Checking high-voltage wires with a multimeter on a VAZ 2114

HF wires (stand for high-voltage) are needed as direct impulse conductors from the ignition device to the fuel ignition system (directly to the spark plugs). If the pulse does not flow or does not flow properly, the gasoline will not burn properly in the cylinder and the engine will not operate as it should.
High-voltage wires VAZ 2114
Naturally, high-voltage wiring tends to fail. Signs of malfunction of high-voltage wires may be the following:
- The wiring is broken
- The wiring is broken, current is flowing past
- On the contrary, the wiring has heated up, the resistance is higher than normal
- The fine conductive vein has ruptured
Content
- 1 Wiring characteristics
- 2 Check wiring
Wiring characteristics
In this case, a basic skill is required on how to check high-voltage wires with a multimeter. By the way, you can probably check in another way, but this is the most correct and logical. But for now let’s talk about something else, even if you realized that the explosive wires of the VAZ 2114 are dead, in any case, you will have to buy new ones.
As it turned out, high-voltage workers have their own GOST number - 14867-79. These numbers indicate the quality of the wires - that they are high-voltage. Also, on domestic wiring there is a brand - PPOV: polyethylene wire, irradiated, with a polyvinyl chloride sheath.
Operating conditions are also special:
- Operating temperature varies from -60 to +110 degrees
- Resistant to oiling and other substances.
The technical specifications are as follows:
- Maximum voltage 22 kV
- Breakdown voltage minimum 40 kV
- Electrical capacity maximum 100 pFm
- Service life 8 years
GOST standards are old, from the Soviet period, but since the fourteenth ones were basically discontinued, the spare parts for them are those that remain in stock.
These parameters do not quite adequately fit the Euro 2 standard, much less a higher class. Such standards require greater power and special requirements in terms of electromagnetic compatibility.
But, whatever one may say, even old wiring can be adjusted to fit the engine of the fourteenth.
The main points that are needed for a competent choice of explosives are the following:
- Resistance of high voltage wires
- Breakdown voltage
- Electromagnetic force
- Price issue
After you have decided on the quality of high-voltage wires, you can master checking high-voltage ignition wires with a multimeter.
Wiring check
Checking high-voltage ignition wires begins with a simple diagnosis, because all of the above symptoms of problems may indicate a breakdown of other parts of the engine system or something else. For a simple check it is better to wait until dark.
Then you need to expose a small section of the wire on one side and the other and close one end to the body of the car or battery, and the second is needed for maneuver: we move it along the wiring joints, plugs, and so on. When there is a hole there will be a spark immediately. The result is obvious - replacement is required.
But this method is primary; it concerns direct current leakage, which is not always the reason for the non-operating state of high-voltage devices. In the case of voltage, such a number will not work.
To measure it, you need to know what resistance the high-voltage wires should have. After all, each wire from a specific manufacturer has its own resistance, technical characteristics and dimensions:
1) Tesla - 6 kOhm, it is often counterfeited, then you can squeeze out as much as 8 kOhm
2) Elephant - from 4 to 7 kOhm
3) ProSport tends to zero
4) Kargen - 0.9 kOhm
Checking high-voltage ignition wires with a multimeter
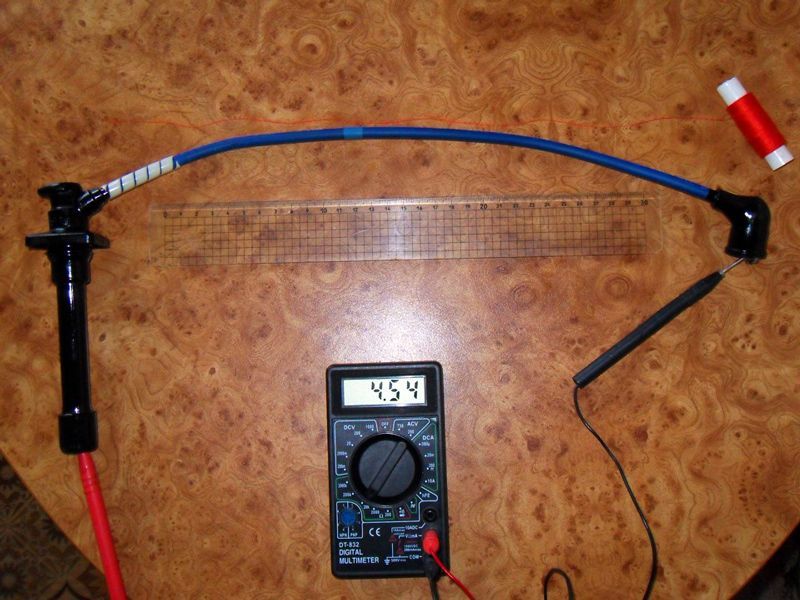
For measuring work, you need a simple multimeter, which we switch to ohmmeter mode. We measure one wire at a time, removing one by one from the cylinders from left to right and from the coil itself. The procedure is simple:
- make sure the car is turned off
- remove the end of the wire from the fastener on the cylinder
- remove the opposite end from the ignition coil mounting
- you need to connect both ends to the multimeter
- read the readings
- write them down so as not to forget
- We do this three more times with the remaining wires
Normal resistance is numbers in the range from 3.4 to 9.8 kOhm. Of course, all this depends on the manufacturer; this parameter is printed on the rubber skin of the wire. If you have a difference with the permissible value, which varies from 2 to 4 kOhm, this is normal. But no more! If more, then the wires are not suitable for driving, they need to be changed.
We always replace wires as a set! Even if one has fallen into disrepair, and the rest are in good technical condition.
That's basically it. Now you should replace the old wires with the purchased new ones.
Source: http://NaDomkrat.ru/elektrooborudovaniye/proverka-vysokovoltnyx-provodov-multimetrom-na-vaz-2114
How to check armored wires with a multimeter

With the development of technological progress, electrical measuring equipment has appeared, which has become widely used for measuring high current values.
The versatility of the measuring equipment lies in the relatively simple automated process providing accurate and fast readings.
A multimeter is popular for monitoring resistance in DC wires, cables and cords.
High-voltage wires and their features
Using a measuring device, the amount of electrical voltage can be assessed and compared. By choosing the right type of multimeter, you can examine the armored wire.
A feature of high-voltage wires is their ability to withstand the highest current.
Intended for installation of networks of radio engineering and electronic equipment with high voltage, they are divided into groups:
- Installation wires.
- Ignition wires.
- Cables of radio-electronic and electrophysical equipment.
- Cables for moving pantographs.
Due to mechanical strength, elasticity with different types of insulation, high-voltage wires are mainly used in the ignition system of engines operating at high voltage, limited switching, pressure and temperature ranges. Despite the resistance to vibration, linear, shock loads, stability, combustion, oils, gasoline, they have limitations and wear.
Diagnostics of the armored wire in the circuit
The advent of digital and analog measuring instruments greatly simplifies and speeds up the process of examining a circuit. Testing of high-voltage wires is based on resistance measurement.
Before starting work, carry out a visual inspection for mechanical damage to the insulation.
The interaction of a multimeter with a wire assumes the presence of a signal, which is a carrier of information and is directly related to the magnitude of the current.
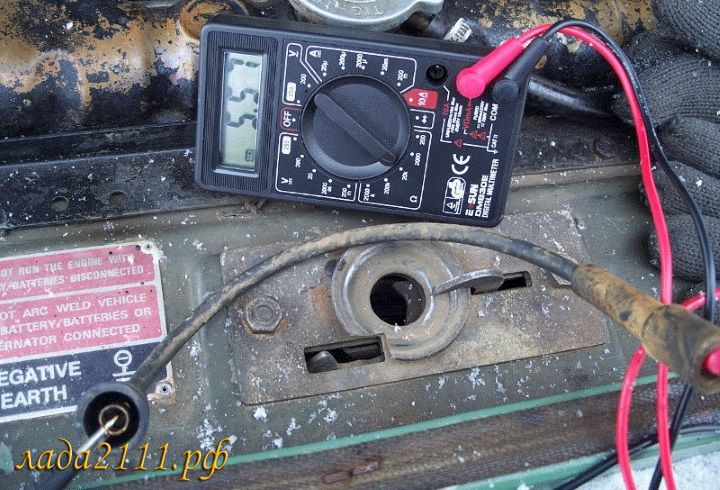
Once a violation is detected, the wire is de-energized, removed and connected to a multimeter, which is connected to the gap where the current needs to be measured.
The regulator on the device sets the resistance mode. The measurement range of its indicators depends on the model of the tester.
If, when checking on the device, there is no signal information, this indicates that the wire has a break and is unsuitable for further use.
Continuity of high-voltage ignition wires
Modern measuring devices for high currents provide an extension of the measurement limits. So, using a multimeter, you can ring the high voltage ignition wires if they are externally in order. Malfunctions are determined by uneven engine operation.
Before checking the armor wires with a multimeter, you need to find out their resistance. The manufacturer of high-voltage wires and cables took care of this by indicating the resistance of each brand on the insulation.
The procedure for testing is to connect the probes of the measuring device to the ends of the wire. The measurement readings must correspond to the cable markings.
An important element of high-voltage wires is insulation.
Improved high-quality insulation makes the wires wear-resistant.
Basics of selecting measuring devices
Today, new technologies provide particularly advanced technical means for measuring, monitoring accuracy and restoring various elements of electric current. Without the use of universal, mechanical measuring devices, oscilloscopes, it is impossible to carry out a number of diagnostic operations.
Control mechanisms have different shapes and technical characteristics. This allows the consumer to select a device with a current measurement system that is most suitable for the requested parameters. Considerable importance when purchasing devices is their cost, which depends on the complexity of manufacturing the structural elements.
Requirements for technical control devices
When choosing, it is necessary to take into account the factor of obsolescence, present requirements for the prospects of devices in an accessible and simple form to show the magnitude of voltage and resistance.
When purchasing a device, you must take into account input protection, ease of control, and delivery set. When choosing measuring instruments, it is important to take into account their classification according to the method of presenting information, when the device only reads the measured value or the readings are presented in digital form. The parameters of the mechanisms are also of considerable importance:
- measurement range (the device is designed for a given value);
- sensitivity threshold (measured value that the device can distinguish);
- accuracy (limits of permissible error, measurement uncertainty);
- stability (the ability to maintain a given accuracy for a certain time).
Models of measuring mechanisms provide testing not only of electrical equipment, wires, cables, but also with their help, the resistance of the ground loop is measured in order to reduce voltage.
Source: https://EvoSnab.ru/instrument/avo/kak-proverit-broneprovoda-multimetrom
How to check high voltage ignition wires?
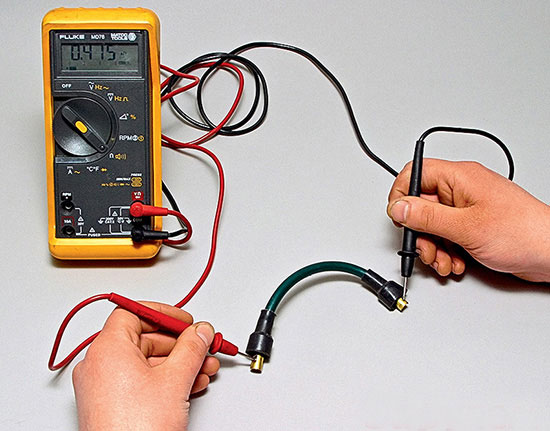
Automotive high-voltage (HV) wires play an important role for internal combustion engines, since they help transmit high current from the ignition coil to the spark plugs.
The serviceability and efficiency of the wires determines the timeliness and intensity of ignition of the fuel-air mixture, and therefore the correct and uninterrupted operation of the engine.
Despite their simplicity, wires have many different “sores” and can cause a lot of troubles to their owner, which in one way or another will affect his nerves and pocket.
Malfunctions of high-voltage wires (common problems):
As a rule, the malfunction boils down to the fact that current either does not flow to the spark plug at all, or it does, but in limited quantities. This can happen for the following reasons:
- There has been a break in the conductor through which the impulse travels.
- There is a current leak, that is, the insulation is damaged and the current flows to the side.
- The resistance exceeds the permissible value.
- Problems in contacts (with a spark plug or ignition coil).
In the event of a break in the current-carrying wire, the effect of an internal spark occurs, in other words, an electrical discharge is formed between the ends of the broken wire, which reduces the voltage and causes an electromagnetic parasitic pulse.
This impulse, in turn, negatively affects the correct operation of many of the vehicle's sensors. One such damaged high-voltage wire can cause vibration and interruptions in engine operation.
Due to a damaged high-voltage wire, ignition in the cylinder occurs late or every other time, as a result, the synchronous operation of the cylinders and the engine as a whole is disrupted.
How to check high-voltage wires? Effective ways:
- First of all, it is necessary to check the explosive for the absence of visible damage (cracks, fractures, etc.).
- Make sure there is no breakdown, this can be determined even without instruments, just look under the hood in the dark; in the event of a breakdown while the engine is running, a spark will be visible on the explosive wire.
- You can check high-voltage wires using a wire. To do this, you need to take a piece of wire in the dark and strip it on both sides. Then one end needs to be shorted to ground (machine body), and the other tip should be drawn along the entire length BB wires, as well as joints, caps, etc.
A spark will form at the breakdown sites.
- You can also check the resistance of the high voltage wires, for this you will need a multimeter.
- Turn on ohmmeter mode.
- Remove the wire from the spark plug of the first cylinder and the ignition coil.
- Connect the multimeter electrodes to the ends of the wire and look at the readings.
In good wires, the resistance should vary from 3.5 to 10 kOhm, depending on the type of wires themselves. Information about resistance is most often indicated on the insulation of high-voltage wires.
Check each wire, the spread between them should not exceed 2-4 kOhm. If there is a large variation, replace the wires. By the way, they are changed as a set, that is, all together.
In conclusion, your resistance reading of the most popular high-voltage wires:
- Tesla - 6 kOhm
- Slon - from 4 kOhm to 7 kOhm (4 kOhm - 1st cylinder and up to 7 kOhm - on the last cylinder)
- ProSport - almost zero resistance
- Cargen - 0.9 kOhm
Note! The resistance of high-voltage wires varies depending on the length, thickness, and material from which the wires are made.
Source: vaz-remont.ru
Source: http://vaz-remont.ru/kak-proverit-vysokovoltnye-provoda-zazhiganiya/
Instructions: How to check high-voltage ignition wires based on the main symptoms

Many car enthusiasts are accustomed to calling high-voltage ignition wires spark plug wires. The second name more clearly describes their task in a car, which boils down to transmitting electric current from the ignition coil to the spark plugs.
From the name you can understand that these wires are different from all the others installed in the car. Their peculiarity is their ability to withstand high voltage passing through them and protect other machine components from it.
Every driver should know how to check high-voltage ignition wires, since operating the car in a faulty condition can lead to failure of expensive devices and parts.
Design of high-voltage ignition wires and requirements for them
High-voltage ignition wires are designed quite simply. They consist of a conductive element with a metal tip, two plastic caps and reliable insulation.
The most important element of spark plug wires is the insulation, which performs two functions:
- Does not allow moisture to enter the conductor;
- Minimizes current leakage during transmission.
Metal tips of spark plug wires are necessary to ensure electrical connection between the wire leads and the contacts of the spark plug and ignition coil. It is necessary that the metal attachments:
- They were securely fixed on the wire and firmly connected to the elements on the terminals, thereby preventing the dissipation of transmitted energy;
- They had increased anti-corrosion protection, which is necessary for long-term operation of the wires.
Plastic caps are also an important element of spark plug wires. Their task is to protect the terminals of the ignition coil and spark plugs from the influence of the external environment. Like metal tips, plastic caps should be connected as tightly as possible to other parts in the current transmission circuit.
Based on the information above, it is possible to identify the main list of requirements that apply to high-voltage wires. They have to:
- Cope with assigned conductive tasks;
- Reduce current leakage to zero during its transmission from the ignition coil to the spark plugs;
- Withstand the aggressive environment of the engine compartment;
- Work at different temperatures.
Heat, vibration, aggressive environment - the developers of spark plug wires try to protect them from all this. Insulation works, but it also has its own service life, which cannot be clearly defined. Over time, high voltage wires will become less efficient and will need to be replaced.
Symptoms of faulty high-voltage wires
If the insulation breaks or the plastic caps are damaged, current will leak, which will lead to the following problems:
- Difficulty starting the engine;
- Unstable operation of the engine in idle mode;
- Increased hydrocarbon content in emissions;
- Radio interference, which can lead to malfunction of the multimedia system, electronic control unit and other devices.
A serious violation of the insulation of high-voltage wires will lead to the fact that all electronic components of the car will begin to act up.
The sensors will begin to give incorrect readings, the ECU will send incorrect commands, and the current will no longer reach the spark plug in the amount required to produce a spark.
This risks disrupting the synchronous operation of the engine cylinders, which will lead to vibration and interruptions in operation.
How to check high voltage wires
Finding high-voltage wires under the hood is not difficult, and diagnosing them is not fraught with any difficulties. There are three ways to check high-voltage wires, each of which allows you to determine whether there is a breakdown in them.
Visual diagnostics
The easiest way to check spark plug wires for insulation damage is to visually inspect them. It is necessary to carefully check that there are no cracks, cuts or severe abrasions across the insulation area.
Another way to visually check spark plug wires is to observe their operation at night. It is necessary to open the hood of the car at night, start the engine, turn off the headlights and watch the high-voltage wires. If they have strong insulation breakdowns, in the dark the “crickets” will be visible to the naked eye.
Wire check
To check the spark plug wires, an ordinary wire with stripped ends on both sides can be used.
In the dark, with the engine running, it is necessary to short-circuit one part of the wire to ground (the car body), and run the other part along high-voltage wires in search of a place where the stripped tip will begin to produce a spark. It is important to check not only the insulating material around the conductor, but also the plastic caps.
Diagnostics with a multimeter
A multimeter in automotive diagnostics is most often used as a voltmeter, but it also has another useful function - the ability to measure resistance.
To take measurements, you must completely remove the high-voltage wires (or disconnect one wire on both sides).
Next, with the probes of the device set to ohmmeter mode, you should touch both sides of the wire, as a result of which the multimeter will display information about the resistance.
The resistance of serviceable high-voltage wires is up to 10 kOhm. At the same time, it can vary practically from zero. This depends on the type of wires themselves, the insulation used in them, the length, the presence of microdamages, and so on.
(340
Source: https://okeydrive.ru/vysokovoltnye-provoda-zazhiganiya-kak-proverit/
Checking high voltage wires
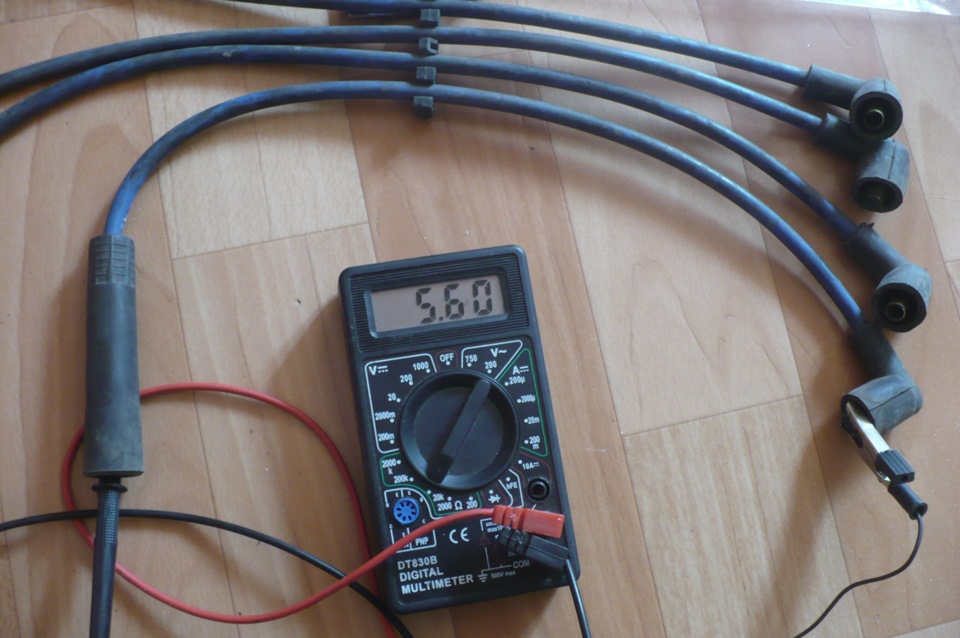

High-voltage wires are an integral part of any car. Their purpose is to supply high voltage electrical pulses from the module or ignition coil to the spark plugs.
Serviceable and high-quality high-voltage wires (hereinafter referred to as VP) should:
- be resistant to temperature changes;
- create a minimum of interference with the electrical equipment of the car;
- Prevent current leakage and withstand high voltage;
- minimize energy losses during pulse transmission.
The main parameter when choosing a VP is resistance. The larger it is, the less electrical interference is created during engine operation. The required value can be found in the vehicle registration certificate. For example, for a VAZ-2109 it is 2.55 kOhm. In foreign cars and modern domestic cars, the resistance value will be higher (up to 25 kOhm) due to the increased number of electrical equipment.
Do not exceed the VP resistance value recommended by the factory. This will lead to increased fuel consumption and may make it difficult to start the engine in winter (up to the complete impossibility of starting it).
Basic faults
Most VP malfunctions lead to either insufficient current supply to the spark plugs or to its complete absence. This happens for the following reasons:
- current leakage due to insulation damage (as well as through contaminated spark plugs, caps, wires and other elements);
- rupture of the conductor;
- oxidation and contamination of spark plug contacts, ignition coil, metal contact of wire and conductor;
- exceeding the permissible VP resistance.
Price
The cost of VP depends on the materials used and the brand of car for which they are intended. On average, the price varies from 500 to 2000 rubles. For domestic cars - from 400 for “classics” to 1500 for injection 16-valve units.
When purchasing, it is best if the packaging with the wires specifically indicates which engines they are suitable for.
Examination
The main methods for checking VP faults:
- Visual inspection. Carefully check each wire for cracks, frays, or fractures. Wipe off dust and dirt with a dry cloth. You can immediately check the contacts on the side of the spark plugs and the ignition coil (just don’t remove all the wires at once - they must be installed strictly in a certain order, preferably one at a time).
- Check for breakdown. In the dark, with minimal lighting, start the car and open the hood. In the event of a malfunction, sparks on the VP will be visible to the naked eye.
- Check with a multimeter. Set the device to resistance testing mode (ohmmeter). Disconnect the VP from the ignition coil and from the spark plug. Check the resistance at the ends of the wire. The resistance value can be read on the wire insulation. The spread should not be more than 2-4 kOhm.
Check result
If the above faults are detected, the high-voltage wires must be replaced. They are replaced as a set. Replacement is also done one by one. Or you can first sketch out the correct location of the wires. It is better to carry out replacement with the battery disconnected.
Source: http://mylada.net/nachinayushhemu-avtomexaniku/proverka-vysokovoltnyx-provodov.html
Have you ordered spark delivery? All about high voltage ignition wires
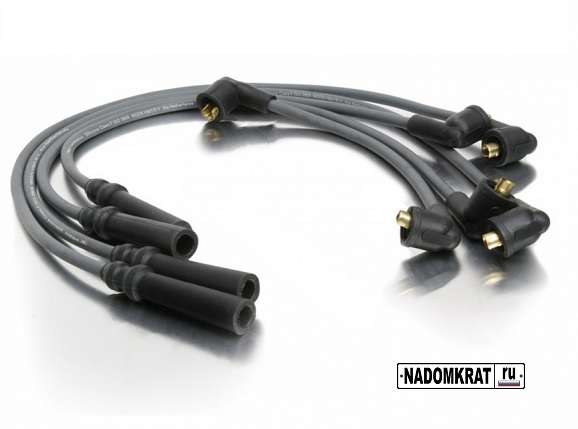

For a gasoline internal combustion engine to operate, two conditions are necessary: the presence of fuel and a spark to ignite it. High-voltage wires serve precisely to “deliver” the spark from the ignition coil to the spark plugs in the cylinders of the power plant.
Photo - blue armored wires using the example of a Renault engine
terms of Use
Wires operate under difficult conditions, accompanied by temperature changes, vibration, moisture and dirt from the road surface, as well as exposure to fuels and lubricants. As the wires are used, microcracks appear on the surface of the wires, causing current leakage.
Moisture and dirt create conditions for oxidation of contacts and disruption of sparking on spark plugs.
The presence of engine vibration causes an unclear fit of the contacts in the connections, which leads to a malfunction of the motor.
High temperatures, especially in the area of the spark plug wells, lead to failure of the spark plug caps.
Why are these wires called “high voltage”?
As follows from combustion theory, to ignite the fuel mixture, a high voltage of several tens of thousands of volts is required to form a spark between the electrodes of the spark plug.
The car's electrical circuit itself is designed to be powered by a 12-volt battery and is not able to create such a voltage. For this purpose, the car’s ignition system has an ignition coil capable of delivering the necessary voltage to create a spark.
Essentially, this device serves to convert low voltage (12V) into high voltage, which is about 35-40 thousand volts.
Low-voltage power is supplied to the coil by a regular wire, but at the output of the coil there is already a high-voltage wire or, as it is also called, an armor wire.
The ignition coil wire is connected to the central contact in the distributor cover, which also has additional terminals for wires, according to the number of engine cylinders.
Device
The design of the wires is quite simple. This is a conductive element (copper, fiberglass impregnated with graphite), covered with a layer of insulation, at the ends of which there are metal tips. One end of the wire is installed in the ignition coil socket, and the other on the spark plug through a plastic, rubber or silicone tip.
BB wire device
Insulation is the most important element, serving three main functions:
• Protection of the conductor from moisture;
• Minimum current leakage during operation;
• Maintains elasticity in operation at different temperatures.
At the same time, metal tips must have reliable protection against corrosion, which will guarantee constant contact in the connections and a long service life of the product.
Causes of malfunction
• Breakage of the central core of the wire;
• Insulation breakdown;
• Oxidation of contacts;
• Damage to the caps.
Damaged armored wire
The appearance of the listed malfunctions is reflected in the operation of the engine, which is expressed in the following symptoms:
• Poor start;
• Unstable idle, as well as under medium and high loads;
• Misfire;
• Increased fuel consumption, decreased power;
• The appearance of radio interference leading to malfunction of electronic systems and multimedia;
• Inability to start the engine if the central wire from the coil is damaged.
Faults manifest themselves most clearly in wet weather.
Methods for checking high-voltage wires
There are several options for checking wires that are available to anyone, even a novice car enthusiast, and consist of the following steps:
• Visually
The most accessible way is a visual inspection of armored wires. The insulation should not have any cracks, abrasions, kinks or traces of melting. In addition, the wires must be flexible, since they can often become stiff due to overheating or after prolonged use.
A faulty wire insulation can be very clearly detected if you open the hood at night while the engine is running, turn off the outside lights and look at the engine. If the wires are faulty, they will look like flickering garlands. Plus, you can also notice the place of poor contact, since sparking will be noticeable in this place.
If the integrity of the insulation is violated, characteristic clicks can be heard. Clicks will also be heard if you remove the tip from the spark plug while the engine is running and keep it at a minimum distance from it, which will additionally indicate the integrity of the wire.
• Using a multimeter
The wires must be removed and each one checked separately. The device is set to test resistance in ohmmeter mode. The probes of the device touch both sides of the wire and the test data is reflected on the scale.
Checking explosive wires with a multimeter
Serviceable products should show a resistance of about 3.5 -10 kOhm, depending on the material used and the length. When the distributor or ignition module is located at the end of the engine, the length of the wires and their resistance will be different accordingly. The difference in readings between the wires should not be more than 2-4 kOhms, otherwise the entire set must be replaced.
The resistance value is usually indicated on the wires themselves.
• Check for spark
Take a piece of ordinary wire stripped on both sides. At night, with the engine running, you need to touch the ground with one end of the wire (motor, car body), and run the other along the wire along its entire length, as well as along the spark plug tip. If there is a breakdown, then a spark will jump in this place.
You can check the wire itself directly by securely fastening it at a short distance from the metal parts of the engine. When the starter cranks, a spark should “jump” between the tip of the wire and the engine ground.
Life time
According to GOST 14867-79 in relation to GDP (high-voltage wires), their service life should be 8 years, and the warranty period should be 5 years, counting from the date of start of operation of the product, not exceeding 2000 engine hours, or 40 thousand kilometers.
These parameters are given for PPOV brand wire - a wire in polyethylene insulation, irradiated with a polyvinyl chloride sheath.
In real life, wires can either fail before the prescribed period or fail for a much longer period of time, and they are replaced as signs of their malfunction are detected.
Choice when purchasing
When purchasing wires, it is better to give preference to products designed for a specific make and model of car. In this case, you need to pay attention to the accompanying inscriptions, both on the packaging and on the wires themselves. The font must be smooth, without errors or any smudges.
The packaging must also indicate the manufacturer, material of manufacture, and operating instructions.
Silicone products have the best characteristics of wires that do not lose their properties for a long time. They are more elastic and are able to operate reliably in the temperature range from -30 to +30 degrees Celsius, taking into account the temperature of the engine compartment, which is about 100 degrees.
The elasticity of the wire is important for the operation of the engine, since the stiffer the wires, the faster the contacts in the connections loosen.
These are products from such companies as: Denso, Bosch, NGK, Champion, Tesla, Slon, Finwhale.
However, you need to be careful, since there are many fakes on sale, where even the word “silicon” itself is often misspelled.
Price policy
The cost of GDP from different manufacturers can vary greatly and on average ranges from 500 to 1,700 rubles per set.
Finally
It is worth noting that armored wires do not fail suddenly, so you need to make it a rule to pay attention to them from time to time so as not to end up with a failed engine on the highway or in an open field far from shops.
Source: https://avtoexperts.ru/article/high-voltage-ignition-wires/
What resistance should be on the high-voltage wires of the VAZ 2114
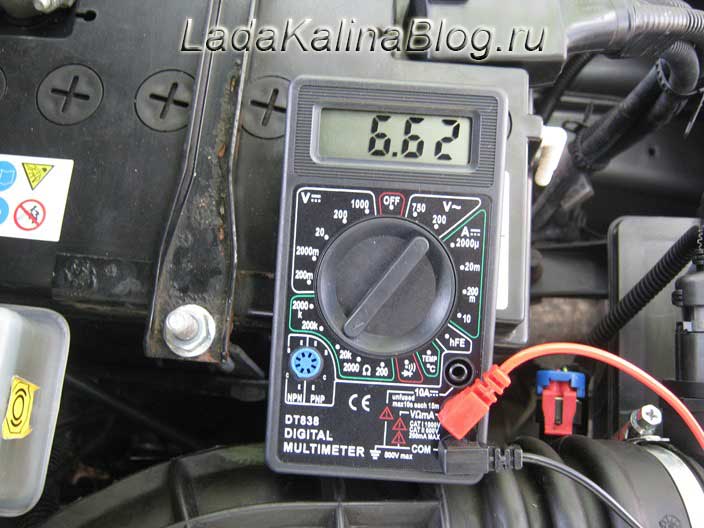

The design of any car requires impulse conductors from the ignition system to the fuel combustion system (directly to the spark plugs). They are also found in the VAZ 2114. These are high-voltage (HV) wires. When the impulse does not pass or the discharge has insufficient power, the gasoline in the cylinders does not burn completely, and the engine operates intermittently.
High-voltage wires VAZ 2102
Therefore, it is very important to know what resistance should be on the high-voltage wires of the VAZ 2114, and what needs to be done if it does not meet the standard.
How the wires are arranged
The wiring structure is the same as that of the electrical wiring in the apartment. A large number of copper wires are combined into a core. On top of the core there is a core and an insulator. The outer insulating layer usually consists of a silicone, polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, rubber shell. The additional shell protects against the destructive effects of fuels and lubricants.
High-voltage wires VAZ 2114
What are the signs of faulty high-voltage wires:
- Broken wiring.
- Leakage current.
- Warming up wiring.
- Rupture of current-carrying conductors and insulation.
How to check the wiring if there are no obvious signs of damage, but the engine malfunctions
If this method of checking does not live up to expectations, test the wiring with a voltmeter. How to check high-voltage wires on a VAZ 2114?
The voltmeter is switched to ohmmeter mode. Measure all the wires, sequentially removing them from the cylinders and coils from left to right. Each indicator must be recorded, so prepare paper and pen (pencil) in advance.
How to measure the voltage resistance of VAZ 2114 wires:
- Turn off the car.
- Remove the end of the wire from the cylinder.
- Remove the opposite end from the ignition coil.
- Connect both ends to the multimeter.
- After counting, write down the readings.
- Repeat the sequence for the remaining three wires.
What resistance is considered normal? Depending on the brand of wiring, from 3.4 to 9.8 kOhm. Normal values are usually stuffed on top of the insulation. If the measurement difference does not exceed 2-4 kOhm from the control value, this is within normal limits. Otherwise, the kit must be replaced immediately.
Normal wiring resistance of different brands:
- Tesla - 6 kOhm (in case of fakes it can reach up to 8 kOhm);
- Elephant - 4-7 kOhm;
- Kargen - 0.9 kOhm;
- ProSport tends towards zero.
Selecting new wiring
You are convinced by external or indirect signs that the wires are faulty. Which wiring is better to choose to replace the retired one?
The products of the Czech company Tesla received the largest number of positive reviews. The wiring has good breakdown voltage, high resistance, and the quality is such that it does not tarnish or crack even at low temperatures. Also in auto stores there are products of the brands Slon, Ween, Cezar, Horse, Finwhale. All of them are suitable for operation in Russian conditions.
Connecting new wires
Each engine cylinder, when the wire is connected, corresponds to the number of the ignition module socket. All landing slots are numbered. Ignition coils may differ depending on the VAZ model, up to 2004.
or after 2004, but the socket numbers always match the numbers of the cylinders to which the wiring is connected.
The cylinder numbers for connection are counted from left to right when viewed from the open hood.
To connect the wiring, you need to perform the following sequence of actions:
- Ignition off. Open the hood and remove the terminals from the battery.
- Removing old explosive wires from the coil and cylinder sockets.
- Connecting new wiring according to the diagram.
To check the correct connection, return the terminals to the battery and start the engine.
Wire lifespan
According to the recommendations of the manufacturer (AvtoVAZ), the wiring should be replaced every 30 thousand kilometers. Most often, car enthusiasts ignore these recommendations and do not change them for 100-150 thousand kilometers when there is no mechanical damage.
However, when the service life is exceeded, even if there is no visible damage, the internal resistance increases, which affects the transmission of the electrical impulse.
There may be problems with ignition and acceleration. Due to the delay in supplying current to the spark plugs, the normal rhythm of engine operation is disrupted. It is necessary to follow the manufacturer's advice, changing the wiring every 25-30 thousand.
km run.
Source: https://VAZremont.com/kakoe-soprotivlenie-dolzhno-byt-na-vysokovoltnyh-provodah-vaz-2114
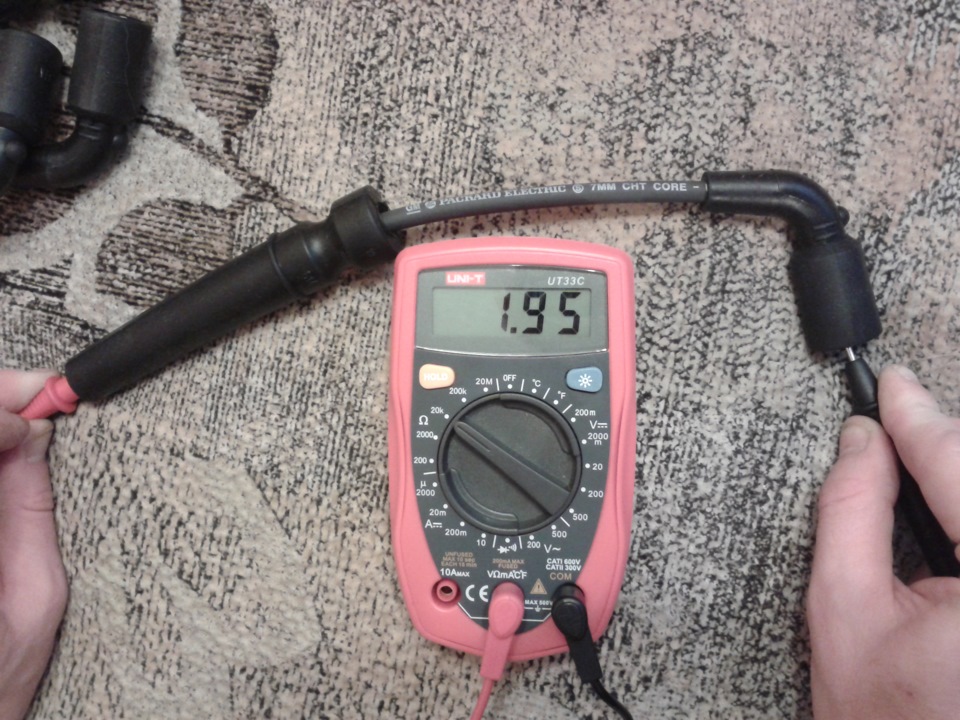
High-voltage wires of the ignition system: diagnostics, selection features, typical malfunctions

Some car enthusiasts often call such wires spark plugs, which quite accurately reflects their function. They connect the car's ignition system coil to the spark plugs.
The operation of not only the engine, but also other vehicle systems as a whole depends on the serviceability of the ignition wires (high-voltage ignition wires).
If problems arise with the wires, the engine begins to work unstably, fuel consumption increases due to incomplete combustion, and problems appear with the electronics of the car. Today we will talk about how to diagnose these elements of the system, as well as the features of their selection.
Design features of cables
The design of a high-voltage ignition wire is, in essence, quite elementary. The main component is a current-carrying core equipped with lugs for contact connections.
The second element is special plastic or plastic caps that insulate the contacts.
The third element is the insulation of the ignition system wire itself, which performs almost the same function as the caps.
BB cable structure: 1 - external silicone insulation; 2 - heat-conducting core; 3 - internal insulating layer of silicone; 4 - contact;
5 — protective cap.
Both insulating elements are designed to solve the following problems:
- Significant reduction in current leakage to increase the output voltage and, as a result, reduce energy losses.
- Elimination of the possibility of penetration of various liquids and lubricants into the cable, leading to a short circuit and rapid failure of the conductor.
- Prevents the occurrence of electromagnetic pulses that can affect the operation of the ignition system, as well as other automotive electronics.
What to look for when buying a cable?
How to choose high-voltage wires for your car, taking into account all the features? The most important point to pay attention to is the resistance produced by the conductor. Its value can range from 0 to 10 kOhm.
It would seem that the lower the value, the less electricity losses, but not everything is so simple. The fact is that as the resistance decreases, the current increases, which can lead to the appearance of electromagnetic pulses, which we will talk about later.
It is for this reason that it is better to first check the documentation for the car, which should indicate the optimal value for a specific car model.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UeK9vNJr0xg
The second point is the material from which the conductor is made. Affects the resistance and other properties of the product. Copper conductors have the lowest resistance of all, but be aware of electromagnetic impulses. However, if you definitely want to use copper, then you can install additional resistors that block such waves.
Other materials used for the production of high-voltage cables include various polymers and fabrics: fiberglass, flax thread, Kevlar, graphite, etc. The central part of the core is made from them, which is subsequently wrapped with wire.
The resistance of such products ranges from 2 to 10 kOhm. Their advantage over copper conductors is that polymer wires emit much less electromagnetic interference (of course, if the protective braiding does not have breakdowns).
However, you should make sure that the coil supplies enough voltage for this type of product.
The third point is the type of insulation. The high-voltage wire is located in close proximity to the engine, battery, crankcase and other elements of the car, so it is constantly exposed to aggressive substances. To make the conductor last longer, you should choose products with good protective braiding. The best option is silicone high voltage ignition wires.
Ideally, the cable you are looking for should meet the following requirements:
- Its resistance should be low enough to ensure normal operation of the spark plugs.
- The protection must prevent the penetration of liquids into the conductor, as well as suppress electromagnetic interference.
- The product must function normally at temperatures from -50 to +100 degrees Celsius.
- The contact connection with the ignition system elements must be perfect.
- The device must be capable of operating at high voltages in excess of the required values. This is necessary to avoid emergency situations. The peak voltage a wire can withstand can be measured using a multimeter.
You can ignore the service life specified by the manufacturer. Due to the aggressive environment in which the product is used, even the most reputable company cannot guarantee anything.
Typical faults of HF cables
Symptoms indicating a malfunction of the high-voltage ignition wires generally coincide with those of broken spark plugs.
When the cables fail, the engine begins to behave quite unstable: the car jerks when the gas pedal is pressed, the internal combustion engine sputters at high speeds. At idle, unnecessary vibrations may appear.
All this is due to the fact that due to damage to the high-voltage wires, the spark plugs cannot function normally.
The injector that injects fuel into the combustion chamber does not ensure full engine operation, which leads to disruption of the functioning of the entire system as a whole. Problems often arise when starting the engine.
If one of the cylinders stops working, fuel consumption increases significantly. This can be visually determined by the changed color of the exhaust gases. In particularly severe cases, popping noises (detonation) may be heard. An increase in fuel consumption is associated with incomplete combustion, since the ignition and exhaust cycle is disrupted.
If the cable is punctured or the current-carrying core is broken, a short circuit occurs between the broken parts of the conductor. The same thing happens if the contact connection between the spark plugs or the coil is broken.
This leads to the appearance of a strong electromagnetic pulse, due to which all car electronics work extremely unstable, and sensors installed on the dashboard begin to give incorrect readings.
In addition, a short circuit in itself is dangerous and can cause heating of the wiring or other undesirable consequences.
Damage to the outer protective braid can also result in an electromagnetic pulse and a short circuit. However, in the latter case, the matter is complicated by the fact that various liquids can get on the conductor, which will only aggravate the situation.
Simple methods for diagnosing spark plug wires
There are several ways to check high voltage ignition wires for faults.
Visual inspection is the simplest method. You should disconnect the cable from the spark plugs and coil, and then carefully inspect it. Signs of malfunction - cracks in the insulation, breaks, abrasions, clearly visible physical damage.
How to check high-voltage wires for the presence of a spark while the engine is running? You should open the hood and start the engine. If there is damage to the insulating layer, you will see sparking and air glow that occurs during a thunderstorm. This behavior indicates that there is a problem.
Please note that the method only works at night or in a sufficiently dark room. Otherwise, the spark may not be visible.
Additional diagnostic methods
What methods are there to more accurately determine the problem?
The first option is to use an additional wire as a tester. Connect one end to ground (which can be, for example, a metal surface of the car), then open the hood and start the engine. Then run the other end of the wire along all the BB cables. The breakdown can be determined by the sparking that occurs when the tester wire comes into contact with the break point.
The second option is to use a fully functional product alternately instead of each of the installed cables. Using the elimination method, you can find the “hero of the occasion.”
The third option is to use a multimeter. What device is suitable for this? Yes, almost anything. However, we recommend using a digital tester as it provides more accurate data and has many features that can be useful, for example, when testing the battery under load.
Checking the high-voltage ignition wires with a multimeter is carried out as follows:
- Disconnect the cable completely.
- Switch the device to resistance measurement mode.
- Connect two multimeter probes to both ends.
The resistance of the high-voltage ignition wires should range from 0 to 10 kOhm. It should be noted that these figures may change over time.
Do-it-yourself repair of high-voltage conductors
Please note that the methods described below cannot be used for full repairs. With their help, you can eliminate the problem for a short time and only until new cables are purchased.
- Cleaning and checking contacts. It often happens that problems arise not due to damage to the conductor, but due to a poor contact connection. In such cases, simply cleaning the contacts from oxidation and dirt helps.
- Use of electrical tape or other appropriate materials. An electromagnetic pulse, like current loss, can be significantly reduced by wrapping the breakage area with electrical tape. The method only works for a limited time, since physical factors, as well as high temperatures, penetrate this material very quickly.
- Ringing the conductor using a multimeter. The method allows you to accurately determine the location of the break, after which you can use a soldering iron to temporarily restore the contact connection. In any case, the wire that the multimeter rang and in which a break was detected, even after repair, will not last long.
conclusions
As a conclusion, I would like to give a little advice. Choose high-voltage wires from one manufacturer and replace them as a set. Replacing just one defective cable can negatively affect the operation of the engine due to the fact that the technical characteristics of different conductors are quite different.
Source: https://bodyshop-info.ru/diagnostika-i-remont/vysokovoltnye-provoda-zazhiganiya







