How to check the lambda probe and replace it
Many drivers know that the lambda probe plays a vital role in the operation of the car’s engine and exhaust system. This means that most of them are interested in the question of how to check the lambda probe? This is not difficult to do. In this article we will look at ways to check the lambda probe and tell you how to replace it if necessary.
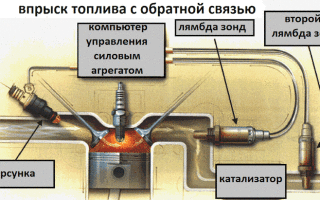
A lambda probe or, in other words, an oxygen sensor is a special device located in the exhaust manifold.
It is the readings of this oxygen sensor that allow the electronic control unit of the injector to maintain the optimal composition of the air-fuel mixture (the lambda probe gives a signal to the electronics if a too lean or too rich mixture enters the combustion chamber, and the computer corrects it).
According to the theory, in order for the combustion of 1 kg of fuel-air mixture to occur, almost 15 kg of oxygen is required. That is why the serviceability of the lambda probe directly affects the operation of the power unit and fuel consumption.
But not everyone clearly understands what a lambda probe is. In addition, before you start checking the sensor, you should know the reasons why it fails, as well as the consequences that a lambda probe failure can lead to.
How the lambda probe works (working principle)
The design of the lambda probe includes the following components:
- metal body (with threaded threads for fixation);
- ceramic insulator;
- seal (ring);
- wiring and special cuffs to seal it;
- a protective housing with a hole drilled in it (provides ventilation);
- conductive contact;
- ceramic tip;
- spiral (placed in a special container);
- protective shield (has a hole designed to release gases).
A special feature of such probes is that exclusively heat-resistant materials are used for their production, because the lambda probe itself operates at high temperatures.
There are 4 types of probes (depending on the number of wires that fit to it):
- Single wire;
- Two-wire;
- Three-wire
- Four-wire.
The main causes of lambda probe failures.
The causes of malfunctions can be either third-party factors or improper care of certain elements of the car, such as:
- Antifreeze or brake fluid getting inside the housing;
- Cleaning the case using products that were not originally intended for this purpose;
- Lead content in fuel is too high;
- Overheating of the body - this problem occurs when refueling with low-quality fuel. This happens when the coolant sensor, pressure regulator, or worn fuel filter are faulty. All this leads to contaminated gasoline entering the combustion chamber.
Consequences of a lambda probe failure
When a lambda probe breaks down, the car owner immediately feels changes in the behavior of the car:
- jerks in movement;
- increased fuel “appetite”;
- incorrect operation of the catalyst;
- unstable engine speed;
- increased concentration of toxins in exhaust gases.
All this makes it necessary to carefully monitor the operation of the oxygen sensor. It is worth checking it at least once every 10,000 km.
Lambda probe testing methods
To begin with, you can try to evaluate the performance of the lambda probe visually, and then check it using electrical measuring instruments (voltmeter or oscilloscope).
Visual check. Of course, this is not a panacea, but this method is the simplest and most understandable, so it is recommended to start comprehensive measures with it.
First, you should inspect the connectors to which the wires are connected - they all must be securely fixed in their seats.
Next, you need to carefully examine the oxygen sensor itself:
- Presence of soot. Soot usually occurs either in the case of a defective probe heater or in the case of combustion of a rich fuel mixture. All this clogs the device and “slows down” the response of the lambda probe to the exhaust composition;
- Shiny deposits are the first sign of excessive lead concentration in fuel. In this case, the device will have to be replaced, since lead damages the probe itself and the catalytic converter;
- White or gray deposits also lead to sensor replacement. The cause of this malfunction most often lies in the use of fuel additives or engine oil.
Testing using instruments. In order to check the lambda probe, you need to prepare a digital voltmeter turned on in the DC voltage measurement mode.
First, you should warm up the engine, after which you need to find the sensor in the engine compartment and carefully inspect it. If it is covered with heavy deposits of soot, lead or other similar substances, then it is not advisable to continue testing - replacement will be required.
Otherwise, we look for the reason further:
- You need to make sure that there is no mechanical damage to the probe itself and the wires suitable to it.
- If everything is in order, you should start the car, first disconnecting the oxygen sensor from the block and connecting its signal wire to a digital voltmeter.
- After this, you need to increase the engine speed to 2500 and release the accelerator pedal.
- Next comes the vacuum tube, which should be removed from the fuel pressure regulator.
Now you can determine whether the lambda probe is working. To do this, you need to look at the voltmeter readings - if they are at 0.8 V or less (or are absent altogether), then there is a malfunction of the device.
After this, you should check for a lean mixture, which will require causing air leaks using a vacuum tube. The proper operation of the lambda probe is indicated by voltmeter readings within 0.2 V or less. If all tests show a negative result, then replacing the sensor cannot be avoided.
Replacing the lambda probe
Replacement of the lambda probe is carried out only with a cold engine and the ignition is turned off.
You should buy a new sensor with the same markings that are on the old probe.
Replacement is carried out in three stages:
- The wires are disconnected from the sensor;
- Use a wrench to unscrew the old lambda probe.
- A new one is screwed in its place.
The main thing is to work carefully so as not to strip the thread.
After replacement, you need to connect the wiring and check the correct operation of the new lambda probe.
As you can see, checking and replacing an oxygen sensor is not too difficult, so any car enthusiast can handle it if desired.
How to check a lambda probe with a voltmeter
Source: https://unit-car.com/diagnostika-i-remont/100-kak-proverit-laymbda-zond.html
Lambda probe. Principle of operation. Diagnostics
If computer diagnostics do not determine the specific causes of the above malfunctions, the lambda probe is probably not working correctly. Just because computer diagnostics sometimes does not see its malfunction. How the lambda probe works First, why "lambda".
This Greek letter in the automotive industry denotes the coefficient of excess air in the air-fuel mixture. Let me remind you that the optimal fuel/air ratio is 1 to 14.7. Why not a sensor, but a “probe”. Probably because the working area of the sensor is inside the exhaust system, and the exhaust mixture passes through it. Something reminiscent of medical probes.
Most modern lambda probes have the design shown in the figures below
Sensors of this design have a built-in electric heater and at least three, usually four, leads. The heater is necessary for the correct operation of the sensor, which is achieved when it is heated to 300 - 400 degrees Celsius. Some lambda probes do not have their own heating element (single- and double-lead sensors).
Considering that the sensors are installed in the exhaust manifold, after a few minutes of engine operation they independently enter operating mode. But all these “several minutes” the engine works with incorrect lambda probe readings and consumes more fuel.
The main task of the lambda probe is to inform the engine control unit about the quantitative composition of oxygen that did not participate in the ignition process. Therefore, they are often called oxygen sensors (O2-sensor). The working area of the sensor is a tip made of porous ceramics.
It has a complex structure, which can be depicted in a simplified manner: The working element itself is made of zirconium oxide 1 with sputtered platinum electrodes 2,3 (this is why lambda probes are so expensive). One sensor output is connected to ground 4 or to the sensor terminals.
The second output (signal) 5 – to the terminals on the engine control unit. When heated to high temperatures, zirconium dioxide acquires the properties of a solid electrolyte. The voltage at the sensor output (emf) varies stepwise depending on the concentration of the mixture.
Thus, with an enriched mixture, the sensor generates an output voltage of approximately 0.9 Volts, and with a lean mixture, less than 0.2 Volts.
Some cars have two lambda probes: before and after the catalyst. The latter serves to clarify the data, as well as to determine the efficiency of the catalyst.
Checking the functionality of the lambda probe should begin with checking the serviceability of the sensor heating element (for three-wire and four-wire sensors). Its resistance is usually less than 10 ohms.
For measurements, you can use a regular multimeter connected to the terminals of the heating elements (determined from the electrical diagram). It must be said that even with a faulty heater, the sensor will be operational in long-term driving mode if the working element of the probe itself is operational.
A malfunction of the working element can also be determined with a multimeter in the DC voltage measurement mode. To do this, a voltmeter is connected to the output of the lambda probe. Initially, the situation of an enriched mixture is realized (possibly through artificial gas transfer). The device readings should be more than 0.8 Volts.
Then the mixture is artificially leaned (you can create a situation where air leaks into the intake manifold). The voltage should be less than 0.2 Volts. If the voltages are outside the specified values, the sensor is faulty. Diagnostic scanners can look at the voltage at the sensor in real time.
This can also be done using an oscilloscope. The approximate time dependence of the voltage at the output of the working sensor has the form:
If the signal amplitude is smaller, or has a slope towards lower or upper values, the sensor should be changed. Before deciding to purchase a new sensor, you should evaluate the appearance of the working surface of the sensor (ceramic tip).
The following options are possible:
- the presence of soot, which indicates an enriched mixture;
- white or gray coating is a sign of the presence of additives in the oil or fuel;
- shiny coating – too much lead content in the fuel.
The deposits can be cleaned, but it is not a fact that the lambda probe will start working properly; perhaps the working layer of platinum and zirconium oxide in it has long since burned out.
Cleaning the sensors
To properly clean the working tip of the sensor, the protective screen must be removed. Cleaning is done with a soft brush made of natural fibers, after soaking the sensor in phosphoric acid, or, at worst, in carburetor cleaning fluid. You can simply soak the sensor in these liquids for a couple of hours, then shake and dry with an industrial hair dryer.
Replacing the lambda probe
When replacing a lambda probe, the greatest difficulty is removing it from a coked threaded connection. For this, special liquids are usually used.
After dismantling the sensor, you should carefully wipe the surface of the collector to remove any remaining product so as not to clog the new sensor. If a “native” sensor cannot be found on the market, or it is very expensive, you can install a universal sensor.
They work almost identically to the original ones, only instead of a connector they have wires with tinned terminals. The installation depth and thread dimensions of the sensors are, as a rule, universal, but it is necessary to check just in case.
All that remains is to correctly connect these wires to the connector (it can be cut off with the wires from the faulty sensor). The connection is made by twisting plus soldering plus heat shrink insulation.
To make the lambda probe last longer, you should:
- avoid getting foreign liquids into the exhaust system (antifreeze due to a faulty cylinder head gasket, residual ether when using a “quick start”, oil when reducing compression);
- use proven fuel;
- Avoid getting impurities and dust into the collector (change the air filter in a timely manner).
Advertising space
Source: https://autoburum.com/blog/404-lambda-zond-princip-raboty-diagnostika-neispravnostej
What is a lambda probe in a car, what happens if you disconnect the oxygen sensor
Lambda probe (λ probe) is a special device, one of the types of sensor. The task is to control the volume of oxygen in the power unit manifold.
The device estimates the total volume of oxygen or unburnt fuel mixture in the vehicle exhaust.
Lambda probes are often installed in the chimneys of heating boilers and other systems where oxygen control is required.
The lambda value is 14.7 units per unit of fuel. Proportionality is ensured thanks to electronic injection of the fuel mixture and the operation of a lambda probe.
The purpose of the device also depends on its position in the vehicle.
As a rule, an oxygen sensor is mounted in front of the catalyst, which makes it possible to accurately measure the oxygen level in the combustible mixture, and in case of imbalance, give a signal to the injection control unit.
To increase operating efficiency, new car models are equipped with not one, but two sensors, attached to one and the other side of the catalyst.
This design allows for more accurate analysis of the exhaust composition.
Evolution of development
Previously, oxygen sensors were resistive, which reduced the accuracy of measurements and the reliability of the devices themselves.
A modern lambda probe works as a threshold device. In this case, the signal received from the sensor allows you to accurately record the level of oxygen ratio in the exhaust and correct it.
The optimal ratio is 14.7:1 (actual to required air volume). If the parameter λ corresponds to this standard, then the mixture is ideal.
If the indicator is exceeded, the mixture is lean. If λ , on the contrary, is smaller, then there is a lot of mixture in the exhaust and the volume of oxygen is not enough for combustion.
The lambda probe was first manufactured in 1960 by Robert Bosch GmbH. The project manager was Günther Baumann.
The device entered mass production only 16 years later (in 1976). The first manufacturers to start production were Saab and Volvo.
Main device types
Today there are several types of oxygen sensors. All of them may differ according to several criteria:
- by number of wires - from 1 to 6;
- on the organization of the sensory element (there are two types - plate and finger);
- for fasteners in the exhaust pipe - flanged or threaded;
- according to the measurement range of the lambda parameter - broadband (measurement is made in the range from 0.7 to 1.6 ) or narrowband, controlling the lambda level at a level above unity.
Each type of device has its own characteristics.
One contact devices.
Equipped with one signal wire. It is through it that the signal generated by the device is transmitted.
2-pin sensors.
Equipped with two wires. One is a signal, and the second performs the function of grounding through the device body.
Using the grounding conductor, you can accurately determine the performance of the signal wire.
3-pin.
There is a signal wire, one ground wire and a third wire going to the heating device.
The peculiarity of such sensors is the rapid achievement of the desired temperature, an increased service life of the device, as well as lower requirements for the exhaust system.
The heating element, which is mounted in the system, has a power of 12 or 18 W.
4-pin devices.
They have four wires:
- signal conductor,
- the wire,
- feeding the heating device;
- the third wire is “ground”;
- fourth wire - can be used to solve any other problems (depending on the vehicle control system).
This may be the position of the contacts.
For example, it can be used as grounding or to power a heating element.
The peculiarity of modern lambda probes is that they are interchangeable and have a similar design.
For example, you can replace heated sensors with non-heated ones. In this case, there may be problems with the connectors or the inability to power the device.
If there are not enough wires, you can lay them yourself and use the car contacts as a connector.
The markings may vary, but the signal wire is always painted black.
The "mass" may be yellow, gray or white.
The design of modern oxygen sensors
The oxygen sensor has two electrodes - internal and external.
The first is made of zirconium, and the second is made of platinum coating, which makes it more sensitive to oxygen.
The lambda probe is mounted in such a way that it passes the entire volume of exhaust gases of the vehicle.
As gases pass through, the external electrode evaluates the oxygen level in the exhaust gases, which leads to a change in the potential between the electrodes.
The greater the volume of oxygen, the higher the voltage level. The operating temperature of the zirconium with which the electrode is coated is 300-1000 degrees Celsius.
That is why oxygen sensors are structurally complemented by heaters, which are necessary at the time of start-up.
There are two types of sensors - point-to-point and wideband. They are similar in appearance, but differ in design and principle of operation.
Thus, a 2-point sensor consists of two electrodes. Its task is to fix the coefficient of increased air volume in the fuel mixture.
As for the broadband device, this is a more modern design. Its main feature is the use of injection current.
In this case, the design of the broadband sensor consists of two ceramic devices - a pumping device and a 2-point one.
Operating principle
Oxygen contains negatively charged ions. They are assembled on platinum electrodes and when the desired sensor temperature is reached (about 400 degrees Celsius), a potential difference (voltage) is created.
If the mixture is too lean, then the volume of oxygen in the gases will be high, and vice versa, if the mixture is rich, then there will be little oxygen.
In the first case, the voltage is 0.2-0.3 Volts, and in the second - 0.7-0.9 Volts.
The motor control system maintains a voltage level of about 0.4-0.6 Volts, that is, the lambda level is 1.0 .
During movement, the operating modes of the motor change, which helps to adjust the voltage parameter in both directions. In this case, a narrowband sensor can only capture those parameters that are above zero.
The lambda probe, which is installed after the catalyst, has the same principle of operation.
After treating the gases with a catalyst, the oxygen level remains unchanged. This, in turn, allows you to maintain an optimal potential difference within 0.4-0.6 Volts.
Wideband lambda probe: main differences, operating principle
A broadband sensor for measuring oxygen levels is a lambda probe, which is installed in modern cars.
Its peculiarity is that it acts as a catalyst at the entrance to the device. The required parameters are measured using the input current.
The main difference between a broadband sensor is that it contains two working elements - a pumping element and a 2-point ceramic heater.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CxhGVt5_YUA
During the injection process, oxygen is passed through the corresponding element under the influence of current.
The operating principle of the broadband probe is based on maintaining the voltage within 450 mV .
The potential difference itself appears between the electrodes of the two-point element. Achieving the required voltage is guaranteed by changing the pumping current.
If the volume of oxygen in the exhaust decreases, the voltage between the electrodes increases, and the ECU receives the corresponding command.
After this, a signal of the required current strength is generated, which leads to voltage equalization.
The current strength is analyzed in the computer, after which the control unit acts on the injection system.
Normal operation of the oxygen sensor is possible at a temperature of 300 degrees Celsius, which is achieved using a heater.
What does a probe malfunction lead to?
The first trouble that results from the failure of the probe is an increase in the “gluttony” of the car and a deterioration in the overall dynamics.
The main reason is a distortion of the sensor readings, which leads to a deviation in the oxygen-to-fuel ratio.
If one sensor fails, the car remains on the move (much depends on the vehicle itself).
There are models in which failure of the mechanism leads to large amounts of fuel being consumed. As a result, urgent repairs may be required.
If the lambda probe breaks down, it should only be replaced with a similar mechanism.
If you install a device of a different type, the vehicle’s on-board computer may simply not perceive the signals from the new sensor.
If two sensors break down at once, the car becomes completely immobilized.
Read more here -.
Causes of failure
It is worth noting that the oxygen sensor has increased sensitivity to breakdowns.
The cause of failure may be:
- Low quality fuel. With bad gasoline, certain parts of lead remain on the lambda probe. The appearance of such sputtering impairs the sensitivity of the electrode to the fuel mixture. Some time passes and the sensor can be thrown away.
- Mechanical failure. The oxygen sensor itself may fail. In this case, the main damages include a housing defect, a violation of the device winding, and so on.
The problem is solved by installing a new sensor. As for repairs, they are useless in case of such breakdowns.
3. Excessive volumes of fuel supplied to the engine cylinders simply do not have time to burn and fly out into the exhaust system in the form of soot.
Over time, black deposits accumulate on the components of the vehicle’s exhaust system, including the oxygen sensor. As a result, the lambda probe begins to work incorrectly.
As a “treatment” you can use special cleaners and rags to remove dirt. If the sensor clogs regularly, then it is better to change it.
How to identify a breakdown?
A malfunctioning lambda probe can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- increasing the overall toxicity of exhaust vapors. Of course, it is impossible to determine this indicator by eye. Only a special device can help here. If the CO level has increased significantly, then we can confidently say that the oxygen sensor has failed;
- An increase in the car’s “gluttony” is a problem that can be seen almost immediately. The only thing is that an increase in flow rate does not necessarily indicate a sensor malfunction;
- The Check Engine light coming on is another signal that something is wrong with the system. As practice shows, the lighting of this light is associated with a breakdown of the lambda probe. To more accurately determine the error and identify the defect, you need to go to the service.
How to check the lambda probe for serviceability.
Is it possible to turn off the lambda probe?
Disabling the oxygen sensor takes a few minutes for a specialist. But the benefits of such work raise serious doubts.
From the moment the lambda probe is turned off, the ECU switches to average fuel supply parameters to the engine, which affects reliability and fuel consumption (usually for the worse).
In addition, if the oxygen sensor is disconnected, it may be necessary to reflash the car’s ECU itself, because an error will constantly appear.
Therefore, if the lambda probe fails, it is advisable.
Lambda probe decoy: what is it?
When replacing the catalyst with a flame arrester or dismantling the device, the signals from the two lambda probes will be identical. This, in turn, will inevitably lead to errors.
The problem is solved by installing a lambda probe blende.
It comes in two types:
1. Mechanical.
By design, it is a spacer made of bronze and having certain dimensions. Inside the unit there is a special crumb with catalytic spraying, which helps harmful substances burn out.
2. Electronic.
This decoy is a device based on a microprocessor that analyzes the entire process of exhaust gas passage and processes data from the first sensor.
The task is to ensure correct operation of the engine control system in conditions where the catalyst is broken or removed.
Bottom line
Despite its compactness, the lambda probe is one of the most important components of the car. It not only reduces harmful emissions, but is also responsible for a number of other functions.
The absence of this device may cause increased fuel consumption, deterioration of engine dynamics, or complete inability to operate the vehicle.
Source: http://PortalVAZ.ru/chto-takoe-lyambda-zond-v-mashine-chto-budet-esli-otklyuchit-datchik-kisloroda/
It's all about oxygen - signs of a malfunctioning lambda probe
Most cars produced from the late 70s to early 80s are equipped with catalytic exhaust gas converters (in common parlance - catalysts), which can significantly reduce the toxicity of waste materials, reducing the damage caused to the environment.
A rather interesting fact is that the catalyst can maintain functionality only under conditions of ideal mixture formation, in which 1 part of fuel contains from 14.6 to 14.8 parts of atmospheric air with a normal oxygen content.
To prevent the mixture from becoming over-rich or over-lean, it is necessary to use electronic control of the fuel supply - in such a system, the quality of the combustible composition is controlled by a lambda probe. Despite its location in an aggressive environment, this device is quite fragile and unstable, and is subject to frequent breakdowns.
If the lambda probe in your car has stopped working, signs of a malfunction can be detected without specialized equipment - it is impossible to continue operating the vehicle.
The lambda probe evaluates the quality of burned fuel
The lambda probe determines the chemical composition of exhaust gases by searching for oxygen in them and determining the percentage.
In the normal state of the mixture, this figure is 0.1–0.3% - small fluctuations are allowed due to the fact that the fuel supply mode to the engine cannot be stable over a significant period of time.
The lambda probe is installed directly into the exhaust manifold - usually its installation is carried out at the junction of the pipes extending from various cylinders (in common parlance - “pants”), although there are other options.
There are various modifications of lambda probes - on economy class cars, as well as vehicles of previous years of production, the devices have a two-channel layout.
They can only determine the presence of a deviation in the oxygen content in a positive or negative direction, which is accompanied by a change in the voltage of the electrical signal transmitted to the electronic unit.
However, all modern cars of the middle and elite classes are already equipped with broadband-type lambda probes, which are already designed to determine the percentage deviation of the content of the required element from the norm. Thanks to this, a significant improvement in engine performance is achieved:
- Increases the stability of maintaining idle speed;
- Fuel costs are reduced;
- The resource of the vehicle increases.
If you are interested in the electrical engineering side of the lambda probe, then it is worth mentioning that this device cannot generate a uniform signal.
Due to the fact that the standard lambda probe is located in the exhaust manifold, when the exhaust gas reaches its location, several operating cycles may already have passed. In this case, the quality of mixture formation deteriorates by 3–5%, which is accompanied by some destabilization of the engine.
The lambda probe reacts to this by changing the voltage supplied to the central injection control unit, which takes the necessary measures.
Determining the breakdown
External signs
If the lambda probe malfunctions, there is a significant deterioration in the quality of the fuel mixture, which is externally expressed in deterioration in engine performance. It is worth saying that there can be many reasons for the malfunction - among them the following main ones can be identified:
- Depressurization of the sensor housing, penetration of atmospheric air and exhaust gases;
- Overheating of the lambda probe as a result of a malfunction of the ignition system and inept engine tuning;
- Failure as a result of prolonged exposure to an aggressive environment (aging);
- Blocking of the working surface of the lambda probe with combustion products of low-quality fuel;
- Disturbances in the normal power supply and interruption of the line leading to the control unit;
- A strong blow to the lambda probe housing with destruction of internal components, for example, during active driving on bad roads.
In all cases, except for mechanical damage accompanied by depressurization, malfunctions of the lambda probe appear gradually, with a stepwise deterioration in engine performance.
Another exception is a broken wiring - however, it cannot be considered a malfunction of the lambda probe itself, so it should be considered in a separate topic for discussion.
For everyone else, the following stages of malfunction development can be distinguished.
Video on how to check the lambda probe:
Initially, the device ceases to normally perform its functions in extreme operating conditions of the engine, when its electrical characteristics have already deteriorated so much that the sensor cannot generate the required signal.
A malfunction of the lambda probe manifests itself in destabilization of the idle speed, which begins to “float” in a fairly wide range, the length of which is 300–600 rpm.
When reaching very high speeds that do not belong to a critical level, a sharp change in the quality of the fuel mixture may occur.
In this case, the car may twitch violently, in some cases abrupt popping noises can be heard from under the hood, and a warning light flashes on the dashboard, signaling abnormal engine operation. When the speed decreases, all signs of a lambda probe failure disappear, but they cannot be ignored.
At the second stage, the device stops working on a cold engine - until the temperature reaches the maximum possible, the car will show all signs of a malfunction in the intake system or gas distribution mechanism.
In particular, you will notice a significant reduction in power, extremely slow responses to changes in the position of the gas pedal, and jerking and popping. If the lambda probe malfunctions, the car may jerk, slow down sharply as a result of a complete stop in the fuel supply, and the engine may begin to overheat.
After about 5–10 minutes of driving in such an unpleasant mode, a visible stabilization of the vehicle’s condition occurs - however, it is exclusively temporary.
If the lambda probe is faulty, you can face a lot of troubles
If you do not take any measures regarding malfunctions of the lambda probe at the previous stage, the device will completely fail, which will cause many negative consequences.
In addition to a significant deterioration in dynamics and the impossibility of normal movement in continuous mode, you will be faced with an increase in fuel consumption by 15–30%, as well as a significant increase in exhaust toxicity, which can be determined by an unpleasant pungent odor with a clearly noticeable hint of fuel.
Modern cars can generally block all driver actions if the lambda probe is faulty by switching to emergency mode.
Worst option
If the above-mentioned depressurization of the lambda probe occurs, it is impossible to continue operating the vehicle, as this may lead to complete engine failure followed by expensive repairs.
In this phenomenon, exhaust gases enter a duct that is used to draw in atmospheric reference air to compare the two types of gases and determine the optimal oxygen content.
If engine braking occurs, atmospheric air with a minimum amount of impurities passes through the cylinders - therefore, the lambda probe sees that there is much more oxygen in the manifold than in the environment! The result of this is the formation of powerful negative signals that completely disrupt the normal operation of the injection control unit.
External signs of such a malfunction are quite easy to determine - the car loses a significant part of its power, in some cases the response to pressing the gas pedal can be very weak - that is, when it is pressed “to the floor”, the speed increases only slightly.
During active driving, loud popping noises are heard from under the hood, accompanied by a cutoff in fuel supply and, as a result, strong jerks. In addition, a malfunction associated with depressurization of the lambda probe leads to fuel combustion in the catalyst.
As a result, a very unpleasant odor becomes heard, soot is ejected in large portions from the exhaust pipe, and also settles on the exhaust valves and spark plug housings.
Electronic diagnostics
If you want to know what signs of lambda probe failure can be detected during a professional inspection, you should find specialized equipment.
When examining a lambda probe, an electronic oscilloscope is used - some experts recommend using a multimeter, but it can only determine the fact that the device has failed.
The device is checked with the engine running, heated to a coolant circuit temperature of 80–90 degrees. When cold, the sensor may give readings that deviate significantly from the norm.
There can be many signs of a device malfunction. They are represented by flat signal characteristics or a level increase not exceeding 0.1 V.
In addition, it is worth paying attention to the shape of the curve - the changes should be quite steep, not allowing a smooth increase in voltage.
Experts say that the lambda probe must change the signal level every 120 ms - otherwise it is possible to talk about its malfunction.
Car repair
Almost all manufacturers of vehicles and individual components for them claim that the lambda probe cannot be repaired - only a complete replacement of the unit is required.
At the same time, its cost from official dealers can be very impressive - especially if you own a car of an elite brand.
A common way out is to purchase a universal sensor equipped with a special adapter for a specific type of vehicle.
Such devices are manufactured by Bosch - using its services, you can even purchase used, refurbished spare parts, which have a reduced cost and a limited warranty period. In addition, you can buy a used exhaust manifold with a pre-installed lambda probe.
If you are absolutely sure that the lambda probe is not functioning properly as a result of combustion products deposited on it, you can try cleaning it. To do this, the device is dismantled at a surface temperature of 40–50 degrees, the protective cap is removed from it and the contacts are immersed in phosphoric acid.
After several washes, the lambda probe is washed with clean water, thoroughly dried and installed in place, not forgetting to lubricate the threads with a special sealing paste. The tightening torque is set by the manufacturer - it usually varies between 40–60 Nm.
This procedure helps in 80% of cases of the described malfunctions.
The main thing is timely diagnosis
If you discover in time that the car’s malfunction lies precisely in the breakdown of the standard lambda probe, you will be able to carry out the necessary repairs even before the consequences affect the engine, leading to its significant breakdown.
In addition, by eliminating such a problem, you will be able to maintain the most important characteristics of the vehicle at the same level, which will help you use it to the fullest and most profitably.
It’s up to you to decide which troubleshooting method you choose, but it’s worth remembering that working with car electronics without the appropriate qualifications is very dangerous.
Source: http://365cars.ru/remont/lyambda-zond-priznaki-neispravnosti.html
How does a lambda probe work in a car?
The exhaust gases of any car have an extremely negative impact on the environment, therefore, in order to somehow minimize the harm caused, the designers have developed a special device - a catalytic converter for exhaust gases.
It would seem that now all the problems will be solved, but for the normal and stable operation of this device it is required that each component of the air-fuel mixture be within clearly defined limits, and in any operating modes.
This is where the oxygen sensor, or, as it is popularly called, the “lambda probe,” came to the rescue.
1. Operating principle of the oxygen sensor
When a car engine is in an active state, the oxygen concentration inside the system and outside (in the environment) will be completely different.
It is because of this difference that oxygen ions move in the solid electrolyte, and a potential difference arises at the electrodes of the measuring element, that is, a certain signal from the oxygen sensor appears.
The control unit uses this signal to maintain the optimal (stoichiometric) ratio of air and fuel liquid in the combustion chamber (a proportion of 14.7:1 is considered almost ideal, where the first value is the amount of air required for the most efficient combustion of the fuel mixture).
The oxygen sensor is mounted in a hole located in the exhaust manifold housing. However, if the design provides for another similar device, then it is screwed into the hole in the exhaust pipe, in front of the catalyst.
The entire operation of the lambda probe is based on the principle of W. Nerst, a German scientist who discovered the possibility of determining the normal electrode potential using oxygen. As for the device we are considering, the electrodes located inside the sensor help determine the amount of oxygen present in the exhaust gases.
Note! The maximum operating efficiency of the lambda probe will be achieved only at a temperature of at least 300 °C. That is why the device is equipped with an electric heating spiral, which creates a suitable temperature regime before the engine warms up.
The oxygen sensor is located in the exhaust gas flow in such a way that the outer electrode is in contact with the gases, and the inner electrode is placed in the atmosphere of atmospheric air.
Based on the difference in the amount of oxygen, an electric charge is formed between the internal and external electrodes, and its maximum power is at the level of 1 V.
This value is transmitted and then processed by the computer control unit for the operation of the power unit.
After this, the signal from the block moves to the fuel injectors, and they, in turn, determine the required amount of fuel. Depending on the nature of the signal, the amount of gasoline in the fuel-air mixture can either increase or decrease.
It must be said that the lambda probe has found its application not only in the automotive industry, but also in other areas of human activity - in particular, where devices for burning fuel are used (for example, water heating boilers).
2. Types of oxygen sensors
Automotive oxygen sensors are divided into types based on several criteria:
– design features: 1, 2, 3, 4-pin sensors;
– method of fastening in the exhaust pipe: threaded and flanged;
– lambda measurement widths: narrowband (detect lambda when the value is >1) and wideband (determine lambda 0.7-1.6)
In addition, on modern vehicles you can find sensors based on two different compositions. The first includes devices based on zirconium dioxide, and the second includes lambda probes based on titanium oxide (titanium). Both types have the same principle of operation, and the only difference is in the design.
It should be noted that the number of wires on the oxygen sensor reflects the features of its internal structure.
Thus, single-contact devices have only one signal wire, through which the electrical impulses generated by the sensor are transmitted.
Two-pin designs already consist of two wires: a signal wire and a ground wire (duplicates grounding through the housing). It is the grounding wire that allows you to more accurately evaluate the readings of the signal wire.
Three-pin oxygen sensors are equipped with one signal wire, a ground wire, and a wire going to the heating element.
This type is characterized by certain advantages: a short time to reach operating temperature (which means that the amount of harmful emissions when the engine is running cold will be reduced), a longer service life, and ease of maintenance.
The design of four-pin sensors includes one signal wire, one power wire (going to the heating element) and one ground wire (functions depend on the design of the motor control system). The fourth wire is either another ground or power for the second heating element.
Narrowband (two-level) oxygen sensors are one of the simplest types of such devices. They have a rather primitive design and are a kind of generator of wave-like signals.
In fact, this sensor is an ordinary galvanic cell, but only in the role of electrolyte there are ceramic honeycombs that freely penetrate oxygen ions (in order for them to become fully conductive, heating to a temperature of 400 ° C is required).
The narrow-band sensor can be installed both in front of the neutralizer and behind it.
The wideband lambda probe is presented in the form of a more modern design, the peculiarity of which is the ability to adjust the mixture formation separately for each engine cylinder, and an almost instantaneous response to changes in processes occurring in the engine. This factor has a positive effect on the performance of the power unit and reduces the amount of harmful substances in the exhaust several times. The broadband lambda probe acts as a catalytic converter input sensor.
3. Signs of a malfunctioning lambda probe
Since the efficiency of the power unit in the car directly depends on the good condition of the lambda probe, there is nothing strange in the fact that a malfunction of this device will lead to operational failures of the “heart” of the car. Thus, with a breakdown of the oxygen sensor, the quality of the fuel mixture entering the combustion chamber significantly deteriorates, which, in fact, remains uncontrolled.
It can be quite difficult to diagnose any malfunctions in the operation of a lambda probe, because it does not break down immediately, but simply stops functioning stably.
For example, the sensor may read the readings incorrectly, which, in turn, contributes to incorrect fuel supply to the engine cylinders.
In cases where the control system does not receive information about the oxygen content in the exhaust gases for a long time, it switches to the mode of using average indicators, thereby disturbing the composition of the working mixture.
The most typical symptoms of a malfunctioning oxygen sensor are:
– increased consumption of fuel fluid;
– unstable operation of the engine at idle;
– exceeding the norm of carbon monoxide (CO) in the vehicle exhaust;
– a sharp decrease in the driving characteristics of the vehicle.
Moreover, if the engine is equipped with two lambda probes, then it will react more sharply to their incorrect activity, and in some cases may refuse to work at all.
4. Why does the lambda probe fail?
Typically, the service life of an oxygen sensor is 30-70 thousand km of vehicle mileage, but detailed figures still depend on the operating conditions of the vehicle.
As practice shows, heated devices with an operating temperature of 315-320 °C can boast a longer service life.
Possible malfunctions of the oxygen sensor, first of all, include non-working heating and loss of sensitivity (reduced performance), but the list of reasons that led to the failure of this device is quite extensive. In particular, it includes:
– the use of low-quality fuel, the components of which simply clog the platinum electrodes;
– oil getting into the exhaust pipe and poor condition of the oil scraper rings;
– contact of various washing liquids, solvents and antifreeze on the ceramic tip of the sensor;
– overheating of the lambda probe housing due to an incorrectly set ignition timing;
– failures in the ignition system and popping noises in the exhaust pipe;
– over-enriched air-fuel mixture;
– when installing the lambda probe, use sealants that vulcanize at room temperature;
– repeated attempts to start the power unit at short intervals (as a result, this leads to the accumulation of unburned fuel residues in the exhaust pipe, which can ignite);
– poor contact, break or short to ground of the sensor output circuit.
Without describing each reason separately, we can say that the reason for the failure of the oxygen sensor is:
– depressurization of its body;
– ingress of air and exhaust gases;
– overheating of the lambda probe (the reason usually lies in poor-quality engine painting and improper operation of the ignition system);
– incorrect or unstable electrical supply that leads to the main control unit;
– incorrect actions of the car owner (expressed in the use of low-quality fuel and careless actions when servicing the car);
– various mechanical damage resulting from careless operation of the vehicle.
It should be noted that in all of the listed cases (except the last one), the breakdown of the lambda probe occurs gradually, so inexperienced car owners who are not familiar with this device are unlikely to immediately notice the malfunction.
The process of oxygen sensor failure can be divided into several stages:
1. The appearance of malfunctions (in certain operating modes of the power unit, the oxygen sensor simply stops sending a signal, which cannot but destabilize the idle speed). At this stage, you can hear popping sounds uncharacteristic of the engine and see the warning light on the dashboard come on.
2. Failure to operate on a cold engine. There is a significant loss of power, a slow response to pressing the accelerator pedal, “popping” noises from under the hood, unjustified jerking of the vehicle and overheating of the power unit.
If the problem is not noticed in time, it is quite possible that the sensor will depressurize, which means that subsequent operation of the vehicle will be impossible. Of course, unless you want to get a much more serious problem - expensive repairs to the power unit.
The main sign of depressurization is loss of power, characteristic knocking in the engine compartment and an unpleasant exhaust smell. Also, when you look under the hood, you may notice visible soot deposits in the area of the spark plugs and on the exhaust valve housing.
5. Replacing the oxygen sensor
Most often, it is simply impossible to repair the oxygen sensor, and this is evidenced by numerous statements from car manufacturers.
However, it should be noted that the inflated cost of this unit from official dealers completely discourages the desire to purchase it, therefore, as an alternative, you can purchase a universal device, which costs much less than the “native” mechanism and is suitable for almost any car model.
You can also try to find a lambda probe that has already been in use, but the warranty period has not yet expired, or completely replace the exhaust manifold along with the sensor located in it.
Sometimes there are cases when, due to severe contamination, the oxygen sensor operates with a certain error.
But in order to verify your guesses, you will have to check the lambda probe on special equipment that is available to service centers.
If the check confirms that it is fully operational, then the lambda probe will have to be dismantled, cleaned and installed in its original place.
In order to remove the oxygen sensor, the surface of its body is heated to 50 °C, and after it is in your hands, you will need to remove the protective cap from it, and only after completing this action can you proceed to direct cleaning. As an effective cleaning agent, experts recommend using phosphoric acid, which can cope with even the most complex flammable deposits.
The final stage of cleaning activities (immediately after soaking the device) should be rinsing it in clean water, thoroughly drying it and installing it in its place. Do not forget about lubricating the threads with special sealing agents that will help ensure complete tightness.
In cases where the diagnostic results showed irreversible damage to the lambda probe, it must be replaced with a new element. Just remember! Any sensor must be removed and installed only using special tools.
If you decide to re-install the same device, then the threads should be treated with a special mounting paste.
Try to avoid getting the mounting compound on the protective tube, as otherwise you can easily cause the device to malfunction.
It should also be noted that oxygen sensors produced today are pre-treated with mounting paste, and all that is required during installation is to observe the tightening torque specified by the manufacturer (usually from 40 to 60 Nm).
Be that as it may, any oxygen sensor requires careful handling, which means that mechanical damage or contact spray, grease or special flushing fluids (used when cleaning the engine) getting into the connector must be completely excluded.
Source: https://auto.today/bok/4175-zachem-nuzhen-lyambda-zond.html