:
- Online store VKorzine.ru, St. Petersburg, Polikarpova alley, 2 Contact phone: 8 (812) 426-11-27;
- LLC Intermet St. Petersburg, Skladskaya street 4 Contact phone: +7 (812) 747-74-44;
- Trading company Litenergo, St. Petersburg, st. Litovskaya, 10, office 1310 Contact phone: 8 (812) 596-39-79.
Video
Watch the video on how to repair an alternator:
Before purchasing any equipment designed to work with electricity, you need to inquire from a store representative about the availability of all necessary quality certificates, and test the device for performance.
Nov 7, 2015 Tatyana Sumo
Source: http://howelektrik.ru/elektrooborudovanie/generatory/ustrojstvo-generatora-peremennogo-toka.html
How does a car generator work?
Use the search bar
to find the material you need
Home Auto How a car generator works.
A car charging system contains three main components:
- battery;
- generator;
- voltage regulator;
The generator charges the battery and provides electrical energy to all parts of the car, headlights, heater, and radio.
Typically the generator is located at the front of the engine and is driven through a belt from the crankshaft, which converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion. Some car models previously used a separate belt, from the crankshaft pulley to the alternator pulley.
Modern cars use a single belt that drives all rotating parts from the crankshaft. Generators are generally attached to brackets using bolts. One fastening is rigid, the other is adjustable, so that the drive belt can be tensioned.
If the belt tension is insufficient, it will slip; if the tension is excessive, a radial load is created on the bearings of the driven mechanisms. The generator generates alternating voltage using electromagnetic induction. This voltage charges the battery and allows the rest of the electrical systems to operate.
By the way, Tesla's work underlies the operation of the alternating current generator. I would like to make a clarification, in fact, alternating voltage and alternating current are related to each other according to Ohm’s law, so when they say an alternating voltage generator or an alternating current generator, they mean the same thing. Let's look at some of the parts of the generator.
The generator housing is made of aluminum because it is lightweight and does not magnetize. Aluminum also dissipates heat well, which is generated when the generator operates, and does not release the magnetic field “outside.” There are ventilation holes on the back and front covers. The drive pulley is mounted on the rotor shaft at the front of the generator.
When the engine is running, the crankshaft rotates and drives the generator pulley through the belt. Essentially, a generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
The generator can be disassembled into the following parts:
- voltage regulator with brushes;
- diode bridge;
- rotor with slip rings;
- stator;
The regulator relay controls the upper voltage limit, that is, it controls that the voltage at the generator output does not exceed a certain value, on average 14.5 volts for passenger cars. Voltage is supplied to the slip rings through brushes. From the stator windings, voltage is supplied to the diode bridge. You can see what the rotor looks like in the picture on the right. A coil is placed on the rotor shaft, which creates a magnetic field when current flows through it. The coil is secured using special metal brackets, the so-called rotor poles. The beak-shaped poles of the rotor are placed in a checkerboard pattern. The rotor is placed inside the stator, with a gap sufficient for rotation. Now let's talk about how the generator produces alternating voltage. When direct current flows through the rotor coil, a constant magnetic field is formed; by constant we mean that its amplitude does not change over time. As the rotor rotates, an alternating magnetic field is induced in the stator. The field becomes variable due to the rotation of the rotor. If you consider a specific point on the stator, then the north and then the south magnetic pole of the rotor passes by it, this is the alternating magnetic field. As is known, an alternating magnetic field generates an alternating electric field. Thus, from the constant magnetic field of the rotor, we received an alternating voltage on the stator windings. All these parts work together, creating the electrical energy necessary for the vehicle. Car generators produce direct current, with electrons moving in one direction, unlike alternating current, where electrons move in one direction or the other with a certain frequency, essentially oscillating. In 1887, Tesla discovered alternating current to people and proved its effectiveness. However, the use of alternating current is not allowed in cars because car batteries are designed to be charged with direct current. Therefore, the alternating current that is generated in the stator is passed through a diode bridge, thereby rectifying it. Three-phase generators have 3 stator windings. These windings are shifted relative to each other by 120 degrees. Each winding creates a voltage that is shifted relative to the other windings in time. There are 2 ways to connect the stator windings - a triangle and a star. A generator whose windings are connected by a “star” begins to charge at lower speeds and has a lower maximum power than a generator whose stator is connected by a “delta” " An alternator with a delta-connected stator windings begins to charge at higher speeds and has a higher maximum power than a generator with a star-connected stator winding. After converting the alternating current to direct current, the generator voltage can be applied to the battery. Very low or too high voltage can damage the battery and other electrical components of the car. One of two types of voltage regulators can be seen in most cars: one of them switches the positive, the other switches the negative. Thus, the alternator is one of the most important parts of the car.
Reasons for generator failure?
The generator consists of many moving parts and is constantly exposed to temperature loads, as a result of which the internal parts gradually wear out. One of the most common failures is bearing wear.
The bearings that allow the rotor to spin freely inside the stator can break due to thermal stress and dirt. If the generator bearing is worn out, it will be audible and it will make noise when rotating. There are several ways to check the serviceability of the generator.
Most cars have a light on the dashboard that illuminates the battery icon when the ignition is turned on. After the car starts, this light should go out, sometimes you need to “give a little gas” for it to go out. If this light bulb burns out, the generator most likely will not work.
To check the health of the generator, you need a regular voltmeter. We turn on the voltmeter to measure DC voltage, the red probe to the positive terminal of the generator, usually a bolt, the black one to the generator housing. We start the car, the voltmeter should show more than 14 volts, if less, the generator is faulty.
Next, turn on the heater and high beams; the voltmeter readings should not fall below 13.5 volts. You also need to check that the voltage on the generator and battery are equal. If the voltages are different, you need to check the wires going from the generator to the battery and the places where the wires are attached, there is probably a bad contact somewhere.
Also, the cause of “poor charging” can be a poorly tensioned belt; it usually gives itself away with a characteristic whistle when you sharply press the gas pedal. Therefore, before repairing the generator, we check the belt.
Generator replacement.
A generator is much cheaper than, say, the same power steering pump or air conditioning. However, there is an alternative: buy a new generator or a refurbished one. The price of a refurbished generator is about a third lower than a new one.
The price of the generator depends on the make of the car; if you are the owner of a 2005 Porsche 911 Carrera GT, then a refurbished generator will cost you $300. Replacing the generator is available to any car enthusiast with sufficient experience and the necessary tools. You can replace the generator in the garage.
In modern cars there is not always good access to the generator; sometimes it is necessary to remove several additional parts. In this case, it is best to contact a specialist who will do this work quickly. Do-it-yourself generator repair will cost from $12 to $30, depending on what needs to be repaired.
One thing is for sure - a poorly functioning generator destroys the battery. The battery can be charged many times before it loses capacity. The average battery life under normal conditions is 48 months.
Generators differ in the maximum current they can deliver, which is from 70 to 120 amperes for passenger cars. If the car has a powerful audio system or other load, sometimes an additional generator is installed.
Source: http://auto.howstuffworks.com/alternator.htm
Source: https://hubstub.ru/auto/13-kak-rabotaet-avtomobilnyy-generator.html
The principle of operation of a car generator
The device of a car generator consists of a large number of elements that interact with each other. I believe that every car enthusiast who respects his car should know everything about the principles of its operation. The pulley mediates the process of transferring mechanical energy to the generator shaft from the engine using a belt.
The housing includes two covers - the front one, which is located on the pulley side, and the rear one, located on the side where the slip rings are located. Their purpose is to hold the stator together, also install the generator on the surface of the engine and place the bearings of the rotor itself.
On the back cover you can see the brush assembly, voltage regulator, rectifier and external leads for connecting the electrical equipment system.
The rotor is a steel shaft on which two beak-shaped bushings are placed. Between them there is a winding from which the leads are connected directly to the slip rings. The equipment of this group of parts mainly consists of cylindrical copper rings.
A three-phase winding is located in the stator slots, in which the power of this generator is generated. The part, called an assembly with diodes, combines 6 very powerful diodes, three of which are pressed into heat sinks.
A voltage regulator is a device that maintains voltage within predetermined limits during load changes.
The brush assembly is a removable plastic structure that contains special spring-loaded brushes that contact the rotor rings.
Generator mounting
The generator is driven by a temporary transmission from the crankshaft pulley. As its diameter on the shaft increases and as the diameter of the same pulley decreases, the generator speed increases. This means that the consumer will be able to receive a stronger current.
On all new cars, the drive is carried out using a poly-V-belt. It is particularly flexible and allows the installation of a small diameter pulley on the generator itself. This gives much higher gear ratios to use high-speed generators. This is done using tension rollers if this part is of a fixed type.
Generators are secured using bolts located at the front of the car engine. Brackets are used for this. The covers have a tension spring, as well as mounting feet. If they are placed using two paws, they will be located on two covers at once, but if there is one paw, it will be placed only on the front one.
How does it work?
When starting the engine, the starter will be the main energy consumer.
The work is accompanied by hundreds of A of current, this provokes a decrease in voltage in the entire battery. This mode provides for the consumption of electricity only with the help of a battery, which at this time is intensively discharged.
If it doesn't work, then the battery will drain too quickly and I strongly advise you to keep this in mind.
The car's generator helps provide the current required to charge the battery, as well as the current to operate electrical appliances. After the battery is discharged, the charging current decreases.
But the generator will still be a source of power, the battery itself simply smoothes out various ripples in the voltage.
If devices that consume a lot of energy, such as a headlight heater, are turned on, and the rotor speed is low, the total current consumption may exceed that for which the generator is designed. In this situation, the load will shift to the battery, as a result of which it will begin to discharge. As you can see, the principle of operation of the generator is quite simple.
Purpose of the voltage regulator
After studying the design of the generator, many people have a question about the role of the voltage regulator, which I once had.
Basically, its task is to maintain voltage within certain limits to ensure optimal operation of electrical appliances that are part of the on-board network.
Each regulator has measuring elements that, in essence, act as sensors. In addition, there are actuators that perform the regulation function.
Generators manufactured using modern technologies, which are equipped with any car today, are equipped with electronic semiconductor regulators, which are usually built inside. There is a variety of designs and schemes, but they all have a similar principle of operation.
Voltage regulators are prone to thermal compensation, which changes the level of voltage supplied to the battery for the optimal battery charge level depending on the air temperature under the hood. As it decreases, the voltage increases, and as it increases, the voltage drops. Some of the regulators are equipped with manual mode switches for “winter” or “summer”.
In other words, the regulator performs such an important function as stabilizing the voltage level while changing the load level and rotation speed by adjusting the excitation current.
In the absence of a regulator, the voltage of the generator itself depends on the rotor speed level and on the magnetic flux that is created due to the field winding. It also depends on the magnitude and strength of the current in a given winding, which is given to consumers.
As the rotation speed increases along with the current strength, the voltage increases.
Electronic regulators measure the excitation current by turning on its winding from the mains, which is powered by electricity, which changes the length of time during which the excitation winding is turned on.
If in order to stabilize the entire voltage it is necessary to reduce the current strength of that same excitation, the total time of the excitation winding is reduced. Well, if you need to increase it, then I advise you to increase it.
Video “The principle of operation of a car generator”
The recording shows the principle on which automobile alternators work.
Source: http://MineAvto.ru/remont/elektrooborudovanie/printsip-raboty-generatora-1280.html
We study the principle of operation of the alternating current generator and the design of the unit
Alternating current is the driving force behind many industries and transportation, particularly automobiles. There are both small models the size of a fist, and giant devices several meters in height.
A generator is the same technical system that converts mechanical (kinetic) energy into electrical energy. How does a generator work?
What phenomenon is used in the design of an alternating current generator?
No matter how the generator is designed, its operation is based on the process of electromagnetic induction - the appearance of an electric current in a closed circuit under the influence of a changed magnetic flux.
The generator is conventionally divided into 2 parts: an inductor and an armature.
The inductor is the part of the device where the magnetic field is created, and the armature is the half where the electromotive force or current is generated.
Its technical structure remains constant: wire winding and magnet.
An electromotive force is generated in the winding under the influence of a magnetic field. This is the basis for the generator. But powerful alternating current cannot be obtained from such a primitive design. Conversion requires a strong magnetic flux.
To do this, 2 steel cores are added to the wire winding, which determine the purpose and design of the alternating current generator. These are the stator and the rotor. The winding that creates the magnetic field is placed in the groove of one core - this is the stator, or inductor. It remains stationary, unlike the rotor. The stator is powered by direct current. They can be bipolar or multipolar.
The rotor, or also the armature, actively rotates with the help of bearings and produces electromotive force or alternating current. It consists of an internal core with copper wire winding.
The generator has a durable metal case with several outputs, which depends on the intended purpose of the device. The number of wire wound spools varies.
We understand the operating features of the unit
Now let's find out what principle the operation of alternating current generators is based on. The operating scheme is quite simple and understandable. Provided the rotor speed is constant, the electric current will be produced in a single stream.
The rotation of the rotor provokes a change in the magnetic flux. In turn, the electric field gives rise to the appearance of electric current.
Through contacts with rings at the end, current from the rotor passes into the electrical circuit of the device. The rings have good sliding properties.
They are firmly in contact with the brushes, which are permanent, stationary conductors between the electrical circuit and the copper wire winding of the rotor.
There is current in the copper winding around the magnet, but it is very weak compared to the strength of the electric current that leaves the rotor through the circuit into the device.
For this reason, only a weak current supplied through sliding contacts is used to rotate the rotor.
When assembling an alternator, it is very important to maintain the proportions of the parts, size, gap sizes, and thickness of the wire strands.
You can assemble an alternating current generator if you have all the necessary parts and a sufficient amount of copper wire in your home. Making a small unit is quite possible.
Or there are detailed instructions for using an asynchronous motor as a generator.
Design and principle of operation of an alternating current generator on video
Source: http://elektrik24.net/elektrooborudovanie/generator/peremennogo-toka.html
Alternating current generator design - operating principle and general purpose
Structurally, the electric generator consists of:
- Conductive frame.
- Magnitov.
It works like this:
- The conductive frame is placed in a magnetic field created between the poles of the magnets. Its ends are equipped with slip rings, which are also capable of rotating.
- Using elastic conductive plates (brushes), the rings are connected to a light bulb.
- The frame , rotating in a magnetic field, constantly intersects magnetic field lines with its sides.
- The intersection of magnetic field lines by the frame causes an EMF to occur and an induced current to be generated.
- Under the influence of the resulting induction current , the light bulb begins to glow. The light bulb continues to glow as long as the frame rotates.
One full revolution of the frame inside the magnetic field leads to the fact that the emerging EMF changes its direction twice, and its value increases twice to the maximum value (the conductors passed under the poles of the magnets) and was equal to zero twice (the conductors moved along the magnetic field lines).
Such a change in the EMF during the process of continuous rotation of the frame causes a sinusoidal electric current in a closed electrical circuit, constantly changing in direction and magnitude, which is currently called alternating.
In modern energy, induction alternating current generators of various types are used. At the same time, the principle of their operation is the same and is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
In general, such devices are a rather complex product consisting of copper wire and a large amount of insulating and structural materials.
Design and principle of operation
Device
Any alternating current generator consists of:
- A direct current or electromagnet that creates a magnetic field. In order to obtain a powerful magnetic flux, special magnetic systems of two cores, which are made of electrical steel, are installed in generators.
- Windings in which an alternating EMF occurs. The windings that create the magnetic field are placed in special slots of one core, and the windings in which the EMF occurs are placed in the slots of the other.
- To supply the supply voltage and remove the resulting alternating current , slip rings and brushes are used. These parts are made of conductive materials. The current strength in the windings of the electromagnet that creates the magnetic field is much less than that which the generator supplies to the external circuit, so it is more convenient to remove the generated voltage from the stationary windings, and apply a low-power supply voltage through the sliding contacts.
In low-power devices, brushes and rings are used much less frequently, since their designs can use rotating permanent magnets, which do not require a supply voltage.
Usually:
- The inner core (rotor) together with the winding rotates around its axis.
- The outer core (stator) is stationary.
- The gap between the rotor and stator must be minimal - only then the power of the magnetic induction flux is maximum. In this case, the magnetic field is created by a stationary magnet, and the windings in which the EMF is created rotate.
However, in large industrial generators, the outer core, which creates the magnetic field, rotates around the inner one, and the windings in which the emf is induced remain stationary.
During operation, an EMF arises in the rotor winding, the amplitude of which is proportional to the number of turns. In addition, it is proportional to the amplitude of the alternating magnetic flux (through the coil).
Operating principle of a synchronous generator:
Application area
It is impossible to imagine the daily life of human society without alternating current. Its widespread use is due to the fact that it has enormous advantages over permanent.
At the same time, the main advantage is that the voltage and strength of alternating current can be easily and practically losslessly converted within a fairly wide range.
Especially, such a transformation is necessary in the case of transmitting electricity over long distances. Electricity has great advantages over other types of energy.
It can be transmitted over long distances with low losses and fairly easily distributed among consumers. In addition, electricity is simply converted into other types of energy (light, heat, mechanical, etc.).
That is why alternating current generators are very widely used in modern conditions. With their help, electricity is generated, which is then used in all industries, as well as in everyday life and in all types of transport.
Classification
Due to the wide variety of generators produced by industry in different countries, a fairly extensive system of their classification has been developed.
Thus, alternating current generators are distinguished by:
- I see.
- Constructions.
- Method of arousal.
- Number of phases.
- Connection of phase windings.
AC electric generators are:
- Asynchronous. Products in which the rotating shaft has grooves designed to accommodate windings. They generate an electric current with slight distortion, the magnitude of which does not exceed the nominal value. Products of this type are used to power household appliances.
- Synchronous. Products in which the inductors are placed directly on the rotor. They are capable of delivering current that has high starting power.
Fixed rotor generator
Structurally, generators are distinguished:
- With a fixed rotor.
- With fixed stator
Designs with a fixed stator are most widespread due to the fact that there is no need to use slip rings and floating brushes.
According to the method of excitation, electric generators are:
- With independent excitation (supply voltage is supplied to the excitation winding from a separate DC source).
- With self-excitation (the excitation windings are powered by rectified (direct) current received from the generator itself).
- With field windings , powered by a third-party low-power DC generator, “sitting” on the same shaft as it.
- With excitation from a permanent magnet.
Electric generators are classified according to the number of phases:
- Single-phase.
- Two-phase.
- Three-phase.
Three-phase generators are most widespread.
This is due to the presence of some advantages, among which we should note the possibility of hassle-free obtaining:
- A rotating circular magnetic field, which contributes to the cost-effectiveness of their manufacture.
- A balanced system , which significantly increases the service life of power plants.
- Simultaneously two operating voltages (phase and linear) in one system.
- High economic indicators - the material consumption of power cables and transformers is significantly reduced, and the process of transmitting electricity over long distances is simplified.
Three-phase generators differ in the electrical circuits for connecting the phase windings.
It happens that phase windings are connected:
- "Star".
- "Triangle".
Description of circuits
To obtain a connected three-phase system, the windings of the electric generator must be connected to each other in one of two ways:
"Star"
A star connection involves electrically connecting the ends of all windings at one point. The connection point is called "zero". With this connection, the load can be connected to the generator with 3 or 4 wires.
The wires coming from the beginning of the windings are called linear, and the wire coming from the zero point is called zero. The voltage between linear wires is called linear.
Line voltage is 1.73 times greater than phase voltage.
The voltage between neutral and any of the linear wires is called phase. The phase voltages are equal to each other and shifted relative to each other by an angle of 120 degrees.
A feature of the circuit is also the equality of linear and phase currents.
The most common 4-wire circuit is a star connection with a neutral wire. It allows you to avoid phase imbalance in the case of connecting an asymmetrical load, for example, on one phase there is an active load, and on the other there is a capacitive or reactive load. At the same time, the safety of switched on electrical appliances is ensured.
"Triangle"
A delta connection is a series connection of the windings of a three-phase generator: the end of the first winding is connected to the beginning of the second, its end to the beginning of the third, and the end of the last to the beginning of the first.
In this case, the linear wires are diverted from the connection points of the windings. In this case, the linear voltage is equal to the phase voltage, and the magnitude of the linear current is 1.73 times greater than the phase current.
All mentioned dependencies are valid only for a uniform phase load. If the load of the phases is uneven, they must be recalculated using analytical or graphical methods.
Practical use
Induction generators find their application in almost all areas of human activity.
Moreover, in any case, the rotational energy of the generator shaft is used to produce alternating current.
This applies to:
- Large hydro, thermal, and nuclear power plants.
- Industrial electric generators.
- Household electric generators.
Generators installed in power plants generate large amounts of electricity, which is then transmitted over vast distances.
They are developed for specific, highly specialized tasks and are highly complex devices, the installation of which requires the construction of separate buildings and structures. In addition, their work is ensured by a specially organized infrastructure.
Industrial generators are used to provide electricity to facilities where there should be no interruptions in power supply.
In addition, they are used to provide electricity to construction sites, rotational camps, remote farms and drilling rigs located in places where installing fixed power lines is impossible or economically impractical.
As a rule, they use diesel fuel to operate, while generating high power alternating current (220 or 380 V). For this purpose, synchronous generators are used, which are capable of ensuring the operation of high-power industrial equipment.
In diesel installations, the generator shaft is rotated by an internal combustion engine (ICE).
Electric generator on chassis
All components included in the industrial generator are mounted on a high-strength steel chassis, which, if necessary, is installed:
- Thermally insulated container.
- Mobile chassis (wheeled, on skids).
Household electric generators have gained great popularity relatively recently.
They are used for the electrification of small cottages, country houses and summer cottages, and also help solve a number of problems associated with the incorrect operation of the centralized power grid and are often used as emergency alternating current sources at previously electrified facilities of this type.
In devices of this type, both gasoline and diesel internal combustion engines are used to rotate the generator shaft. They produce alternating current of low power (from 0.5 to 15 kW) and differ:
- Economical.
- Small in size.
- Low noise level.
When choosing a household alternating current generator, a potential consumer needs to pay attention to:
- Engine type (petrol or diesel).
- The power declared in the accompanying documentation.
- Generator type (synchronous or asynchronous).
- Phasing.
- Control block.
- Noise level.
Source: http://househill.ru/kommunikacii/electrika/stabilizatory/generator-peremennogo-toka.html